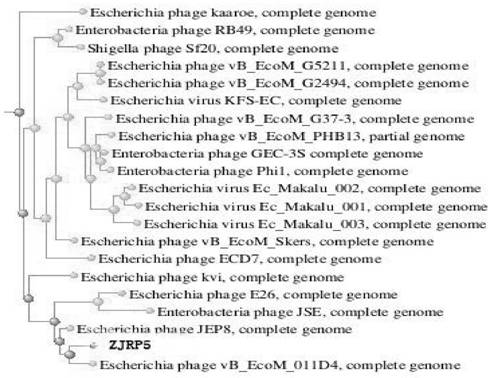
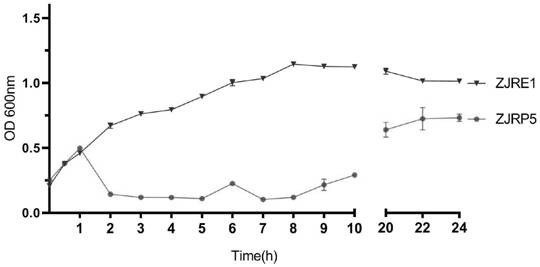
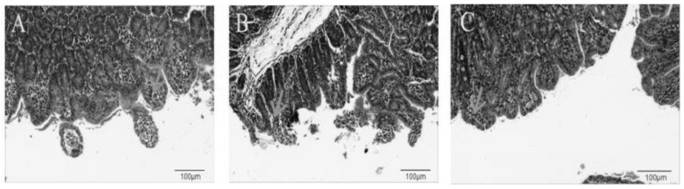
Escherichia coli bacteriophage ZJRP5, application thereof, bactericide and medicine
A technology of Escherichia coli and phage, applied in the direction of viruses/phages, medical raw materials derived from viruses/phages, applications, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] Example 1 Phage Isolation and Purification and Morphological Observation
[0034] Host bacteria: The host bacteria is rabbit pathogenic Escherichia coli: Escherichia coli ZJRE1 (CCTCC No. M2021778), isolated from diarrhea-sick rabbits, is enteropathogenic Escherichia coli, and the host bacteria used in subsequent examples are all rabbits Pathogenic Escherichia coli ZJRE1 (CCTCC No.M 2021778).
[0035] Pre-treatment of test samples: put 50 collected rabbit feces samples into 15mL centrifuge tubes, add 10mL of 0.9wt.% normal saline and 5mL of collected sewage samples, overnight in 4°C refrigerator, 6000r·min -1 After centrifugation for 10 min, the supernatant was taken and sterilized by 0.22 μm filtration to obtain 50 filtered feces and sewage samples, which were stored in a 4°C refrigerator for later use.
[0036] Phage amplification and primary screening: the host bacteria TSA plate (purchased from OXOID company) was routinely cultured in a planned line, and a single o...
Embodiment 2
[0041] Example 2 Phage I pH Stability Determination
[0042] Determination of phage I titer by double-layer plate method: The prepared phage I proliferation solution (refer to Example 1) was serially diluted 10 times with sterile normal saline to obtain the diluted proliferation solution. Make a double-layer plate, the lower layer is 10mL LB solid medium, the upper layer is 100μL diluted proliferation solution, 500μL culture of host bacterial solution (the culture is obtained by mixing the diluted proliferation solution and host bacterial solution in a water bath at 37°C for 5min) and 5mL TSB half Solid culture medium (purchased from OXOID Company), after solidification, was inverted in a constant temperature incubator at 37°C for 18 hours to observe whether there were phage plaques. Each concentration was repeated 3 times, the plaques were counted, and the phage titer was calculated. The calculation formula is as follows: phage titer (pfu / mL) = average number of plaques × di...
Embodiment 3
[0047] Example 3 Phage I Thermal Stability Determination
[0048] Take 500 μL of the phage I proliferation solution prepared in Example 2 (adjust the concentration of TSB to 1×10 9 PFU / mL) in test tubes, respectively placed in 37°C, 42°C, 50°C and 60°C constant temperature water baths, let stand for 1h, take out, and cool in an ice bath for 10min. Take 100 μL of the cooled phage I proliferation solution to determine the phage titer by the double-layer plate method, and the results are shown in Table 2.
[0049] Table 2 The titer of phage I under different micro-temperature conditions
[0050]
[0051] It can be known from Table 2 that as the temperature increases, the survival rate of phage I also decreases. The titer of phage I was 10 at both 37°C and 42°C. 9 About PFU / mL, the survival rate is close to 100%; at 50°C, the phage survival rate is about 80%, but the titer is close to 109 About PFU / mL; and at 55°C, the survival rate of phage I was about 40%; at 60°C, the tit...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Survival rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Potency | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com