High-flame-retardant superfine sea-island filament and preparation process thereof
A technology of sea-island silk and high flame retardancy, which is applied in the field of high-flame-retardant ultra-fine sea-island silk and its preparation technology, can solve problems such as economic loss, threats to people's life safety, and fire easily caused by textiles.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0055] A method for preparing highly flame-retardant ultrafine island-in-the-sea silk, comprising the following preparation steps:
[0056] S1: PET70kg, melamine resin 10kg, carbonyl betaine 1kg, vinylbisstearamide 1kg, nano-zinc oxide 1kg and nano-cerium oxide 3kg are mixed together, melted and dried, and extruded to obtain a PET solution;
[0057] S2: COPET30kg is dried and melted and extruded to obtain a COPET solution;
[0058] S3: Enter the PET melt and the COPET melt obtained by mixing into the spinneret assembly, and cool to obtain the inner layer of island-in-the-sea silk;
[0059] S4: polyacrylate 3kg, zirconium dioxide fiber 10kg, nano-titanium dioxide 3kg, aluminum hydroxide 3kg and red phosphorus 2kg are mixed together to make flame-retardant fiber;
[0060] S5: Immerse the inner layer of the sea-island silk in S3 into the bonding solution, take out the sea-island silk immersed in the insoluble water bonding solution and put it into the flame-retardant fiber in S4...
Embodiment 2-9 and comparative example 1-2
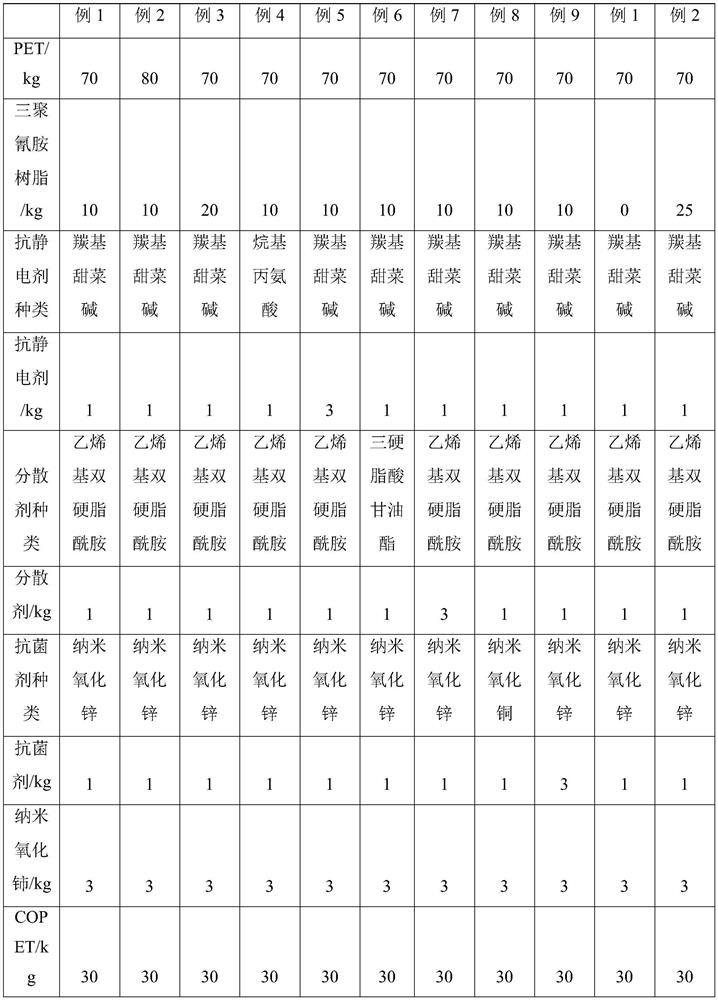
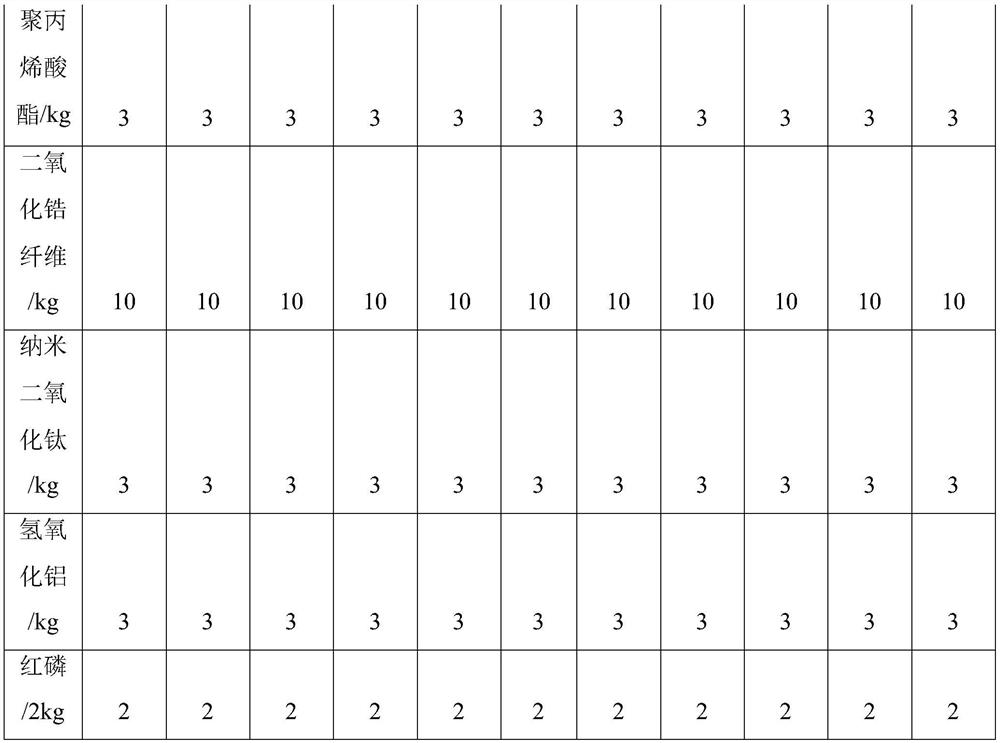
[0062] Embodiment 2-9, comparative example 1-2 are all different from the raw material proportioning of embodiment 1, and concrete raw material proportioning is shown in Table 1.
[0063] Table 1 embodiment 2-9 and the raw material proportioning of comparative example 1-2
[0064]
[0065]
[0066]
[0067] performance test
[0068] Detection method
[0069] Combustion performance test: According to the standard GB / T5455-1997 test, the fabric made of sea-island silk (after the COPET in the fabric is dissolved and the fabric is dried) is tested for combustion performance, and the limiting oxygen index, continuous burning time and smoldering time of the fabric are tested And dripping ignition absorbent cotton experiment.
[0070] Table 2 Embodiment 2-9 and the comparison of the fabric combustion performance of comparative example 1-2
[0071]
[0072] The afterflame time and smoldering time of the island-in-the-sea silk fabrics in Examples 2-9 and Comparative Exam...
Embodiment 10-19
[0076] The difference between Examples 10-19 and Example 1 is that the ratio of raw materials is different, and the specific ratio of raw materials is shown in Table 3.
[0077] The raw material ratio of table 3 embodiment 10-20
[0078]
[0079]
[0080] The concrete raw material ratio of comparative example 3-11 is as follows:
[0081] The raw material ratio of table 4 comparative example 3-11
[0082]
[0083] Embodiment 10-19, the comparison of fabric combustion performance in comparative example 3-11 is as shown in table 5 and table 6:
[0084] The fabric combustion performance contrast in table 5 embodiment 10-19
[0085]
[0086]
[0087] The comparison of fabric combustion performance in table 6 comparative examples 3-11
[0088]
[0089] The afterflame time and smoldering time of the island-in-the-sea silk fabrics in Examples 10-19 and Comparative Examples 3-11 were both less than 5s, and the drippings all caused the absorbent cotton to burn or sm...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com