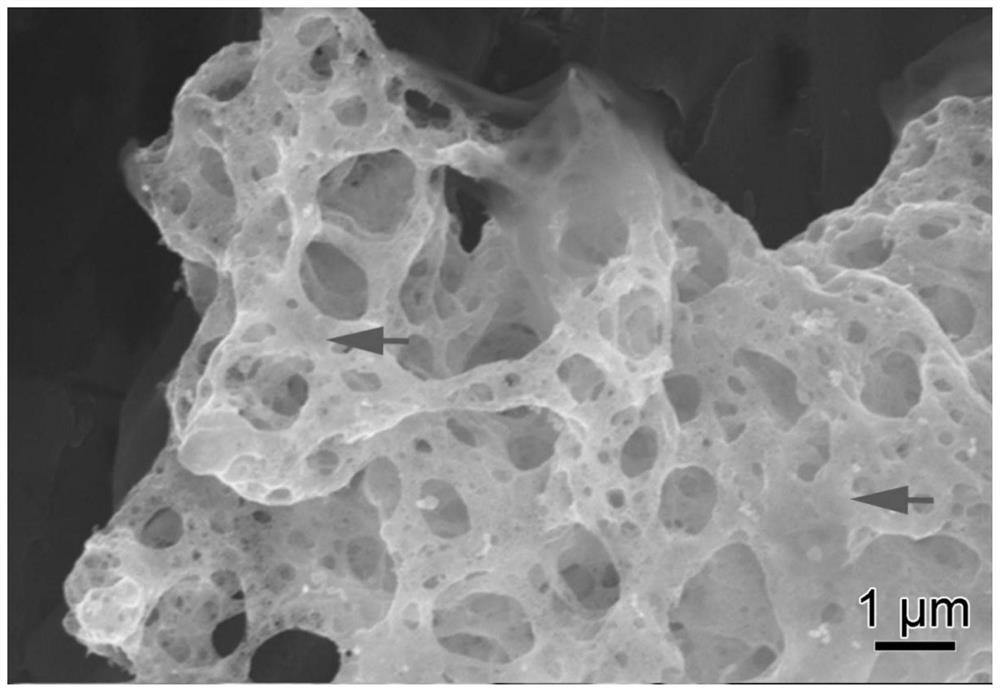
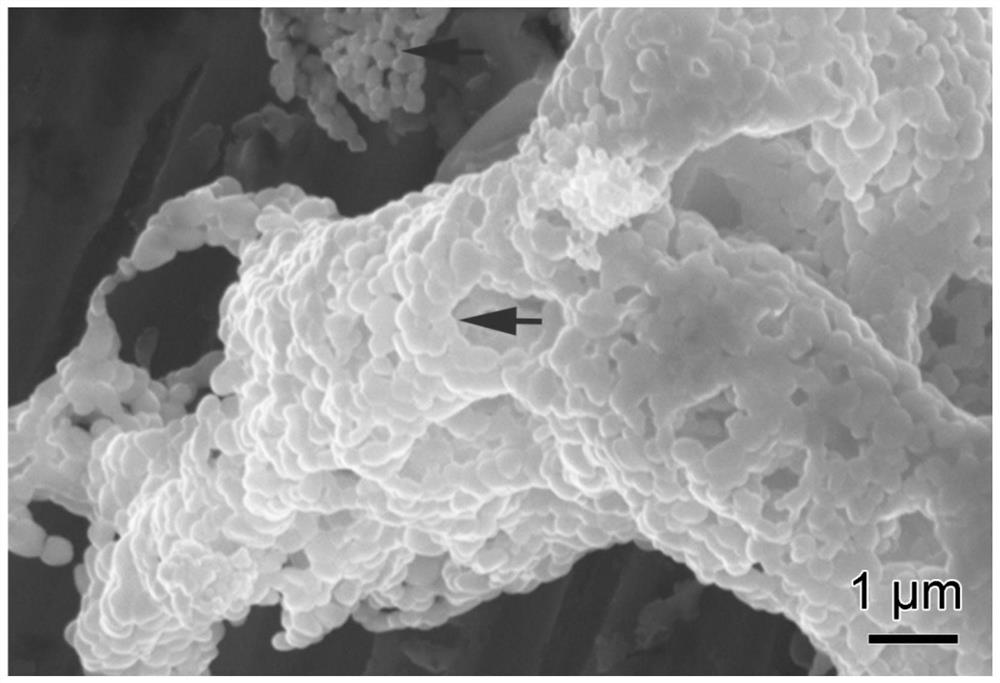
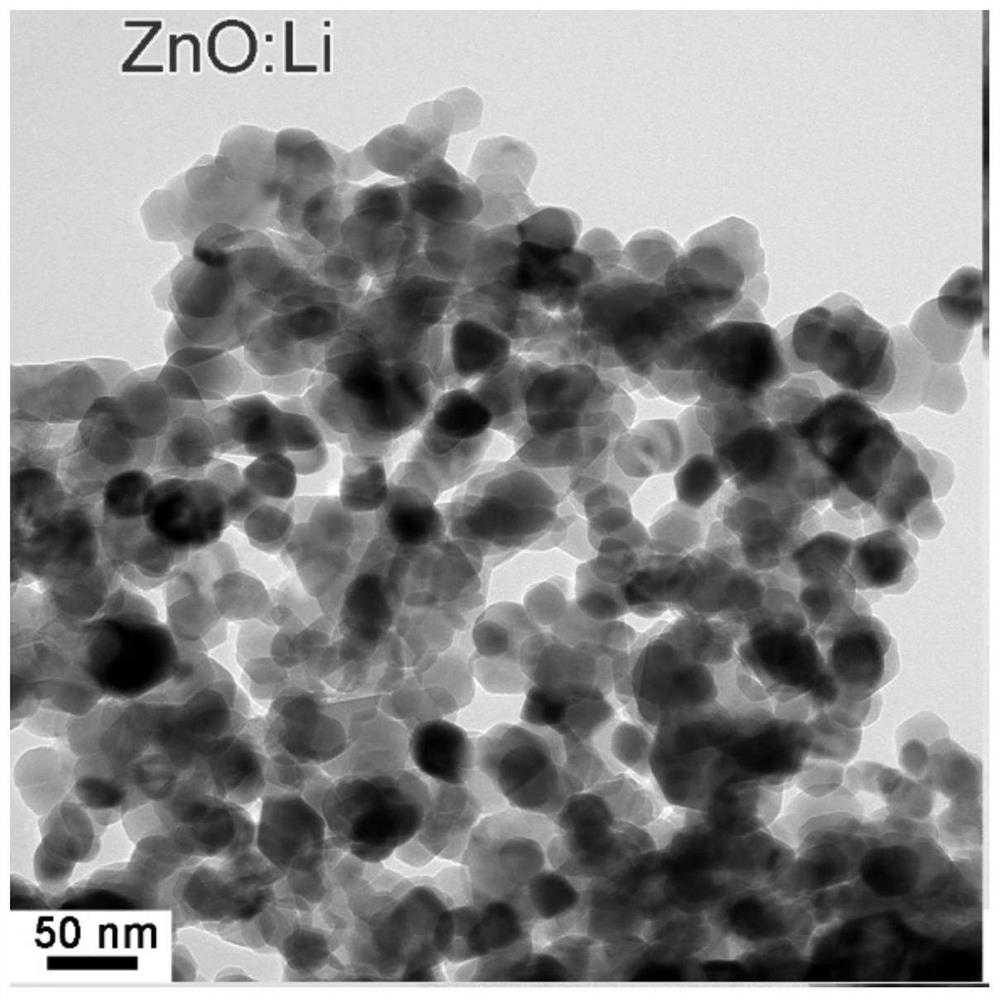
Method for limiting metal oxide agglomeration through low-valence metal ion doping based on first principle calculation design
A metal ion, first-class technology, applied in the field of limiting metal oxide agglomeration, can solve problems such as oxide agglomeration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0024] Specific Embodiment 1: This embodiment is a method based on first-principle calculations to design a method for restricting the agglomeration of metal oxides by doping with low-priced metal ions. Specifically, the following steps are carried out:
[0025] 1. Using the CASTEP module of the Materials Studio software, the generalized gradient approximation (GGA) PBE functional is used to describe the exchange interaction between electrons. Based on the first principles, the ZnO unit cell is geometrically optimized to obtain the most stable ZnO with total energy. unit cell, and determine three key parameters to balance calculation efficiency and calculation accuracy through gradient parameter convergence tests: k-point is 6×6×6, which represents the density of grid division in the calculation model; cut-off is 450eV ( truncation energy), each K point can be expanded with a discrete plane wave basis set, and theoretically an infinite number of plane waves is required, because...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0034] Specific embodiment two: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one is: the metal ion M described in step 4 is Li + . Others are the same as the first embodiment.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0035] Specific embodiment three: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one is: the metal ion M described in step 4 is Ag + . Others are the same as the first embodiment.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com