Application of RGS1 as target spot in adoptive cellular immunotherapy of tumors
A cellular immunity and adoptive technology, applied in antitumor drugs, animal cells, vertebrate cells, etc., can solve the problem that lymphocytes cannot reach tumors, and achieves improved anti-tumor effect, improved tumor treatment effect, and induced tumor cell apoptosis. the effect of death
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
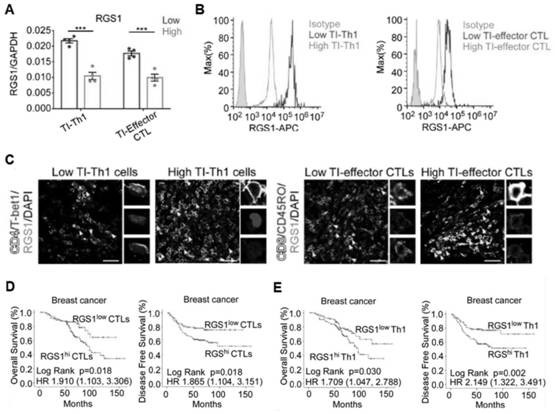
[0085] (1) The expression of RGS1 is related to the weakened recruitment ability of Th1 cells and CTL to breast cancer tissue
[0086] It has been reported that the intracellular signal transduction of G protein-coupled receptors of chemokines that control immune cell trafficking is checked by a group of G protein signal transduction regulators (RGS), but this type of RGS is detected in various human T cells. Expression in cell subpopulations has not yet been elucidated. In order to further explore whether the expression of RGS affects the recruitment of tumor T cells in breast cancer patients, this example uses the qRT-PCR method to compare the expression of RGS1 in Th1 cells isolated from primary tumor tissues of breast cancer patients with high or low Th1 infiltration situation, the result is as figure 2 As shown in A. A similar situation exists for infiltrating effector cell CTLs, such as figure 2 As shown in A. That is, the expression level of RGS1 is higher in Th1 ...
Embodiment 2
[0089] To further evaluate the clinical significance of RGS1, we investigated the expression of RGS1 in peripheral blood (PB) T cells of breast cancer patients. RGS1 expression of Th1 cells and effector CTLs in the peripheral blood of 219 breast cancer patients was correlated with clinical immunological characteristics of the patients. The optimal cut point of RGS1 expression in circulation effect CTL was determined by qRT-PCR and X-tile analysis (relative to GAPDH normalization, ≤0.01 was low expression, >0.01 was high expression), and high RGS1 expression in circulation effect CTL was associated with greater Tumors, more lymph node metastases, higher tumor cell proliferation and less apoptosis were associated, but not with patient age, pathological grade, and molecular subtype of breast cancer. Similarly, patients with higher RGS1 expression in circulating Th1 cells had larger tumor size and less tumor cell apoptosis, but expression was independent of tumor molecular subtype...
Embodiment 3
[0100] RGS1 inhibits intracellular signaling mediated by G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs)
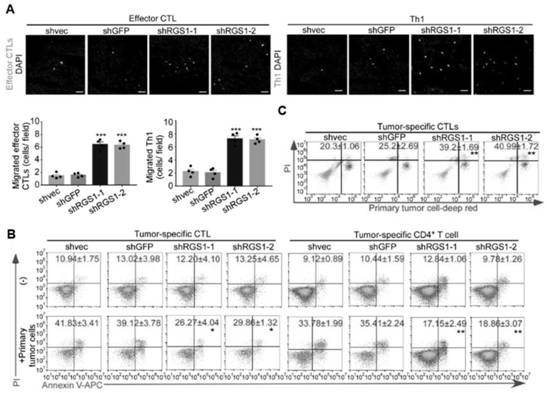
[0101] The RGS family is a class of proteins that interact with G proteins and inhibit G protein signaling by accelerating the activity of intracellular GTPases. In this example, it was investigated whether RGS1 affects the chemotaxis of Th1 and effector CTLs by inhibiting the downstream signaling of chemokine receptors.
[0102] The results of co-immunoprecipitation showed (such as Figure 4 A), RGS1 specifically binds CCR4, CXCR4, and CXCR3, but not CCR5, in effector CTLs, suggesting that RGS1 can regulate the downstream signaling of CCR4, CXCR4, and CXCR3. Furthermore, silencing of RGS1 in effector CTLs suppressed cAMP elevation following treatment with CXCL12, CCL22, or CXCL9 / 10 / 11 (eg, Figure 4 B), and enhanced calcium influx after CXCL12 stimulation (as shown in Figure 4 C shown). Meanwhile, silencing RGS1 significantly enhanced the phosphorylation of ERK and AKT in CXCL1...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com