Method for removing ibuprofen and naproxen in water by weak current stimulation enhanced microorganisms
An electrical stimulation and microorganism technology, applied in the field of environmental pollutant removal, can solve the problems of low removal efficiency of ibuprofen and naproxen, and achieve the effect of high removal efficiency and high removal efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] This embodiment provides a kind of method that weak electric stimulation strengthens microorganism to remove ibuprofen and naproxen in water, comprises the following steps:
[0037] (1) Construct the reactor system of carbon fiber electrode, reference electrode and electrolyte.
[0038] (2) Using 1-10mg / L ibuprofen and naproxen as the selection pressure, using municipal aerobic activated sludge as the inoculation source, inoculating according to the volume ratio of 5%, consisting of sodium acetate (20mM) and basic mineral salts The sterilized culture system was cultured at 30°C for 5-7 days in the dark, and then 5% of the culture was transferred to a new sterilized culture system, and the degradation efficiency of ibuprofen and naproxen reached 70%. above.
[0039](3) Add 10% volume ratio of the enriched solution obtained in (2) to the system composed of sodium acetate (20 mM) and electrolyte, add 5 mg / L ibuprofen or 2 mg / L naproxen, and inject into the reactor In the...
Embodiment 2
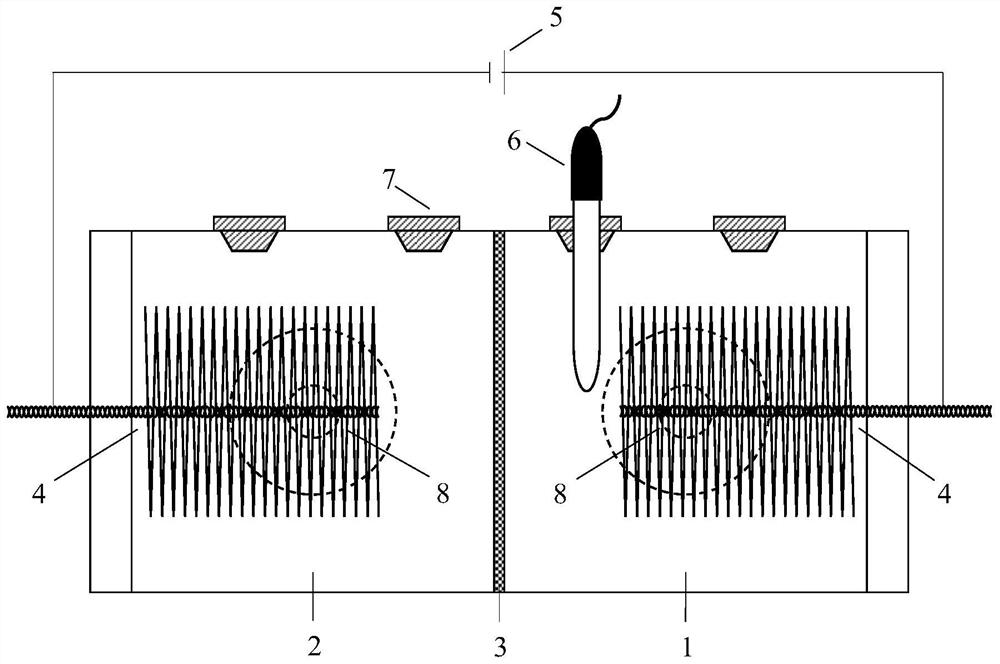
[0052] like figure 1 As shown, the bipolar chamber bioelectrochemical reactor in this embodiment is composed of four parts: a working electrode chamber 1 , a counter electrode chamber 2 , a cation exchange membrane 3 and a carbon fiber electrode 4 . Both the working electrode chamber 1 and the counter electrode chamber 2 are provided with liquid exchange ports 7 and 8 . Carbon fiber electrodes 4 are fixed in the working electrode chamber 1 and the counter electrode chamber 2 . The carbon fiber electrodes 4 in the working electrode chamber 1 and the counter electrode chamber 2 are respectively connected with the positive and negative electrodes of the external power supply 5 through wires. A reference electrode 6 is inserted into the working electrode chamber 1 to monitor current or voltage changes by other equipment.
[0053] like figure 2 and 3 As shown, 50 mM phosphate buffer containing 2 mg / L naproxen or 5 mg / L ibuprofen was added to the working electrode chamber, and ...
Embodiment 3
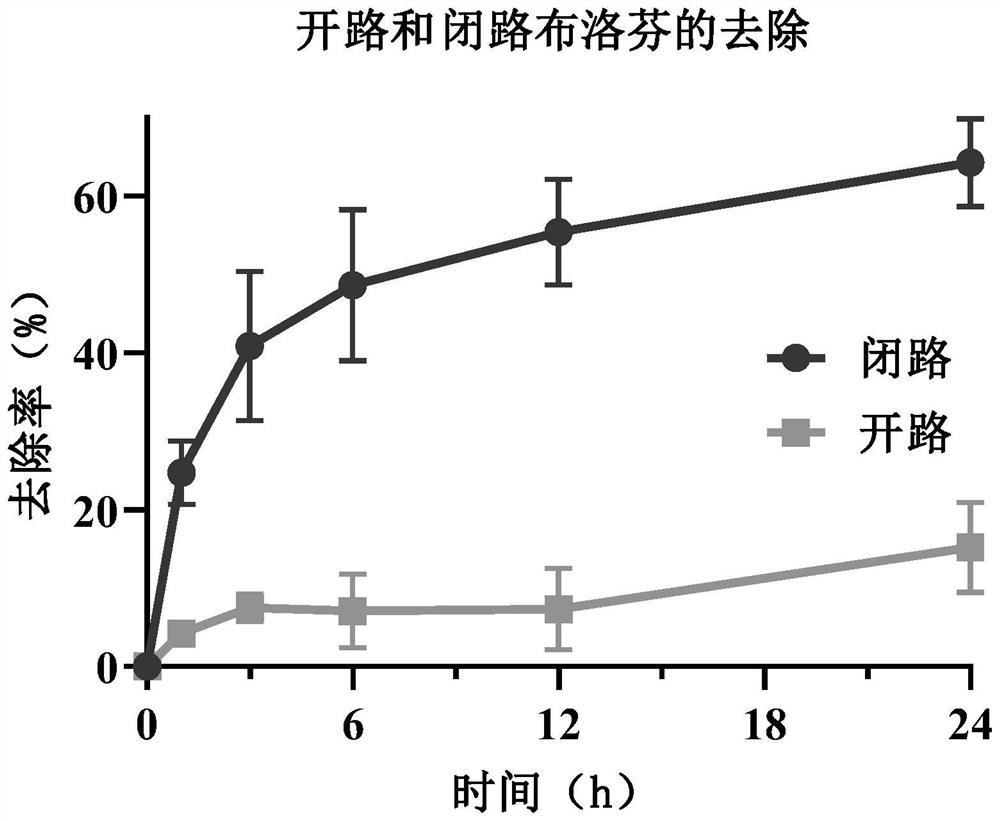
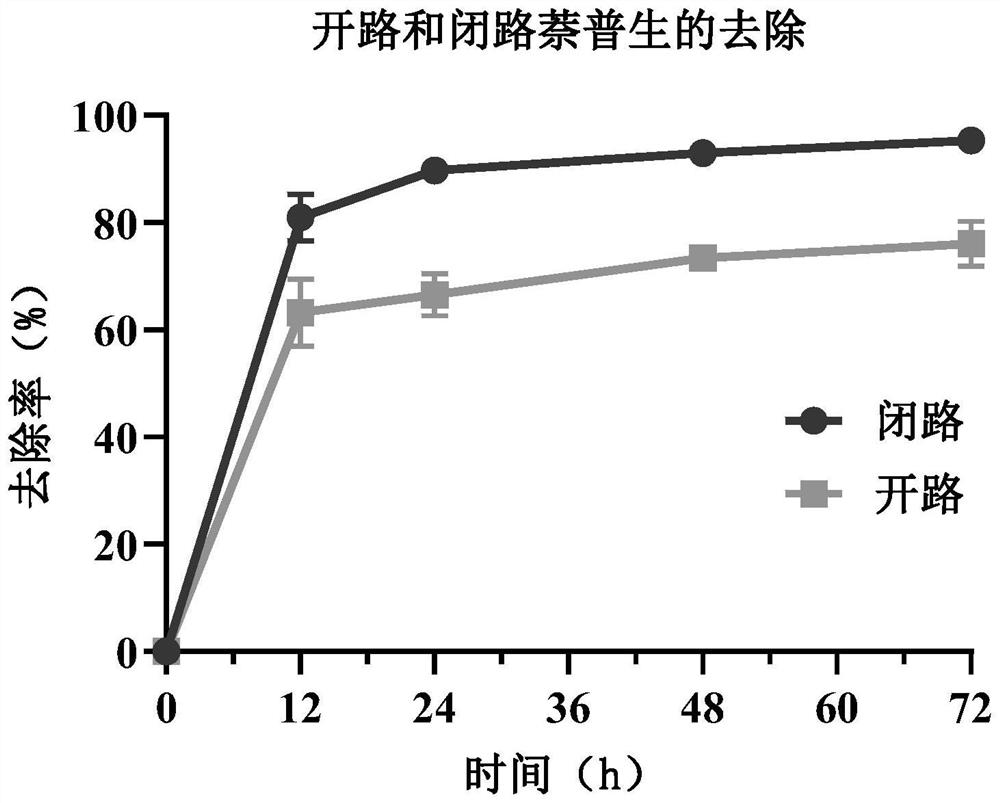
[0055] like Figure 4 and 5 As shown, the difference between this embodiment and the specific example 1 is that the concentration of ibuprofen added to the phosphate buffer in the working electrode chamber is 2 mg / L or 10 mg / L, and the concentration of naproxen is 1 mg / L or 5 mg / L . Externally applied weak electrical stimulation of +0.50V, the removal rates of 2, 5, and 10 mg / L ibuprofen reached 56.5%, 64.3% and 71.1% within 24 hours, respectively, and the removal rate increased slightly with the initial concentration; 1 mg / L of ibuprofen The removal rate of naproxen within 48h was 77.6%, the removal rate of 2 and 5mg / L naproxen within 72h was not much different, and the maximum removal rates were 95.3% and 95.2%, respectively, indicating that the different concentration ranges of cloth Both profen and naproxen were effectively removed.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com