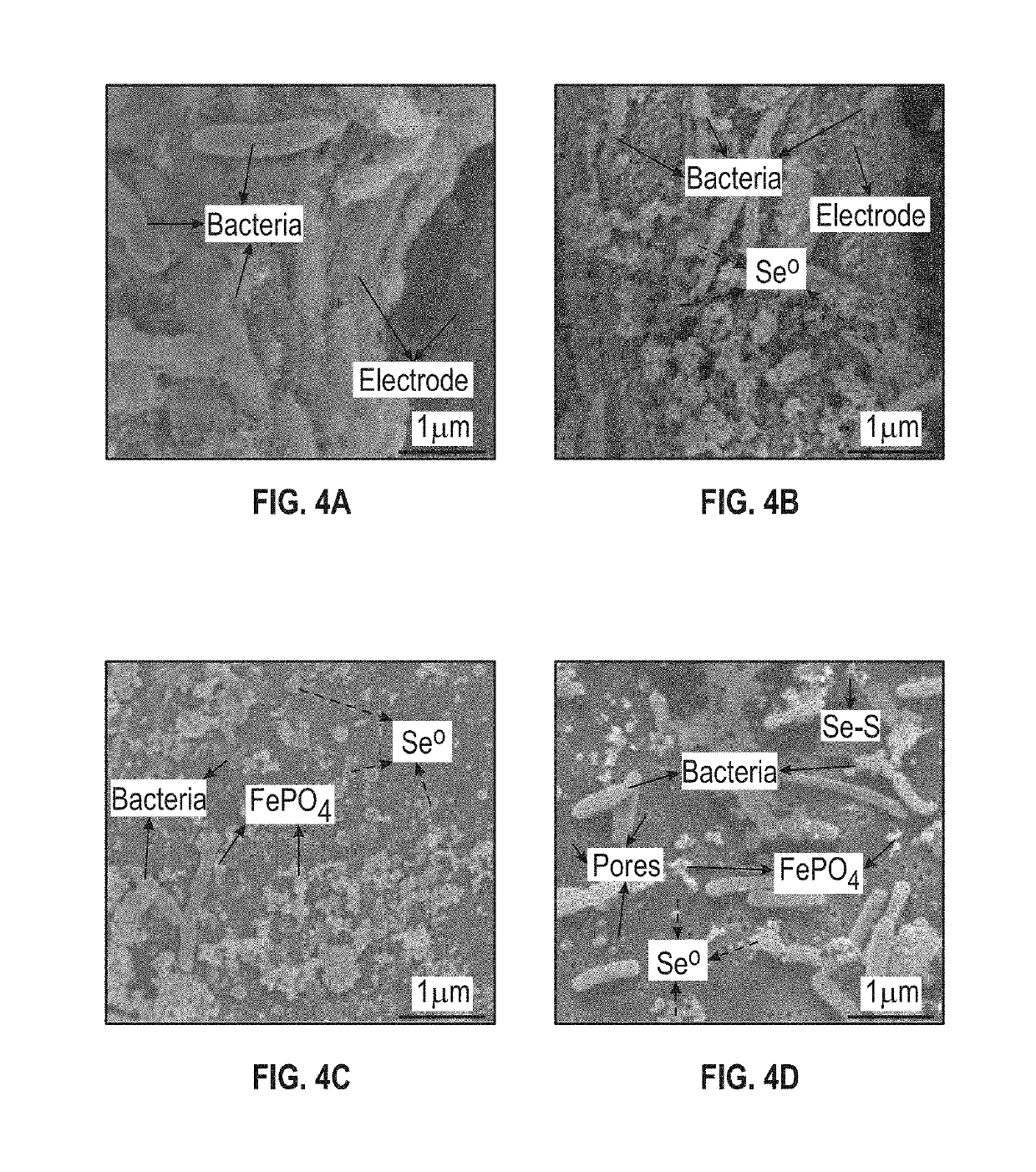
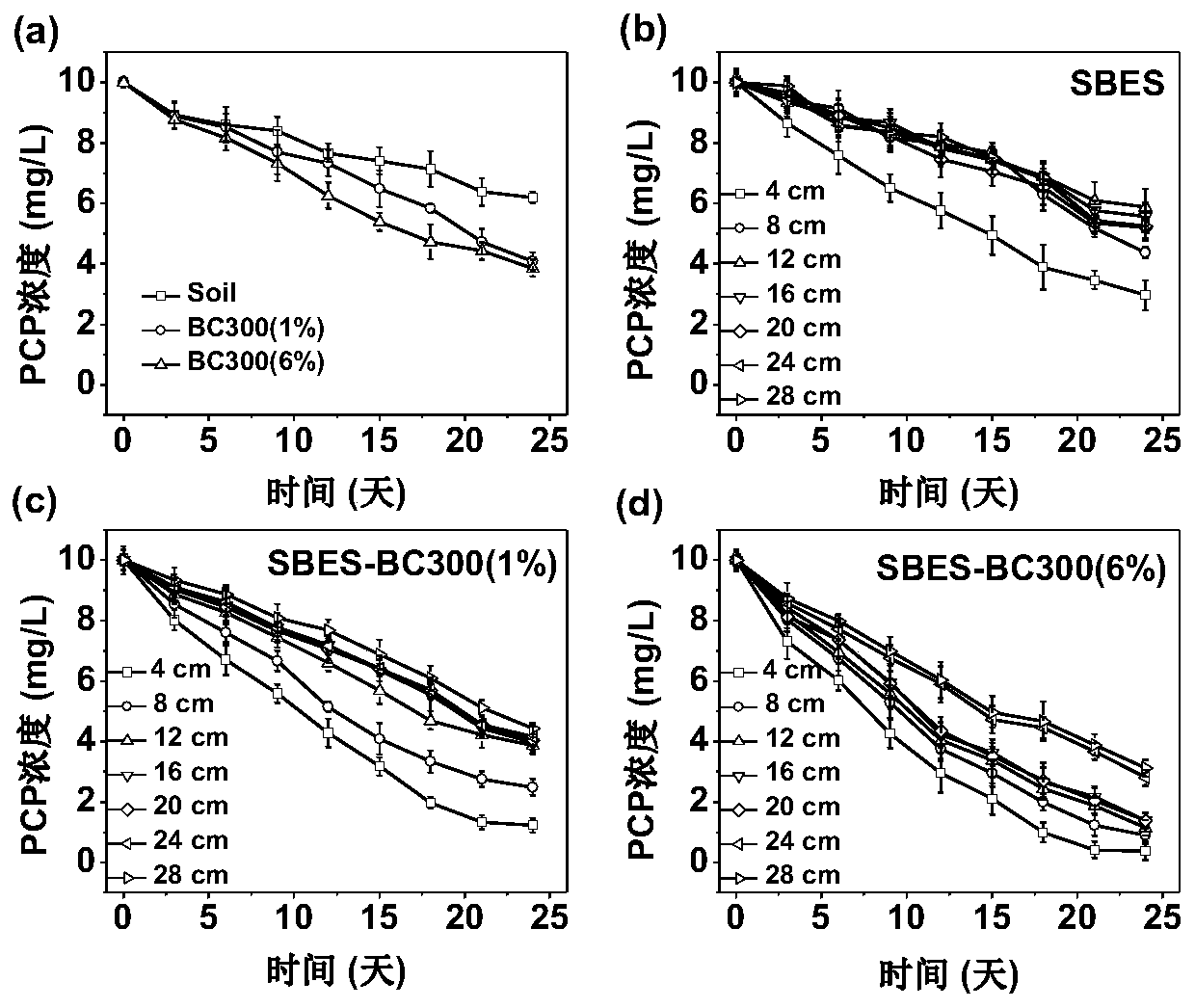
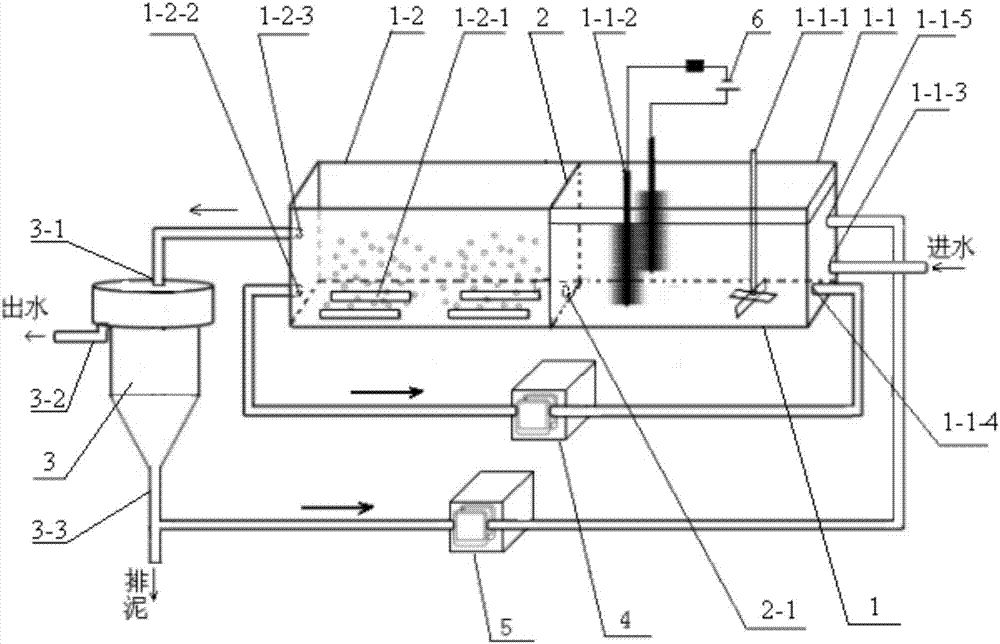
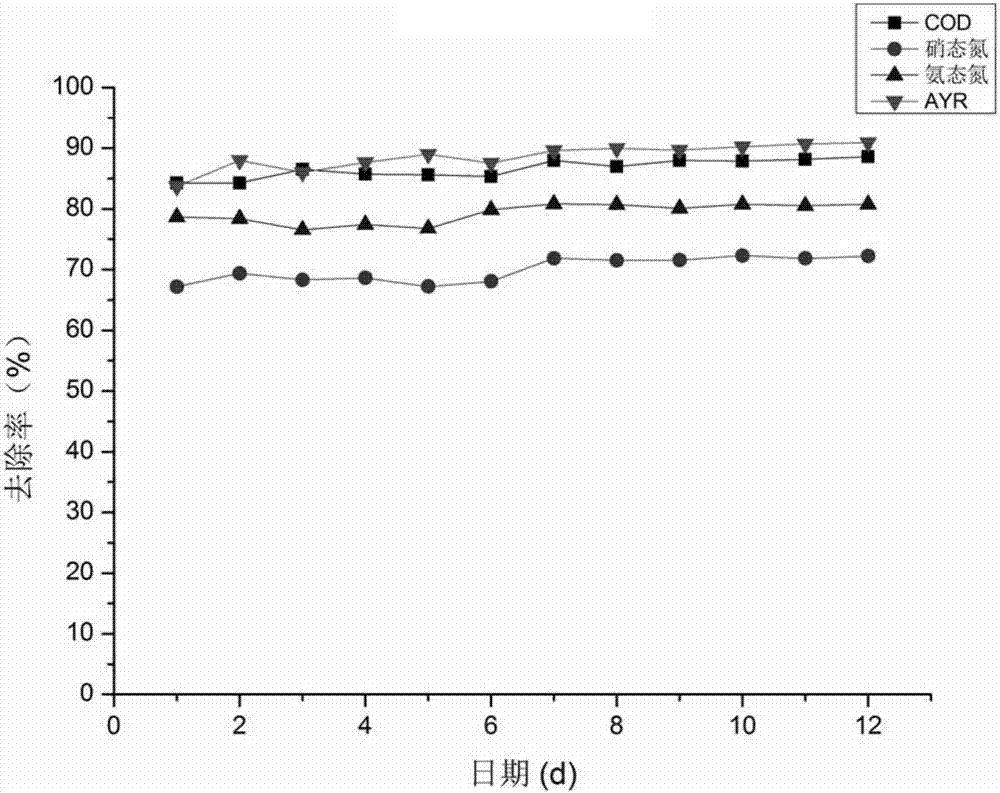
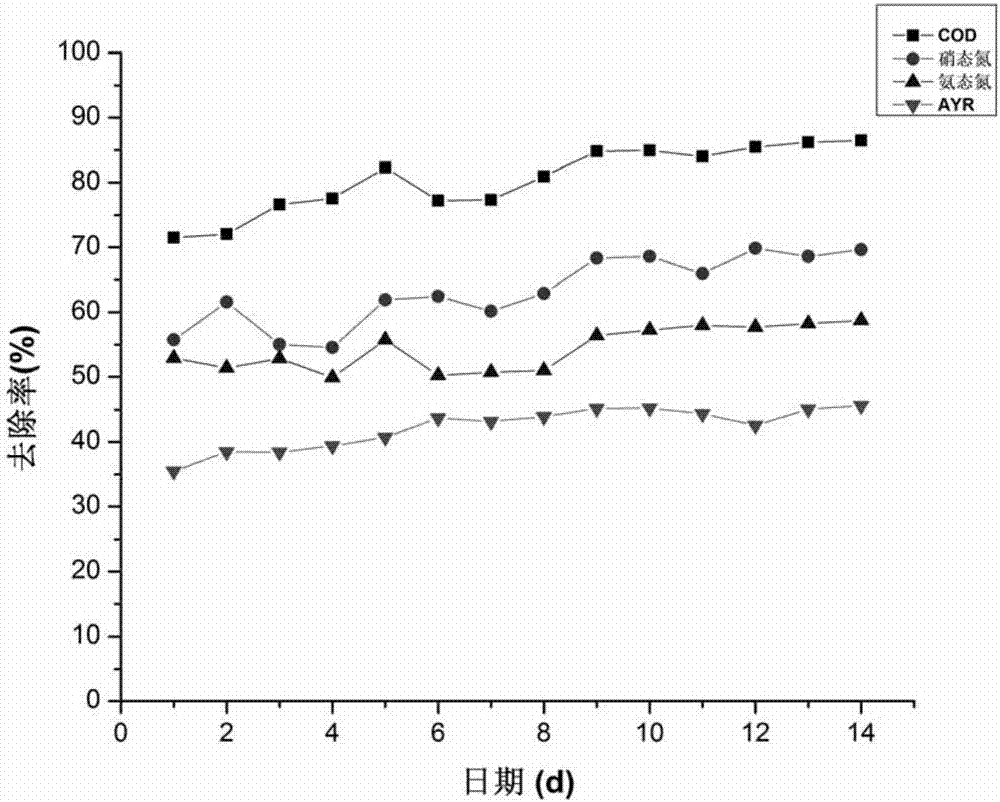
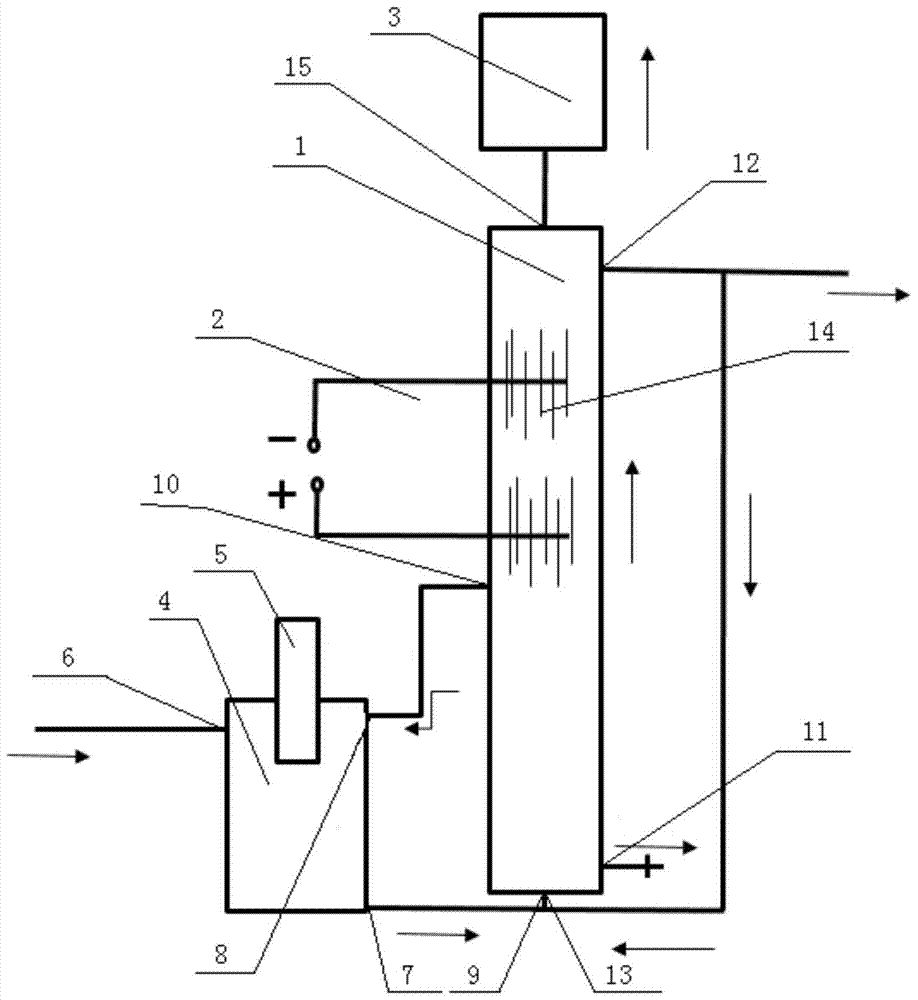
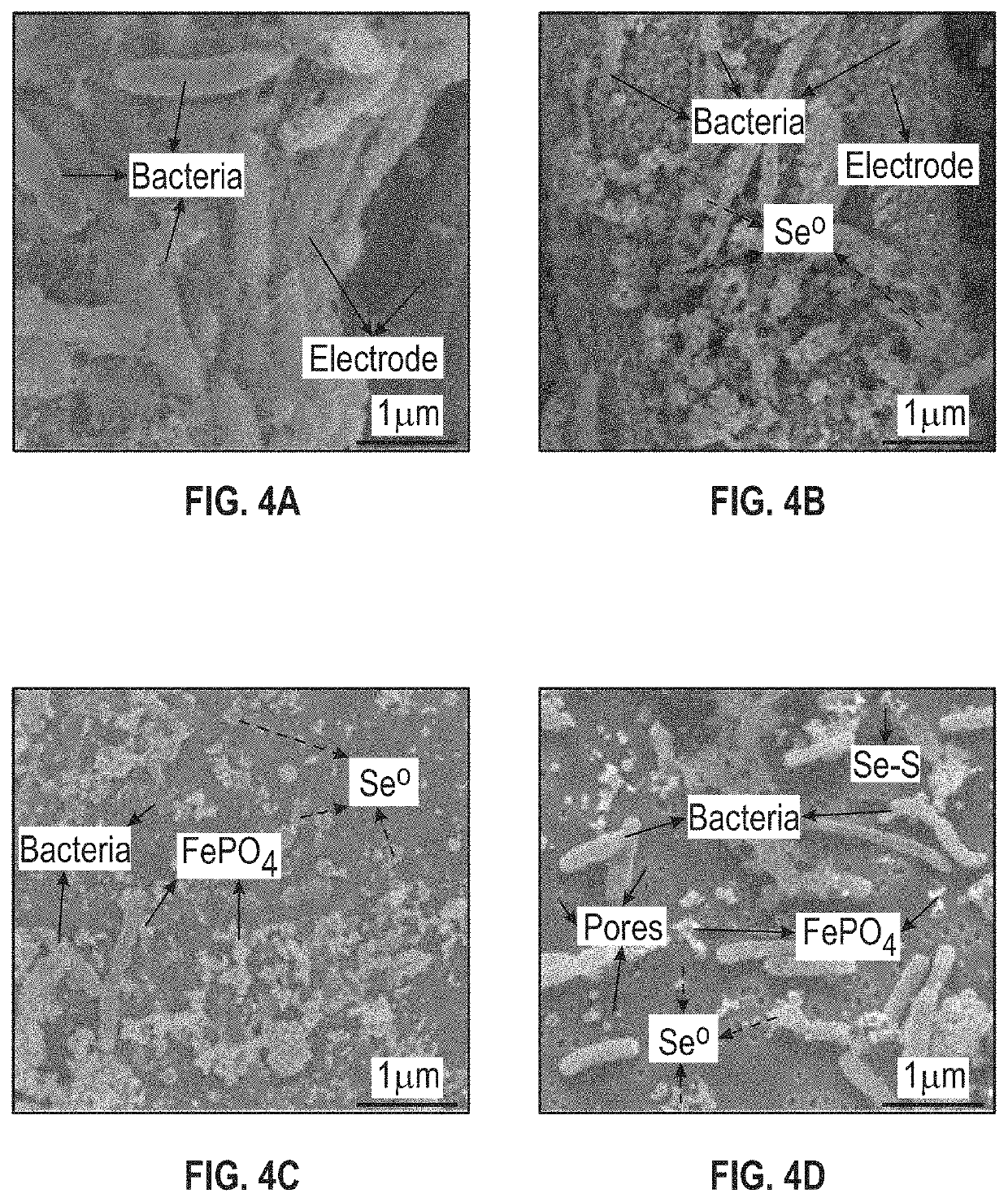
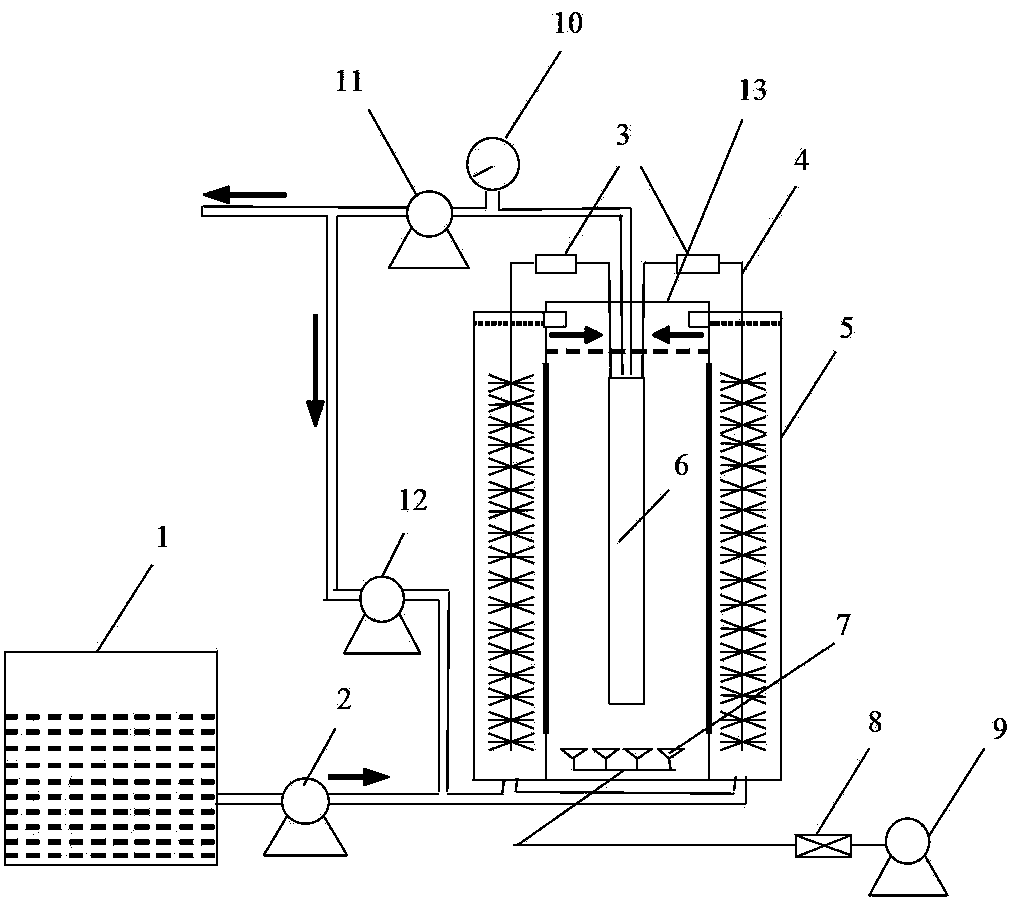
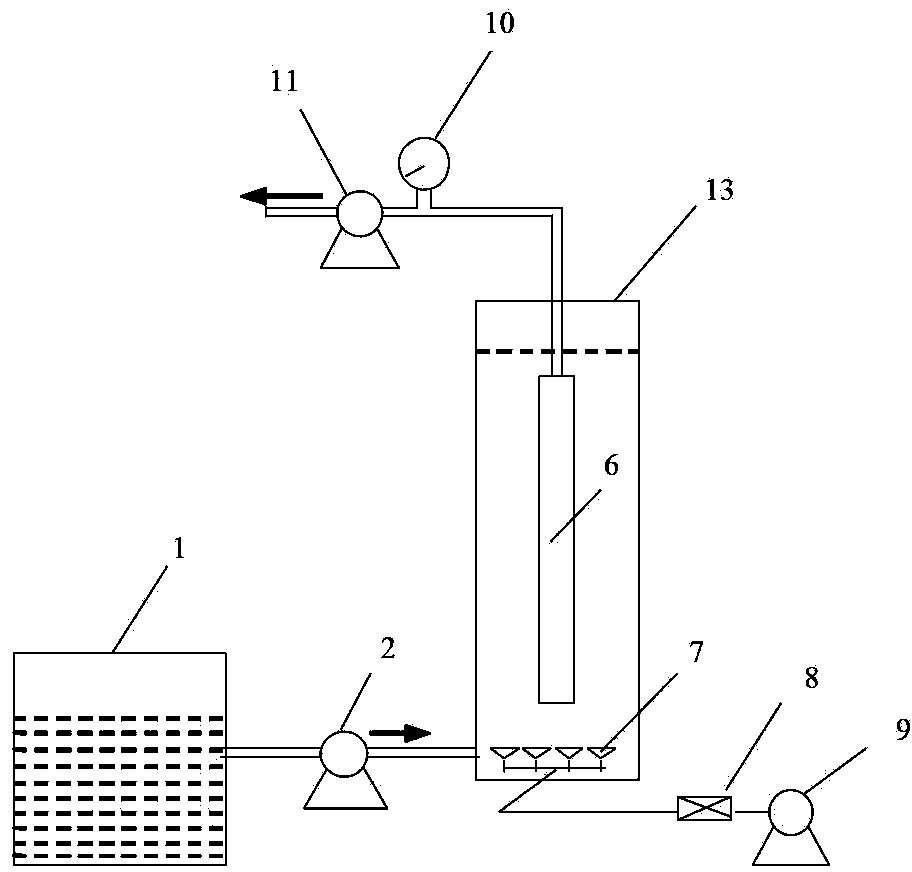
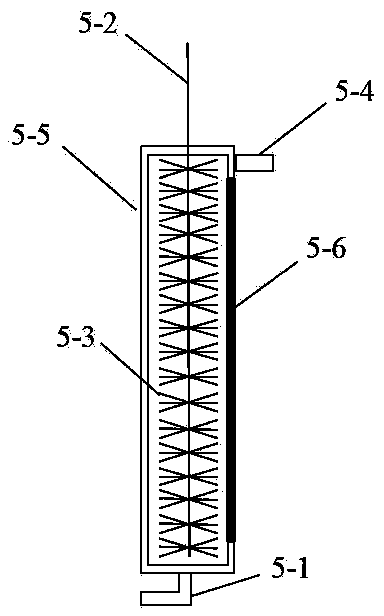
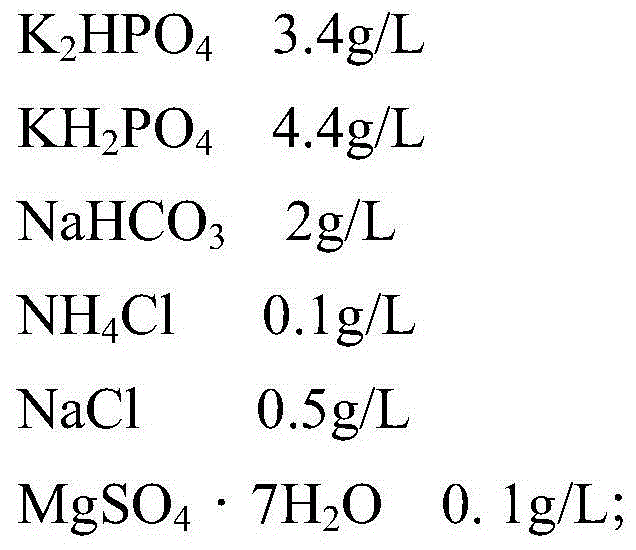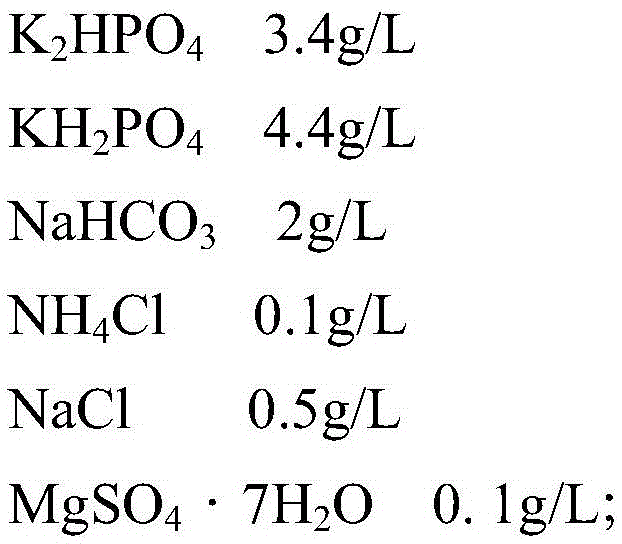Patents
Literature
38 results about "Bioelectrochemical reactor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
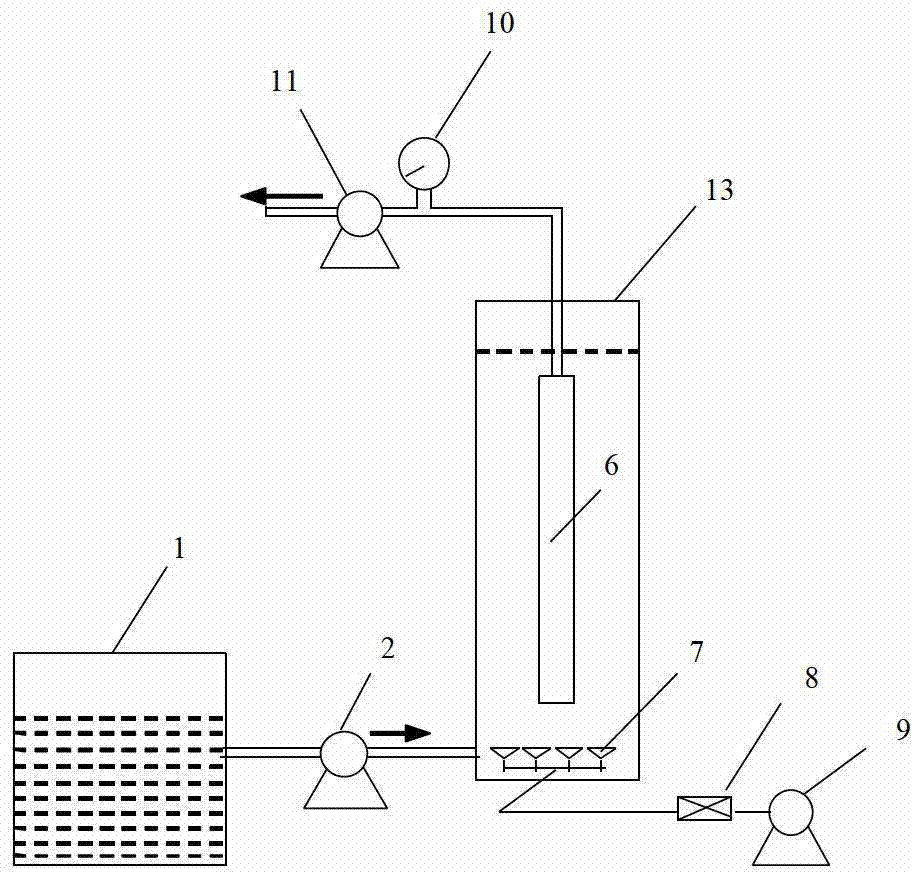
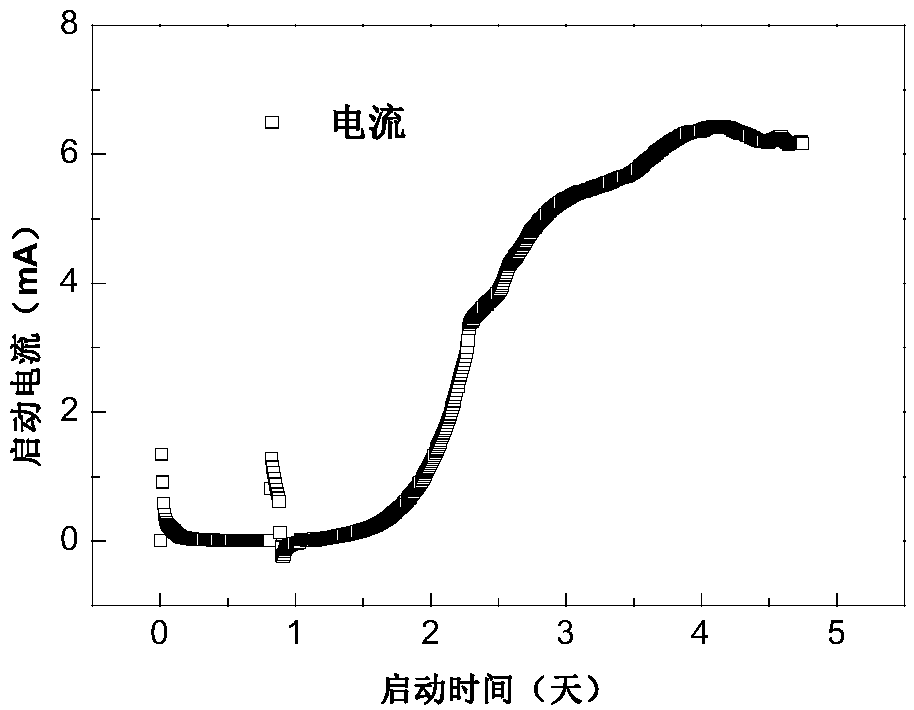
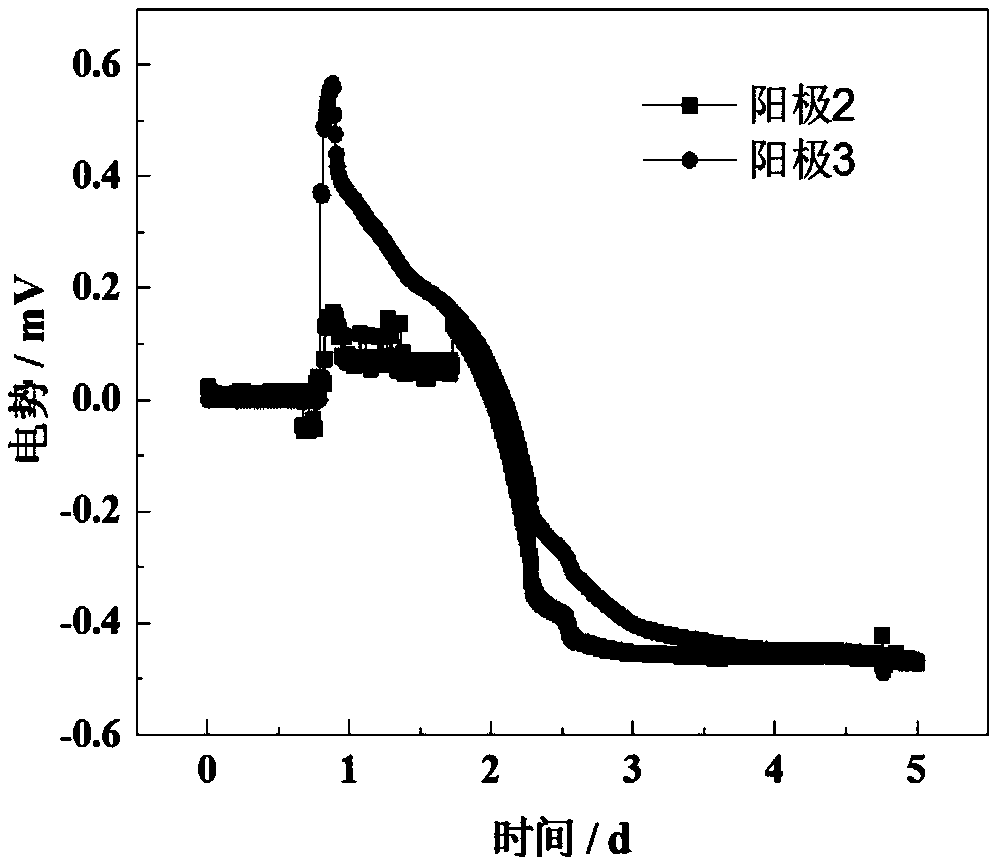
Bioelectrochemical reactors are a type of bioreactor where bioelectrochemical processes can take place. They are used in bioelectrochemical syntheses, environmental remediation and electrochemical energy conversion. Examples of bioelectrochemical reactors include microbial electrolysis cells, microbial fuel cells and enzymatic biofuel cells and electrolysis cells, microbial electrosynthesis cells, and biobatteries. This bioreactor is divided in two parts: The anode, where the oxidation reaction takes place; And the cathode, where the reduction occurs.
Method for processing coal gasification wastewater
ActiveCN101654316APromote degradationImprove nitrogen removal efficiencyWaste water treatment from gaseous effluentsMultistage water/sewage treatmentCoal gasification wastewaterCatalytic oxidation
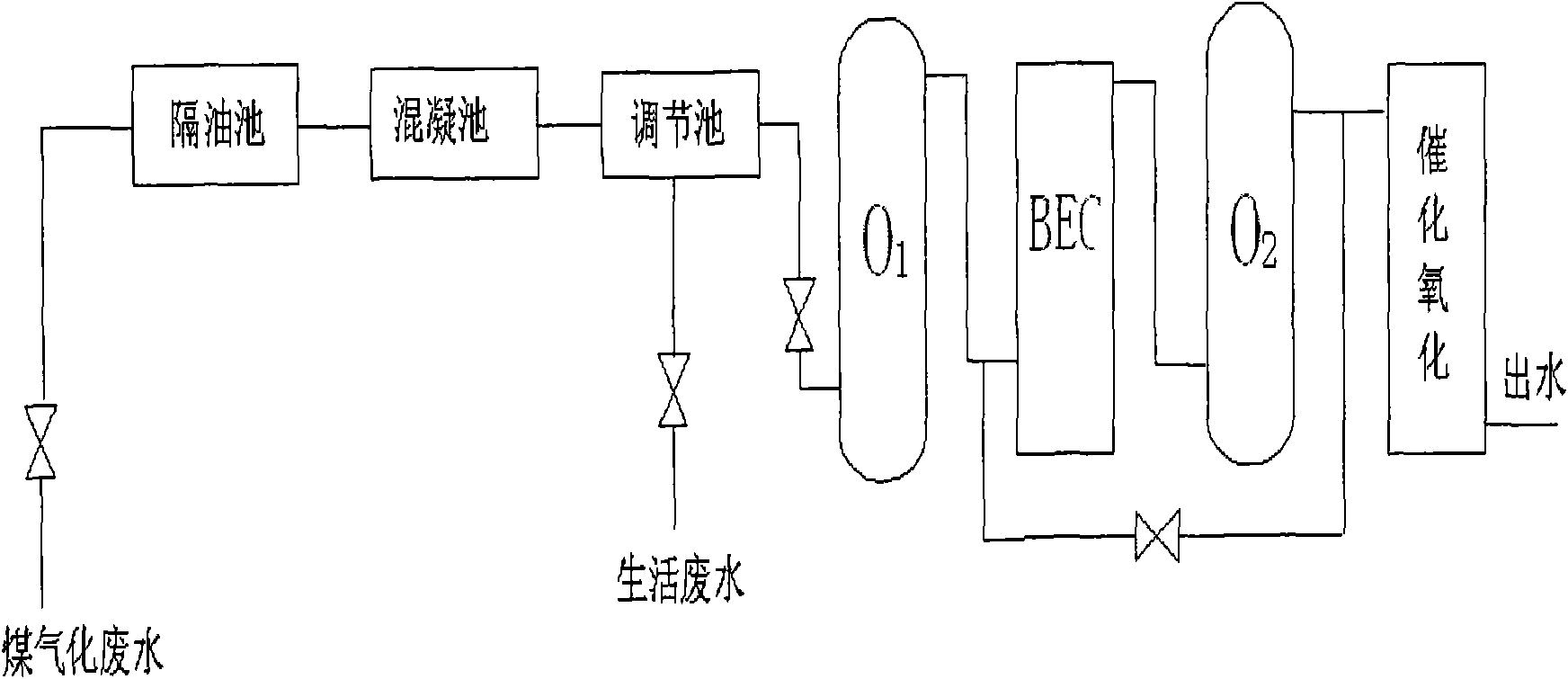
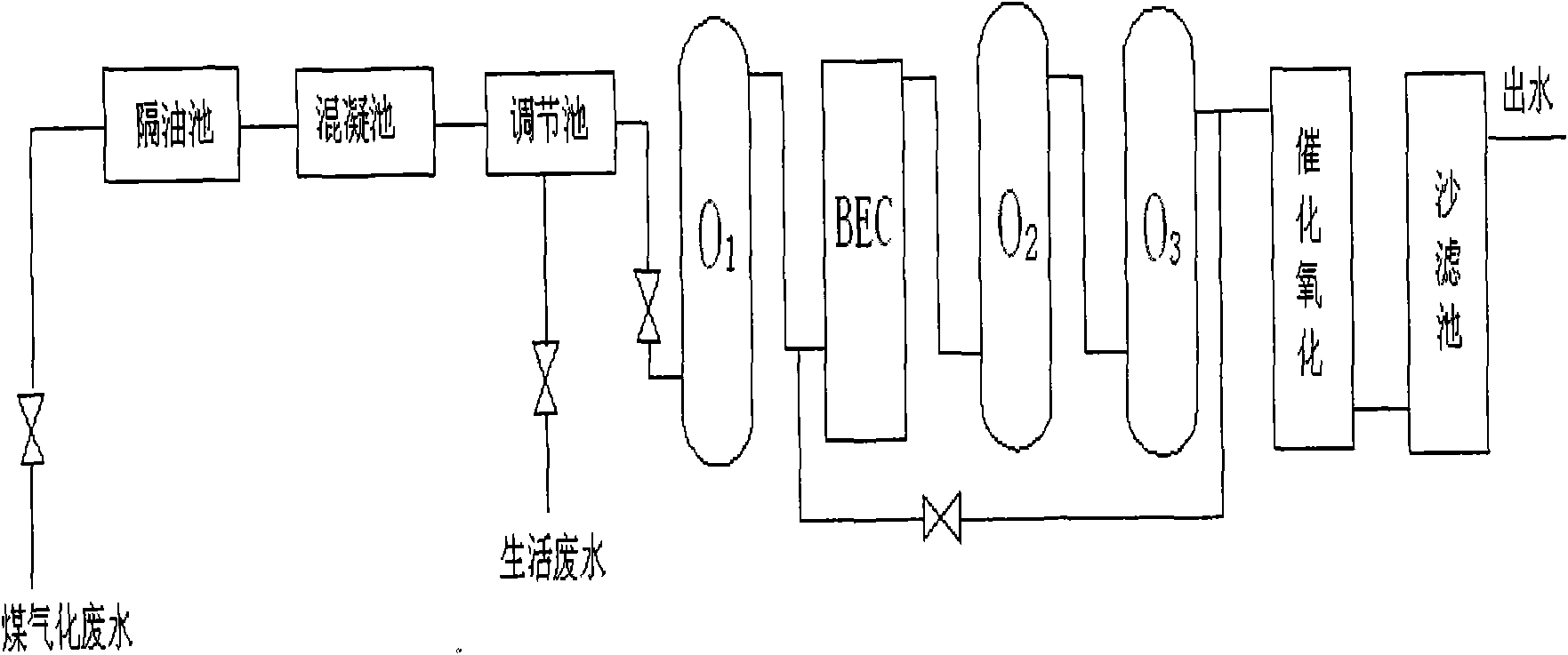
The invention discloses a method for processing coal gasification wastewater. The method sequentially comprises the following steps: a. carrying out preprocessing on the coal gasification wastewater in a preprocessing step comprising oil removal processing, coagulation processing and optional adjustment processing; then b. leading the preprocessed coal gasification wastewater to sequentially flowthrough a first-class bio-contact oxidation reactor, a biological electrochemical reactor, a second-class bio-contact oxidation reactor and an optional third-class or multi-class bio-contact reactor to carry out biological processing; and c. leading the biologically processed coal gasification wastewater to carry out catalytic oxidation processing in a catalytic oxidation reactor.
Owner:ENN ENVIROTECH CO LTD
Membrane biological electrochemical reactor device with high-quality effluent and low membrane pollution
ActiveCN103241895AReduce pollutionRealize denitrificationWater contaminantsMultistage water/sewage treatmentPeristaltic pumpTreatment effect
The invention relates to a membrane biological electrochemical reactor device with high-quality effluent and low membrane pollution, relates to the field of sewage treatment and is used for solving the problems of serious MBR (Membrane Bio-Reactor) membrane pollution, low nitrogen removal rate, poor treatment effect on sewage which is difficult to degrade and the like. The reactor device comprises a water box, a water-inflow peristaltic pump, an MFC (Microfunction Circuit) anode chamber, a stainless steel flat plate membrane, an MBR reactor, a conducting wire, an external resistor, an aeration head, an air flowmeter, an air compressor, a vacuum pressure gauge, a backflow peristaltic pump and an effluent peristaltic pump. As the reactor device is used, the sewage firstly enters the anaerobic MFC anode, and anaerobic electricity generating microorganisms perform hydrolytic acidification pretreatment; then the sewage enters the MBR, and the partial effluent are enabled to flow back into the anaerobic anode chamber, so that the denitrification of the sewage is further performed. Therefore, the energy source recovery and in-situ utilization of the electric energy performed by the MFC, the effective control of the membrane pollution and the efficient treatment of the sewage are realized. As a result, the reactor device is obvious in economic and environmental benefits. The reactor device provided by the invention is applied to the field of the sewage treatment.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
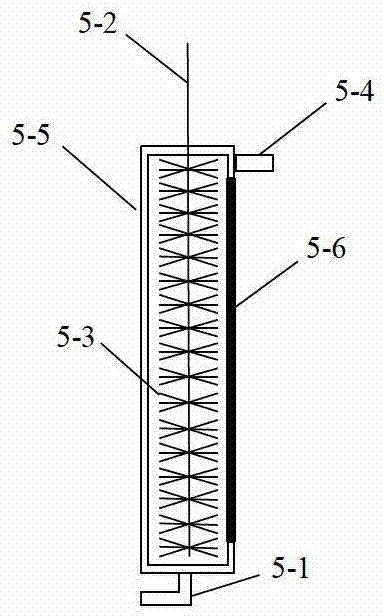
Bio-electrochemical reactor and application thereof in degrading fluoronitrobenzene wastewater
ActiveCN104628090AImprove processing efficiencyEasy to operateTreatment by combined electrochemical biological processesWater contaminantsWastewaterEngineering
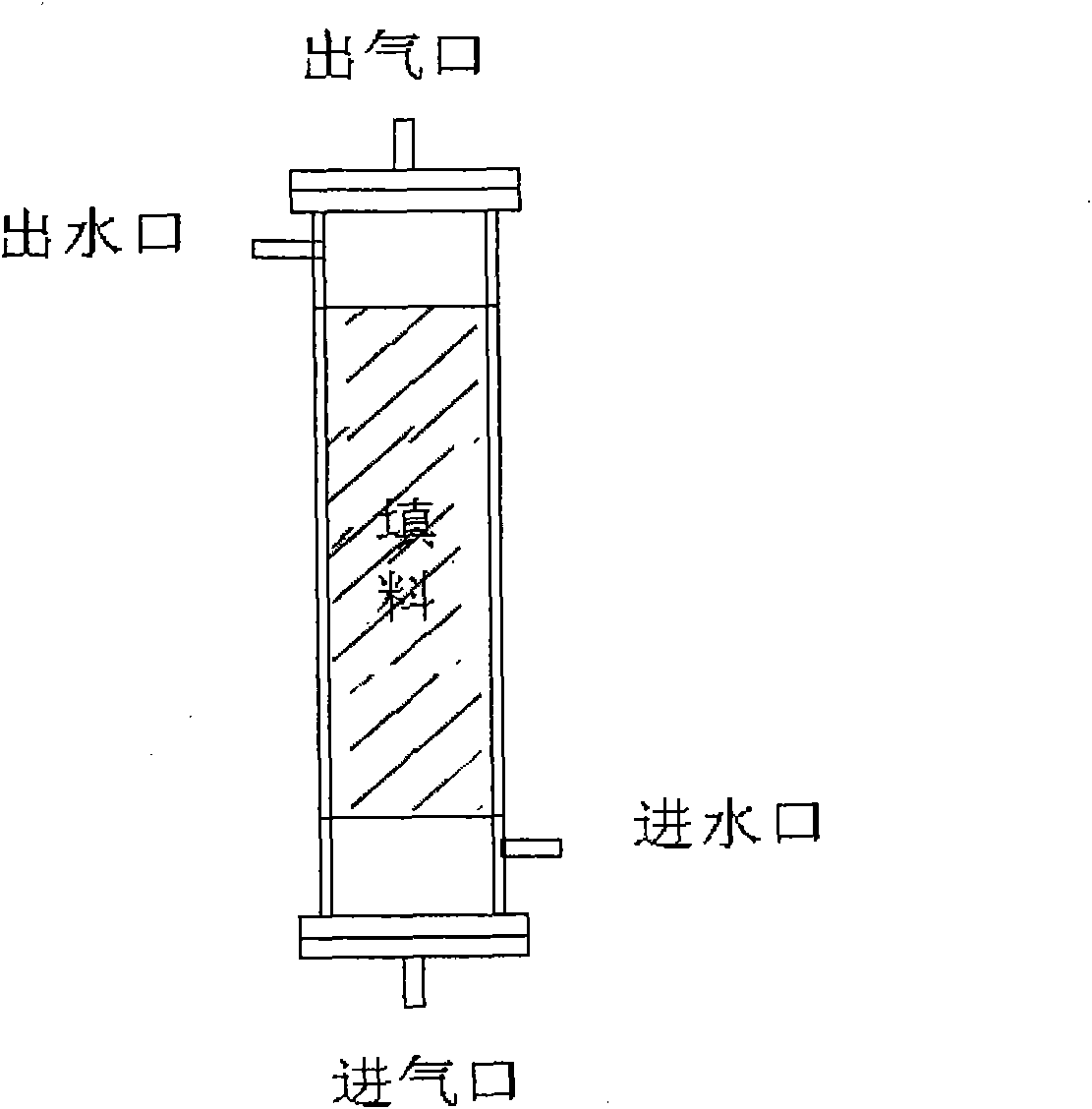
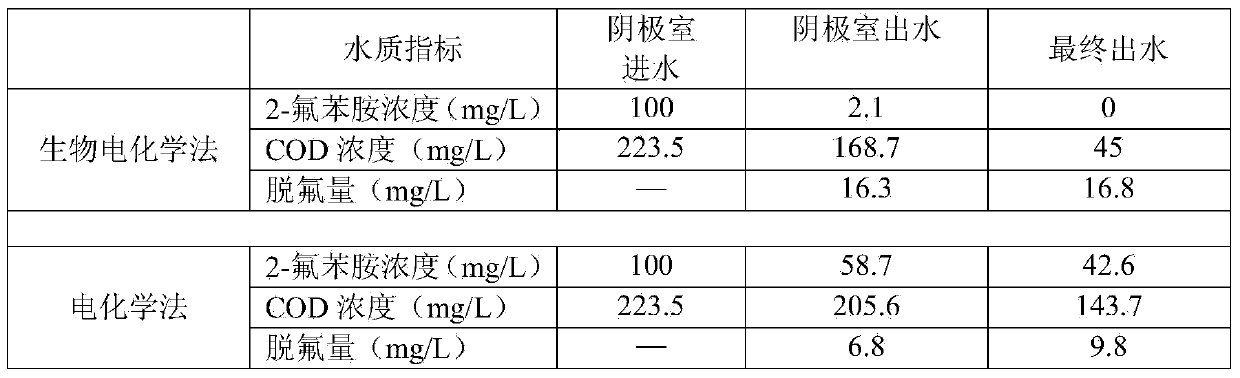
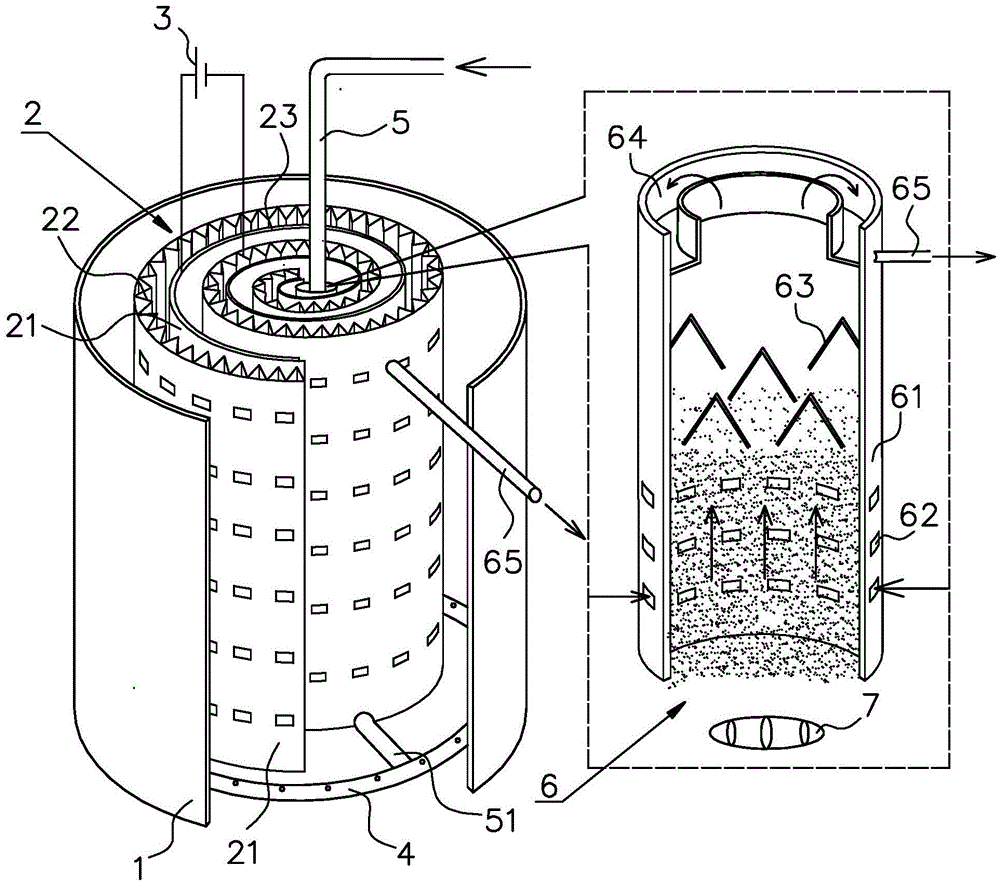
The invention discloses a bio-electrochemical reactor and an application thereof in degrading fluoronitrobenzene wastewater. The bio-electrochemical reactor comprises a bed body, wherein an electrode is arranged in the bed body, the electrode is a spiral coil type electrode which is water-permeable in a radial direction, and a water distributor which is positioned on the periphery of the spiral coil type electrode and a water outlet device which is positioned at a central position of the spiral coil type electrode are also arranged in the bed body. According to the bio-electrochemical reactor disclosed by the invention, the spiral coil type electrode is formed by winding a cathode electrode and an anode electrode which are insulated from each other, and a cathode and an anode can be used for treating pollutants synchronously so as to ensure that the treatment efficiency can be improved, operation steps can also be simplified, and the treatment cost can be reduced. Meanwhile, the water distributor is arranged on the periphery of the spiral coil type electrode, the water outlet device is arranged at the central position of the spiral coil type electrode, wastewater can be permeated to the center from the periphery of the spiral coil type electrode, and a plurality of cathode-anode groups which can be used for treating the wastewater for a plurality of times are formed in the spiral coil type electrode, so that the wastewater treatment efficiency can be greatly improved; and aiming at the fluoronitrobenzene wastewater treated by using the bio-electrochemical reactor disclosed by the invention, the fluoronitrobenzene pollutant removal rate, defluorination rate and mineralization rate can basically reach more than 90% respectively.
Owner:ZHEJIANG GONGSHANG UNIVERSITY
Biochar-bioelectrochemistry coupled soil remediation system and method
InactiveCN111167848AShort degradation cycleIncrease the effective degradation radiusContaminated soil reclamationAuxiliary electrodeEdaphic
The invention discloses a biochar-bioelectrochemistry coupled soil remediation system and method. The soil remediation system comprises a bioelectrochemical reactor and biochar which is to be mixed with to-be-remediated soil. The bioelectrochemical reactor comprises a reaction container used for containing the to-be-remediated soil, electrodes used for being inserted into the to-be-remediated soiland an electrochemical workstation, wherein the electrodes comprise a working electrode, an auxiliary electrode and a reference electrode, and the working electrode, the auxiliary electrode and the reference electrode are electrically connected with the electrochemical workstation. The biochar-bioelectrochemistry coupled soil remediation system provided by the invention is suitable for in-situ remediation of soil, capable of reducing the environmental risk of secondary pollution caused by a physicochemical remediation method, shortening the degradation period of pollutants and increasing theeffective degradation radius of soil pollutant degradation, low in equipment cost, low in energy consumption and capable of being widely applied to in-situ remediation of persistent organic contaminated soil.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
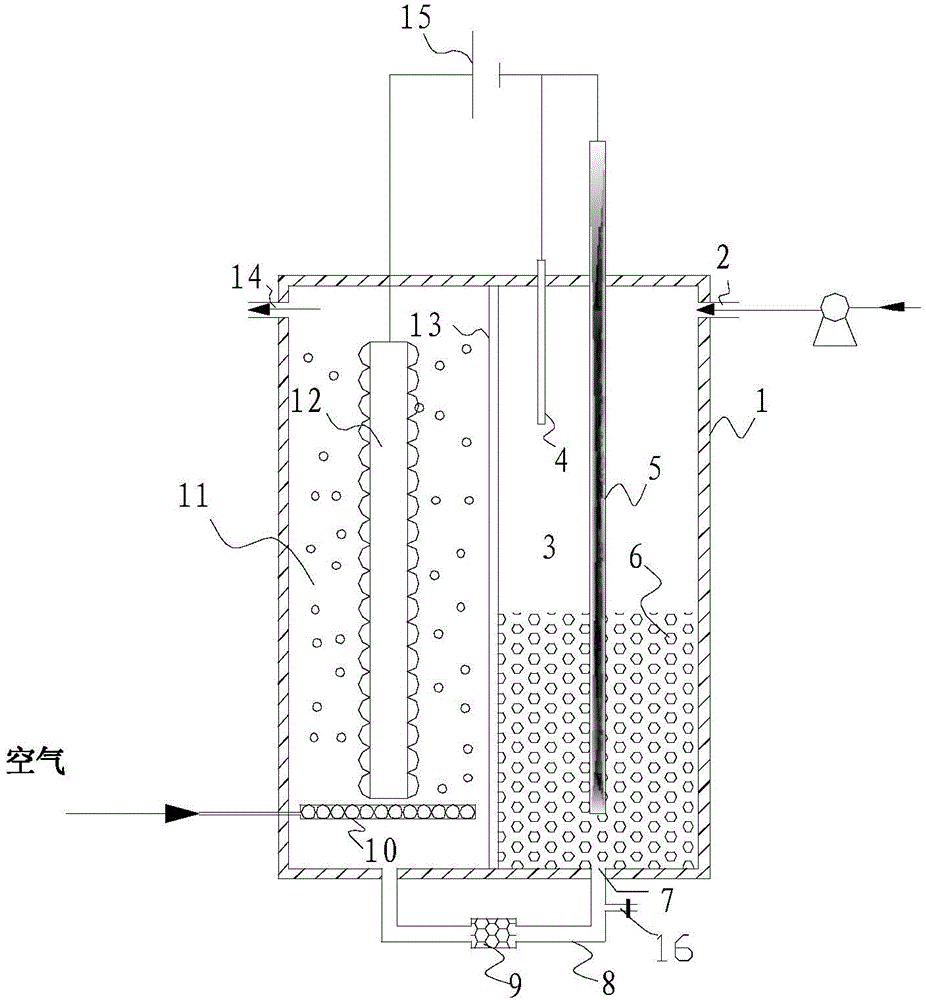
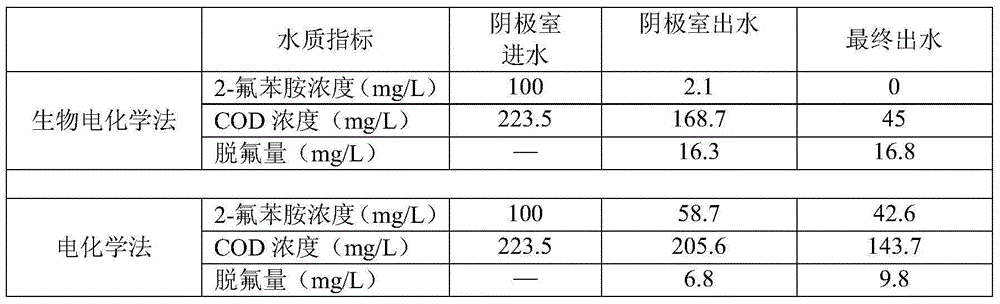
Bioelectrochemical reactor for treating organic fluoride-containing wastewater and treatment method for organic fluoride-containing wastewater
ActiveCN103787490AReduce processing costsEfficient coupling of degradation functionsWater contaminantsBiological water/sewage treatmentMicroorganismElectrochemistry
The invention discloses a bioelectrochemical reactor for treating organic fluoride-containing wastewater and a treatment method for the organic fluoride-containing wastewater. The bioelectrochemical reactor comprises a bed body, a partition plate, a conduit, a biological cathode, a biological anode, a power supply, a water inlet and a water outlet, wherein the partition plate is vertically arranged in the bed body, and divides the bed body into a cathode chamber and an anode chamber; the bottoms of the cathode chamber and the anode chamber are communicated through the conduit; the power supply is connected with the biological cathode and the biological anode; the water inlet is formed in the cathode chamber; the water outlet is formed in the anode chamber. According to the bioelectrochemical reactor and the treatment method, the organic fluoride-containing wastewater is treated in two stages under the catalysis action of cathode and anode microorganisms, so that the treatment efficiency of the organic fluoride-containing wastewater is improved, the overall treatment cost of the organic fluoride-containing wastewater is lowered, and the problem of difficulty in the biodegradation of the organic fluoride-containing wastewater is solved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG GONGSHANG UNIVERSITY
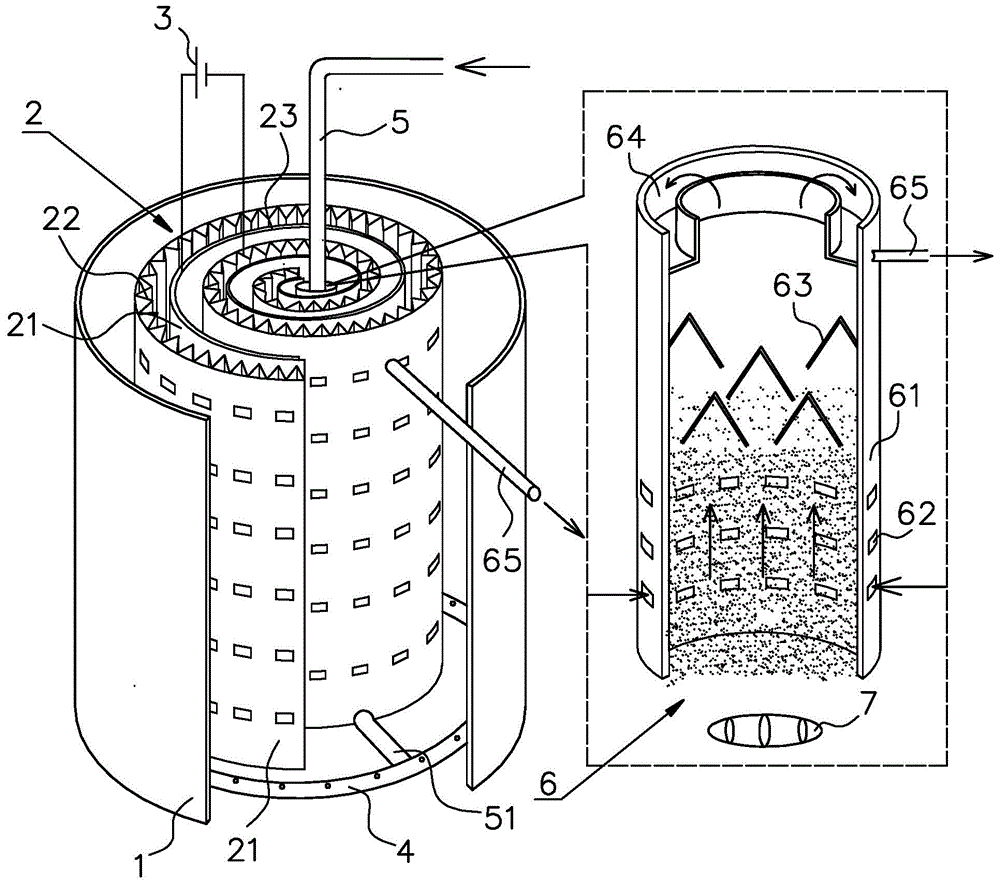
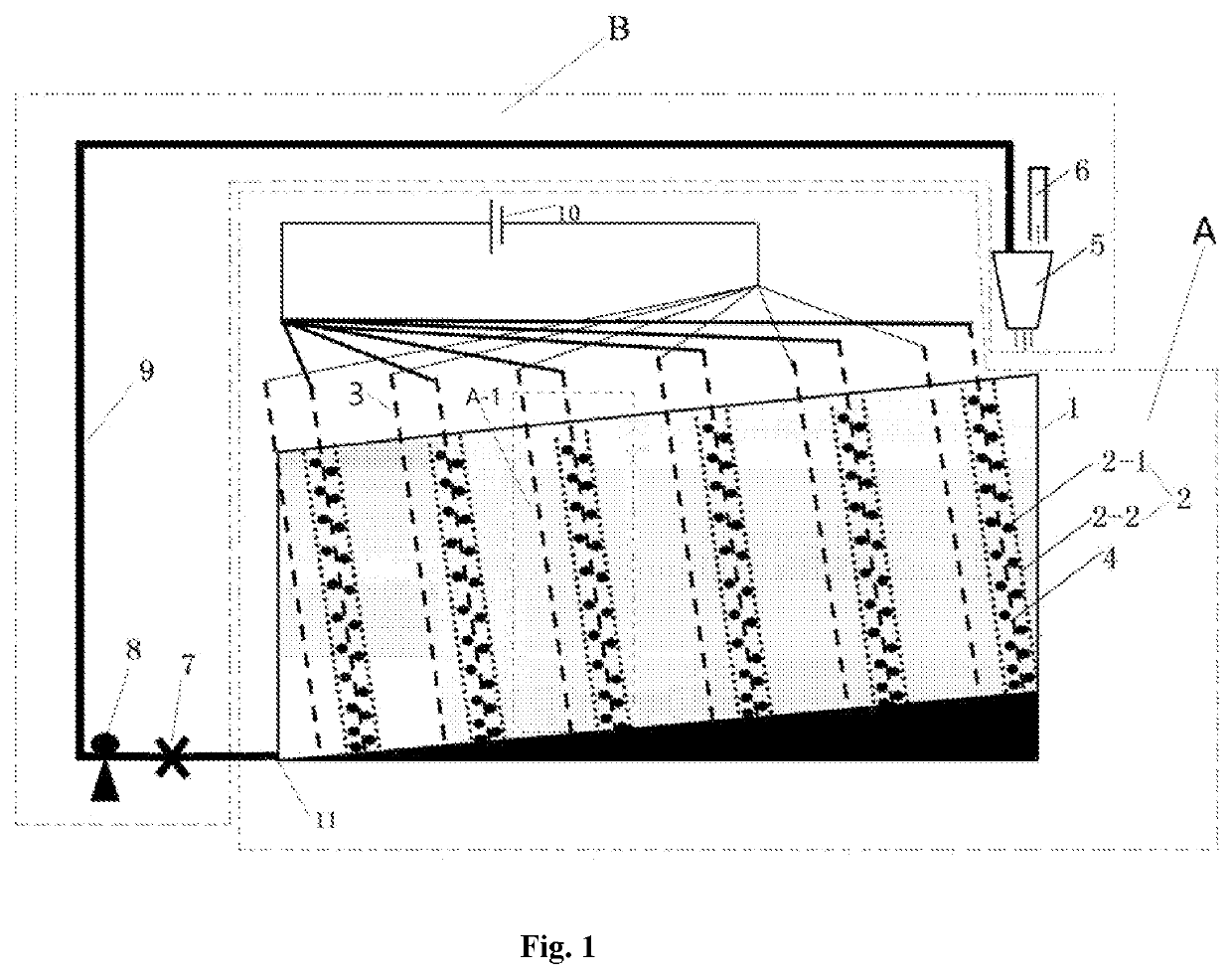
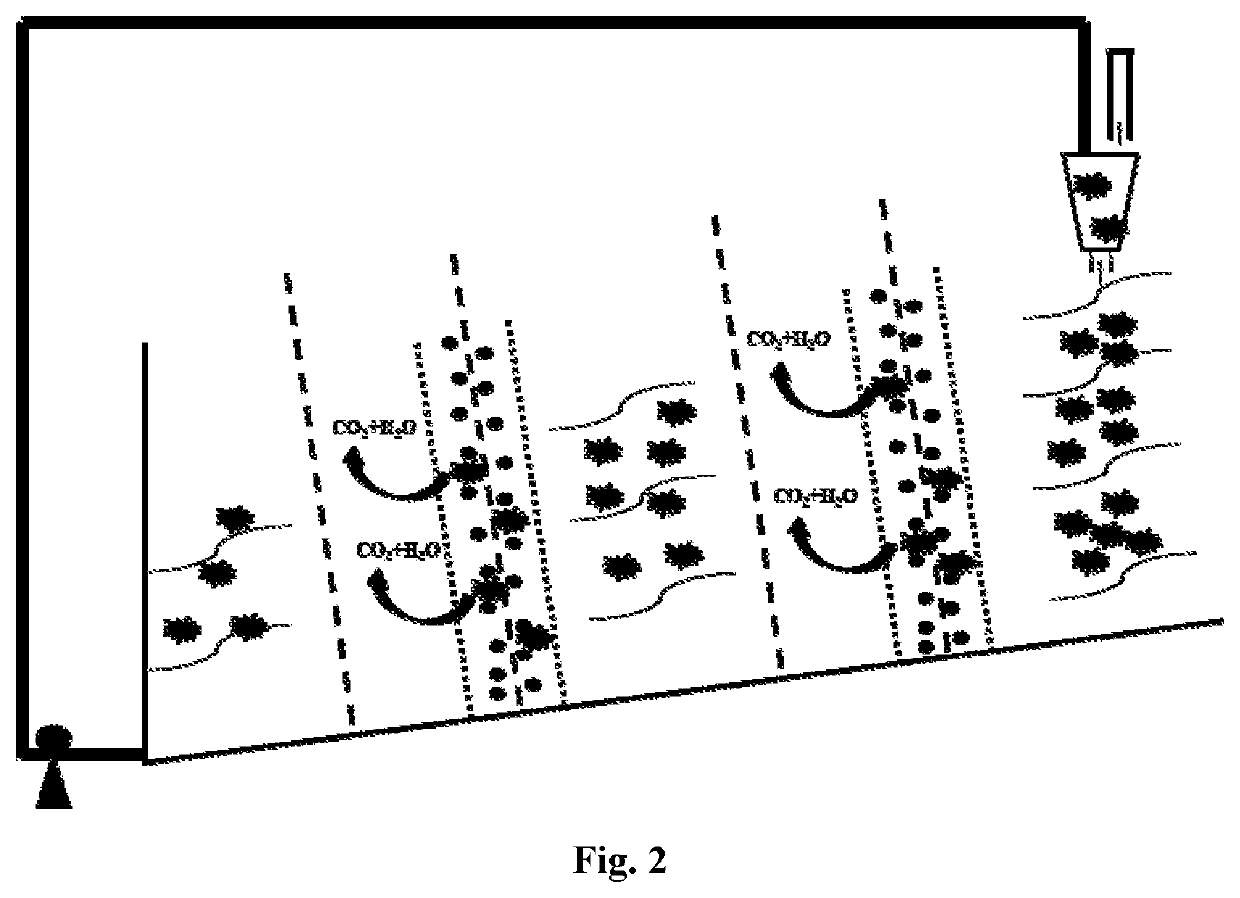
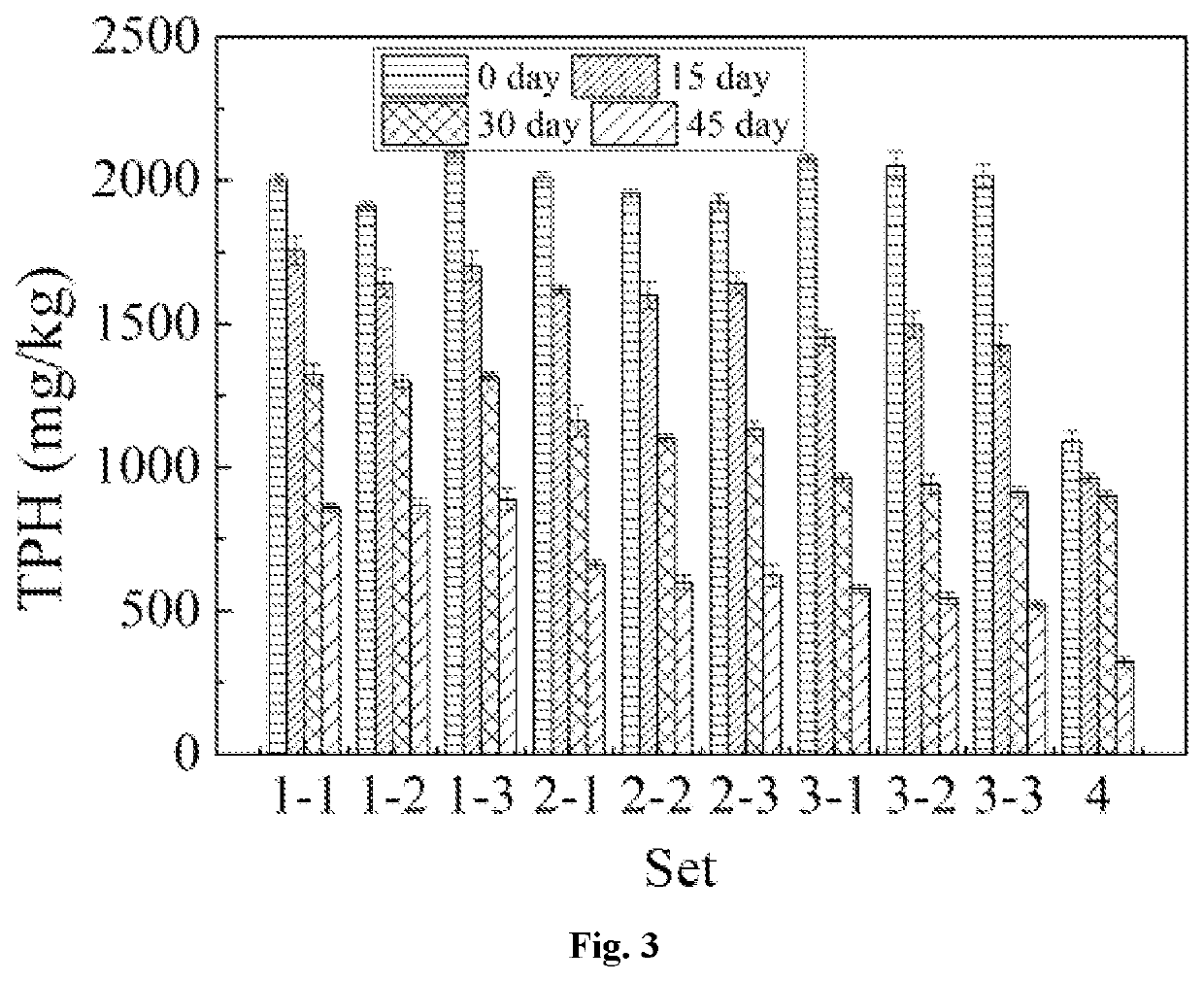
Stacked recyclable microbial electrochemical reactor and degradation method of petroleum hydrocarbon contaminated soil
ActiveCN112872014AImprove degradation efficiencyEasy to operateContaminated soil reclamationWater/sewage treatment apparatusSoil scienceElectrochemical degradation
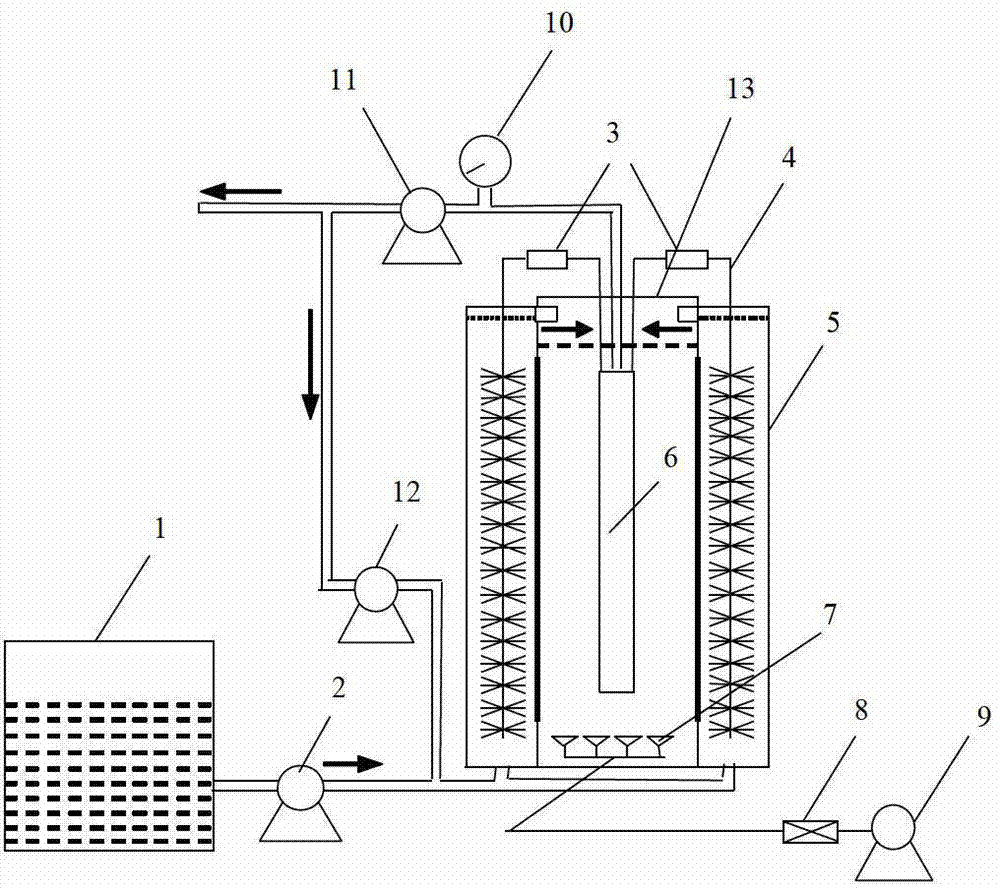
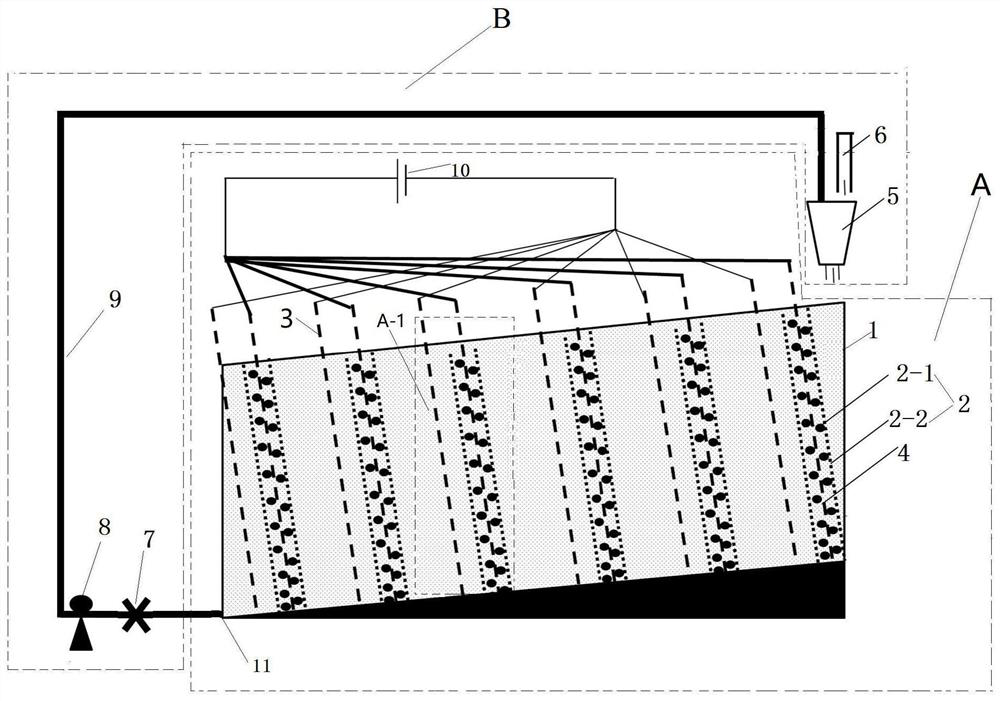
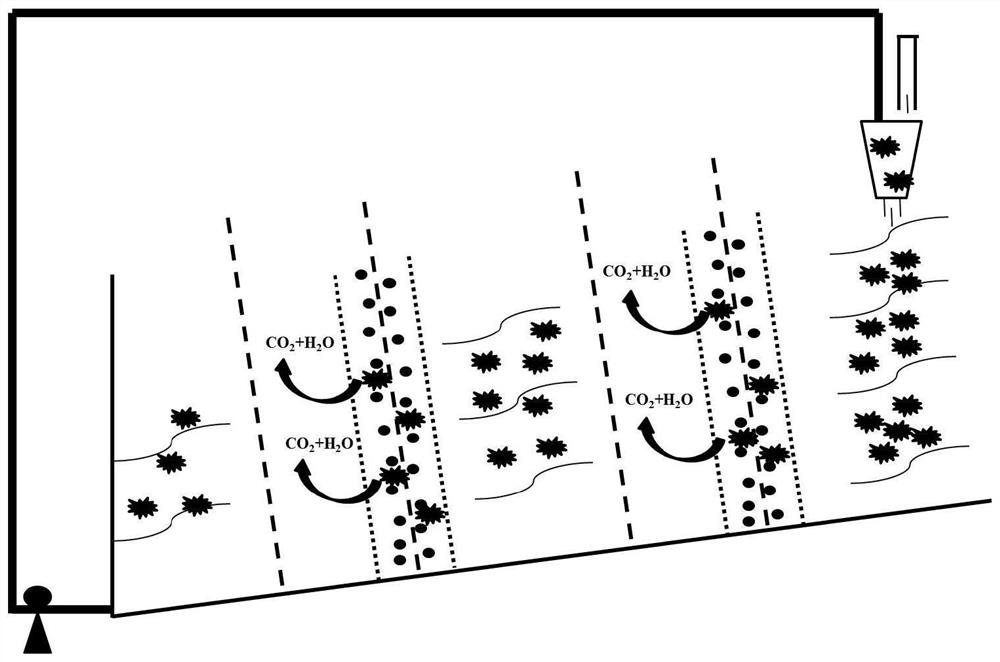
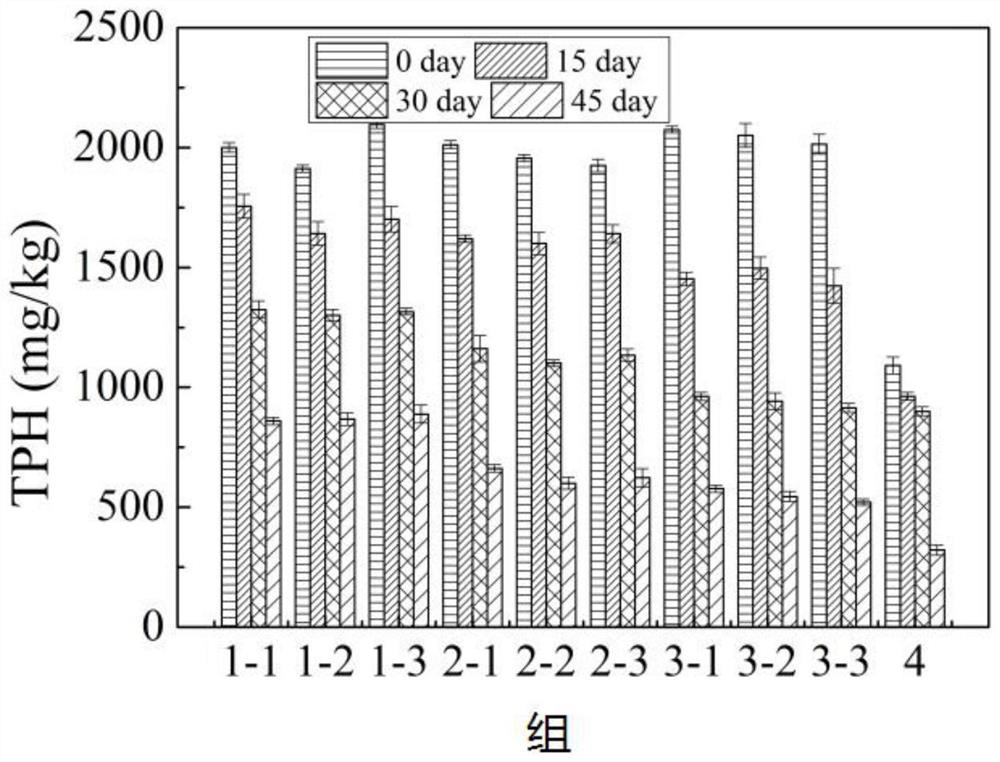
The invention provides a stacked recyclable microbial electrochemical reactor and a degradation method of petroleum hydrocarbon contaminated soil, and belongs to the technical field of microbial electrochemical soil remediation. According to the stacked recyclable microbial electrochemical reactor provided by the invention, the influence range of an anode is increased through a stacked microbial electrochemical system, the movement of petroleum hydrocarbon molecules in polluted soil is accelerated through a water circulation system, and the mass transfer capacity of the soil is improved, so that the efficiency of microbial electrochemical degradation of petroleum hydrocarbon in the soil is improved from multiple angles. The invention further provides a degradation method of the petroleum hydrocarbon contaminated soil, and the degradation method is easy to operate and high in degradation efficiency of the petroleum hydrocarbon in the contaminated soil.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Method for removing azo dye mixed pollutant wastewater through bio-electrochemical reactor system
ActiveCN107082485APromote reductionEasy to handleTreatment by combined electrochemical biological processesWater treatment compoundsReactor systemSludge
The invention relates to a processing method of azo dye mixed pollutant wastewater, in particular to a method for removing azo dye mixed pollutant wastewater through a bio-electrochemical reactor system. The technical problems that according to an existing anaerobic organism method, the azo dye wastewater processing speed is low, the efficiency is low, and the cost of physical and chemical methods is high are solved. The method comprises the steps of setting up the bio-electrochemical reactor system; 2, performing sludge cultivation and acclimation on the bio-electrochemical reactor system; 3, operating the bio-electrochemical reactor system. The removal rates of reactor outflow water COD, inorganic nitrogen and azo dyes can reach 89%, 75% and 92% respectively, the mixed pollutant wastewater containing azo dyes can be effectively removed, and the method can be used for sewage treatment projects.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Pretreatment-egsb-microbial electrochemical combined excess sludge degradation device and method
ActiveCN105541059BChange natureReduce the difficulty of crackingTreatment by combined electrochemical biological processesSpecific water treatment objectivesHigh concentrationParticulates
The purpose of this invention is to treat excess sludge, with the goal of sludge reduction, harmlessness, and resource utilization, and provide a pretreatment-EGSB-microbial electrochemical combined excess sludge degradation device and method, which belongs to the category of excess sludge. Sludge resource recycling and reduction technology field. The device includes a crushing-anaerobic combined preconditioner, an EGSB anaerobic processor, a microbial electrochemical reactor and a gas collector. This method carries out anaerobic digestion and crushing of sludge in anaerobic sludge, so that the solid particles in the sludge suspension are broken and partially dissolved in the water phase, forming high-concentration organic wastewater containing a certain amount of sludge solid particles; The treated sludge is then degraded by the anaerobic granular sludge of the EGSB anaerobic processor, and finally further degraded by microbial electrochemistry. The invention makes the water in the sludge comply with the emission standards, and the organic matter is released in the form of CO2, CH4, H2 and other gases, effectively improving the efficiency of reducing the remaining sludge and resource utilization, and at the same time achieving the purpose of harmlessness.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV LIAONING
Difunctional electrode with nitrification and denitrification activity and preparing method and application thereof
ActiveCN105140529AHigh removal rateReduce manufacturing costCell electrodesBiochemical fuel cellsSludgeEnergy recovery
The invention provides a difunctional electrode with nitrification and denitrification activity and a preparing method and application thereof. A carbon-based material is used as a conducting skeleton of the electrode, an abiological catalyst is loaded on the surface of the electrode to catalyze an oxygen reduction reaction, the electrode is placed in a negative pole chamber inoculated with nitrification and denitrification activity sludge, a system is started and operates until a stable biological membrane is formed on the surface of the electrode, and therefore pollutants in sewage can be removed while electric energy is effectively recovered. The abiological catalyst is used under the oxygen condition to realize the efficient oxygen reduction reaction of the electrode, and meanwhile nitrogen in the microorganism catalyzed sewage is removed. The preparing method of the difunctional electrode is simple, the energy recovery rate of the difunctional electrode is obviously larger than that of a single biological electrode, organics and the nitrogen in the sewage are effectively removed, and the removal speed is higher than that of a single abiological electrode and the biological electrode; the electrode can be used in a microbial fuel cell or other bioelectrochemistry reactors.
Owner:重庆中科德馨环保科技有限公司
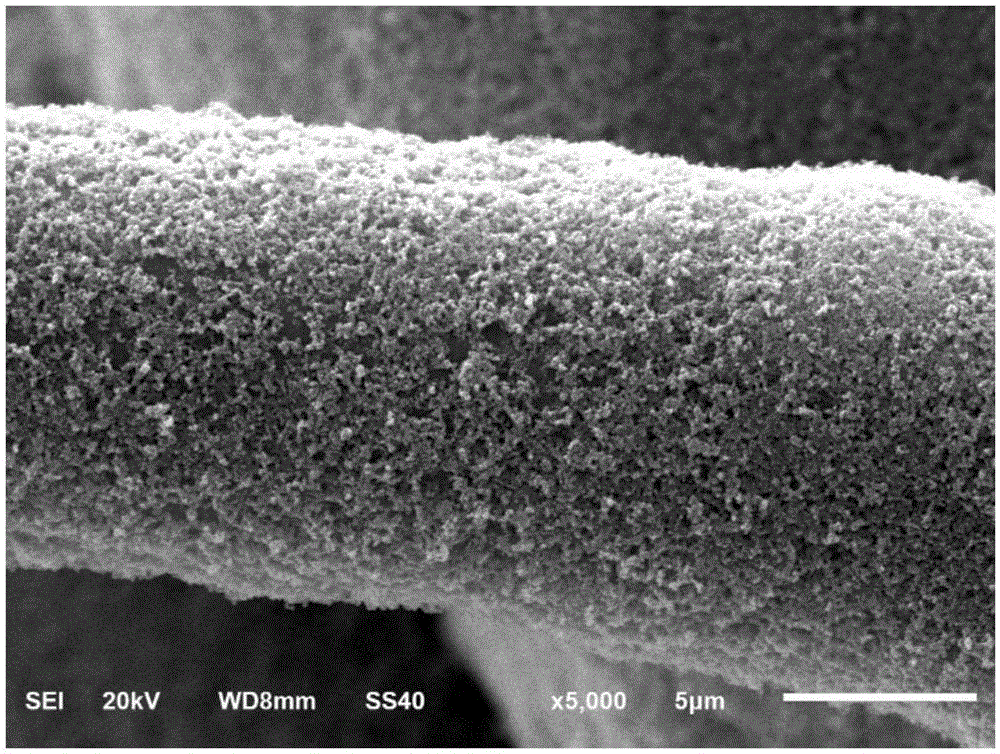
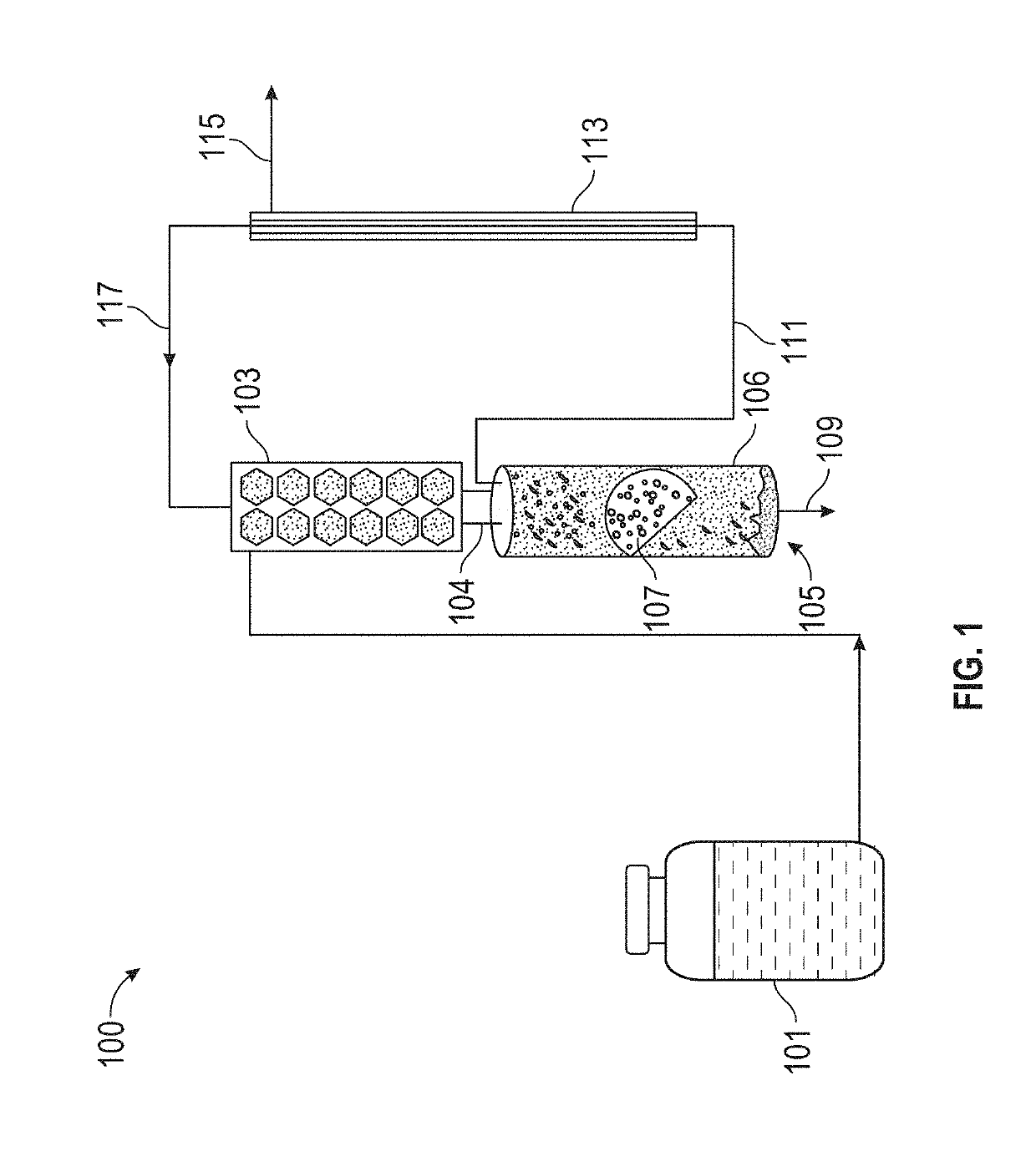
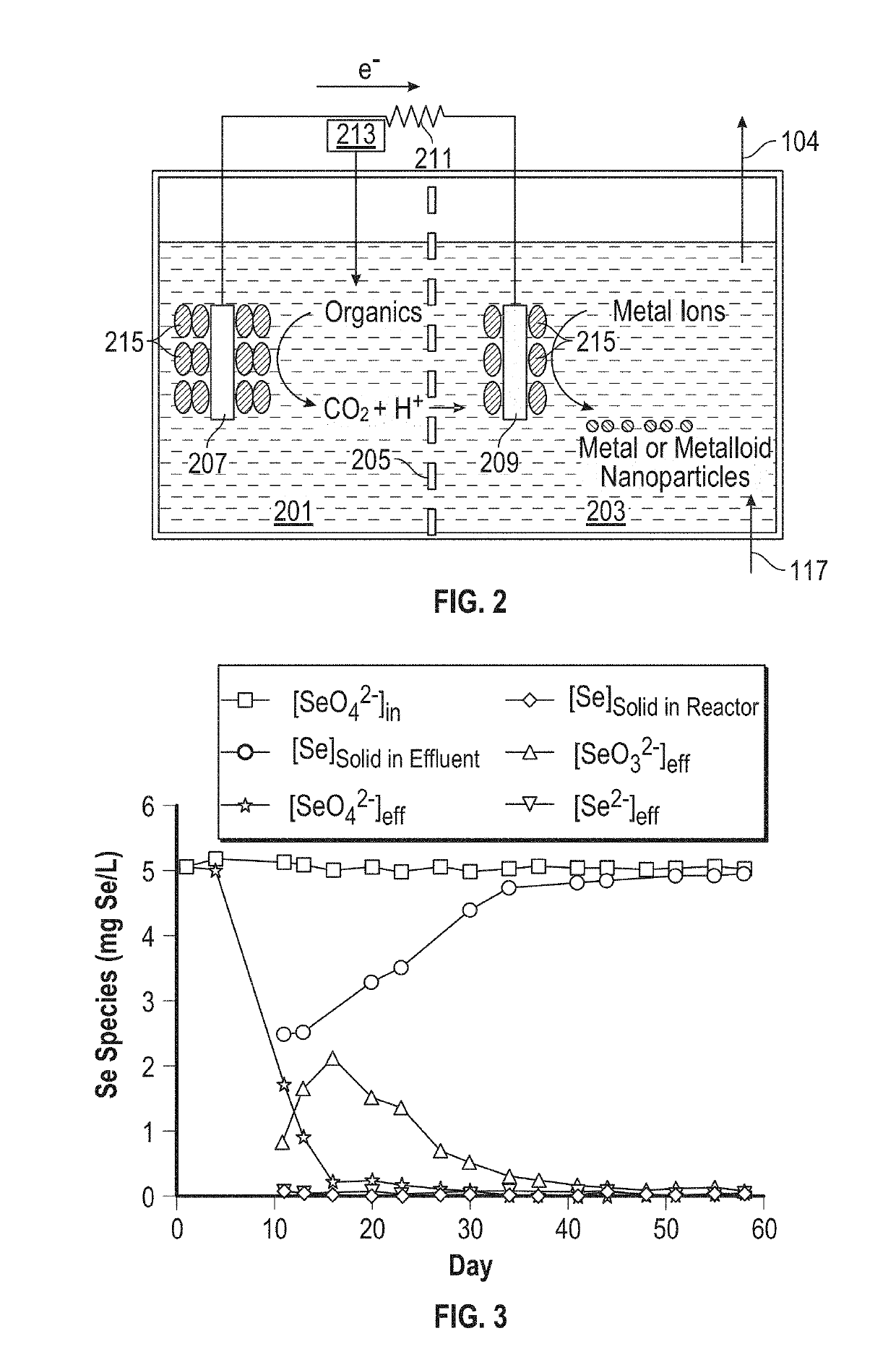
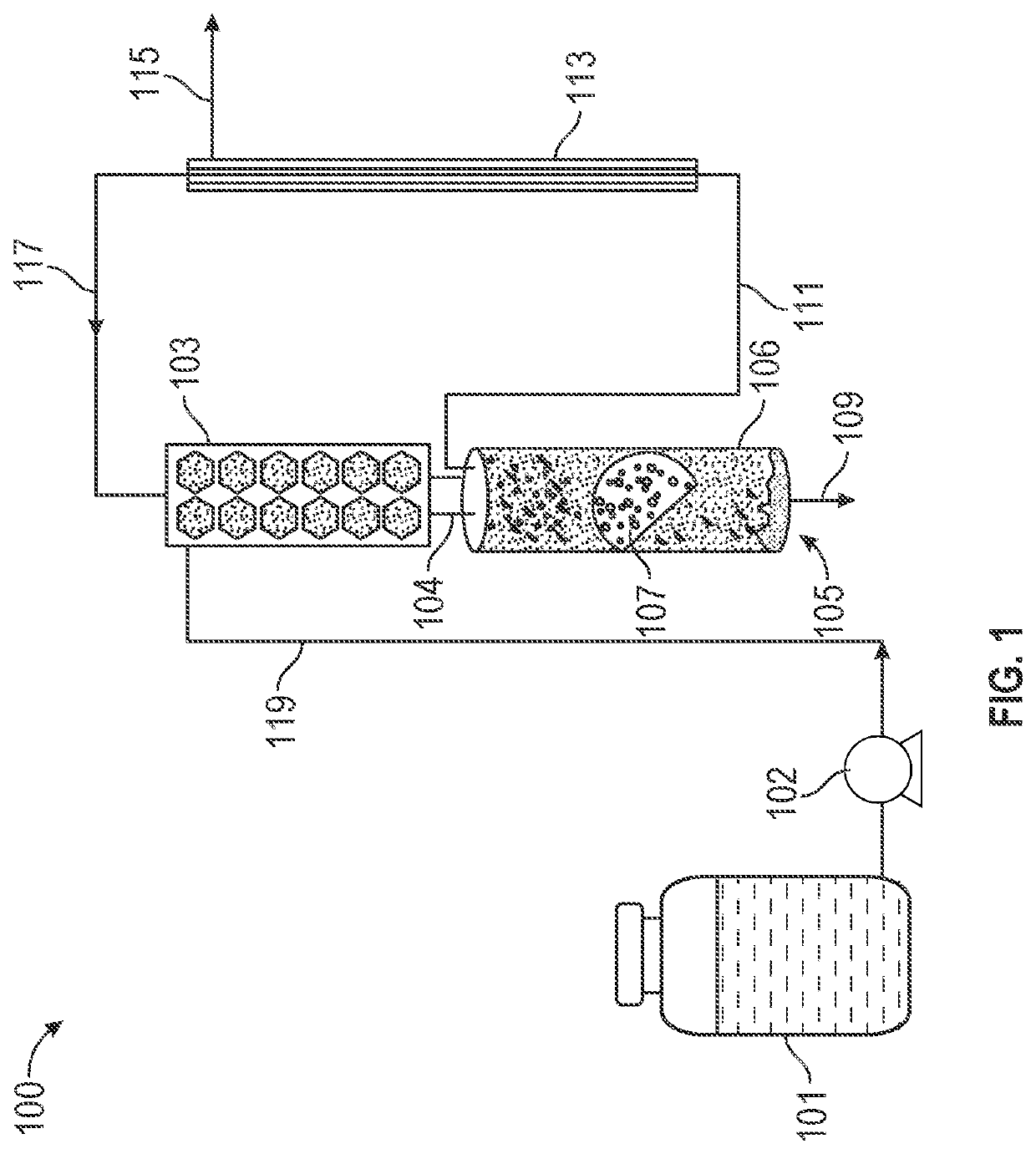
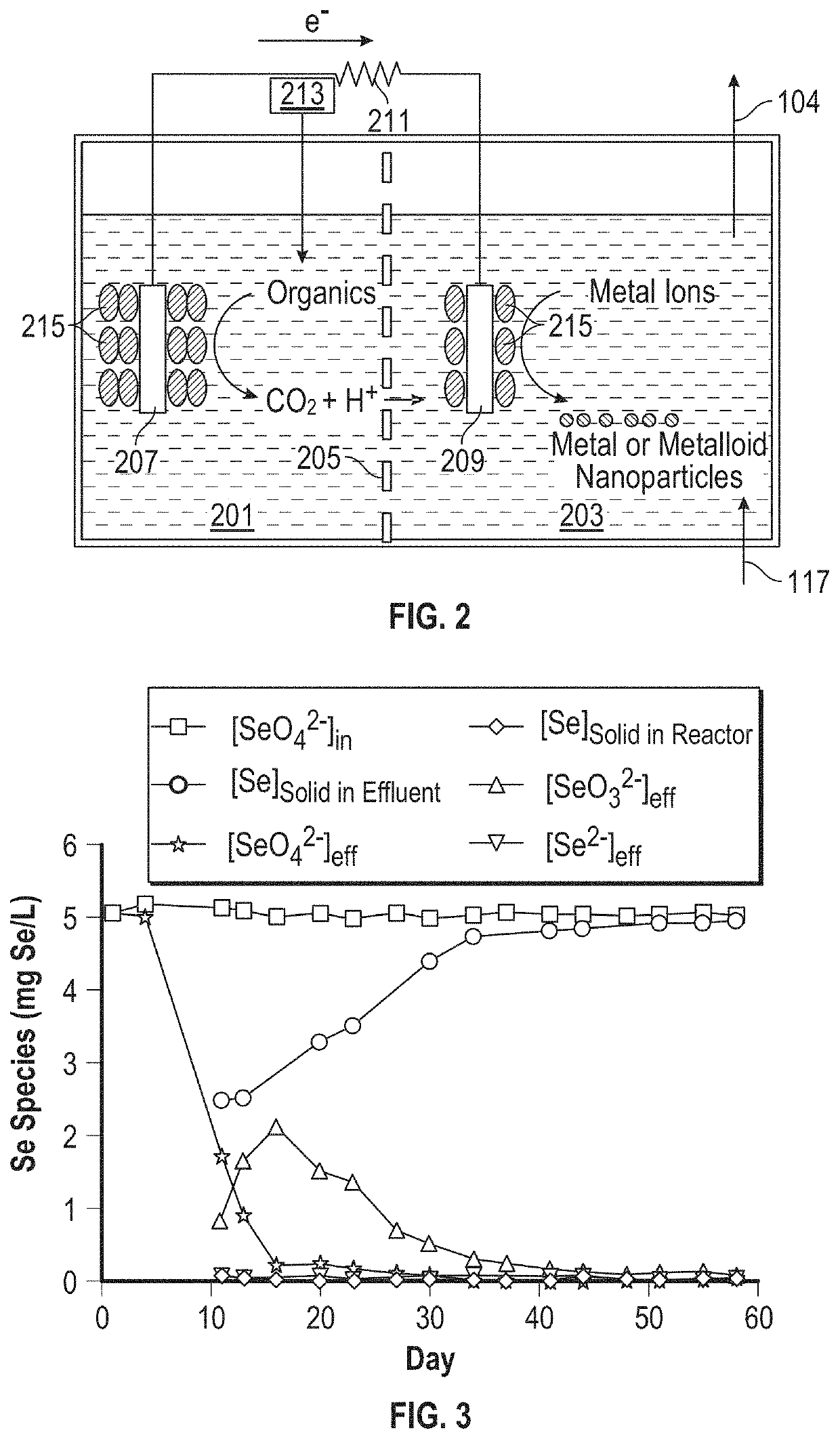
Reactors and methods for producing and recovering extracellular metal or metalloid nanoparticles
ActiveUS20190194040A1Treatment by combined electrochemical biological processesWater contaminantsNanoparticleFiltration
Systems and methods for treating a metal or metalloid ion-contaminated liquid are provided. The method may include (i) feeding the metal or metalloid ion-contaminated liquid into a bioelectrochemical reactor containing a bacteria selected by the cathode to produce extracellular metal or metalloid nanoparticles; and (ii) operating the bioelectrochemical reactor anaerobically to reduce the metal or metalloid ions in the metal or metalloid ion-contaminated liquid to extracellular metal or metalloid nanoparticles. The method may further include separating the metal or metalloid nanoparticles from the bacteria with no energy input. A bioelectrochemical reactor system for production of extracellular metal and metalloid nanoparticles may include a bioelectrochemical reactor, a separation device, and a tangential flow filtration unit.
Owner:FLORIDA STATE UNIV RES FOUND INC
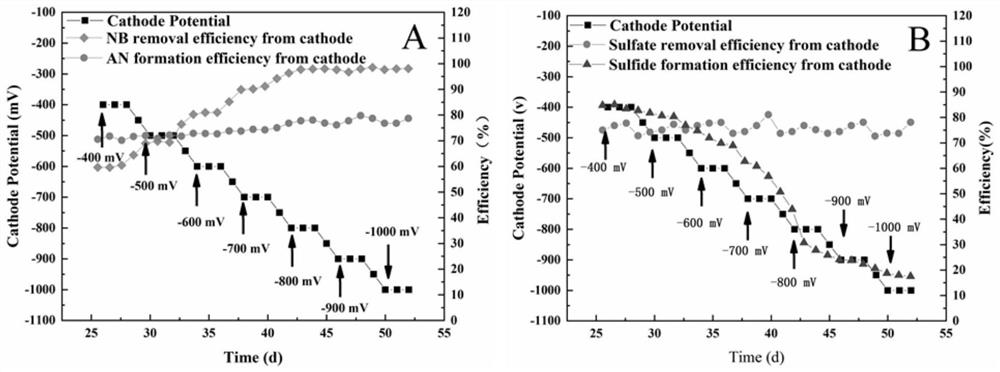
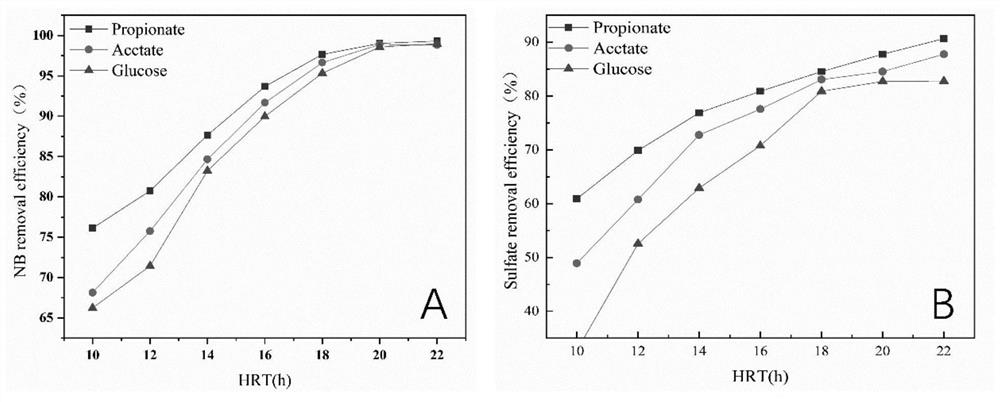
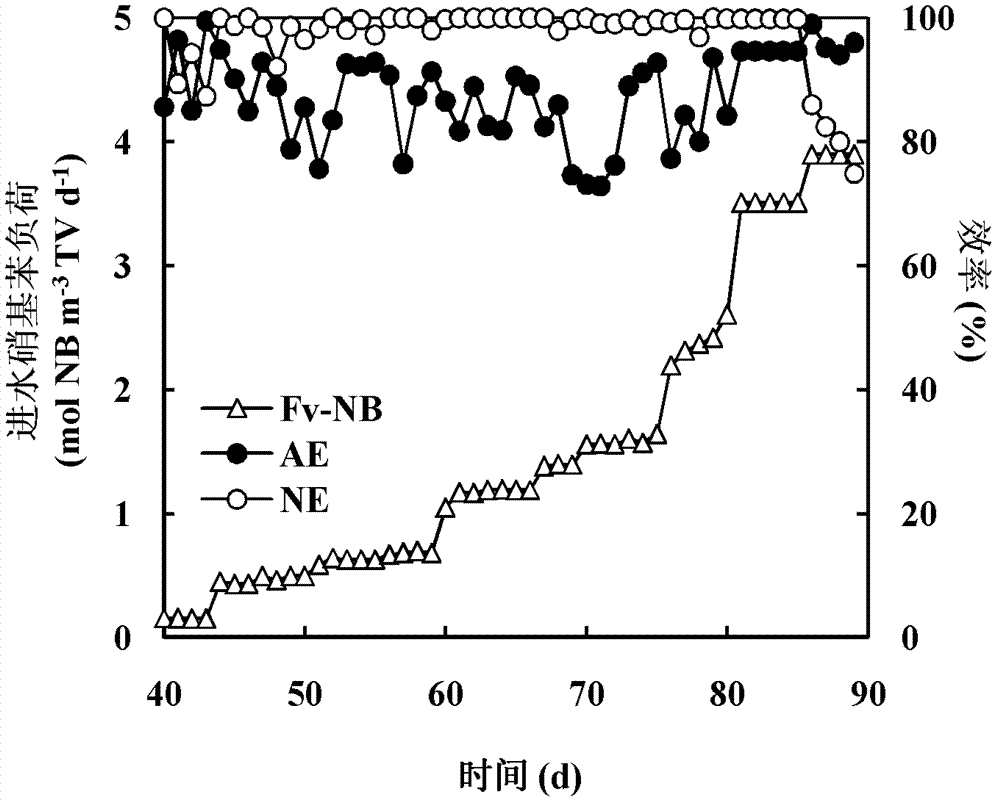
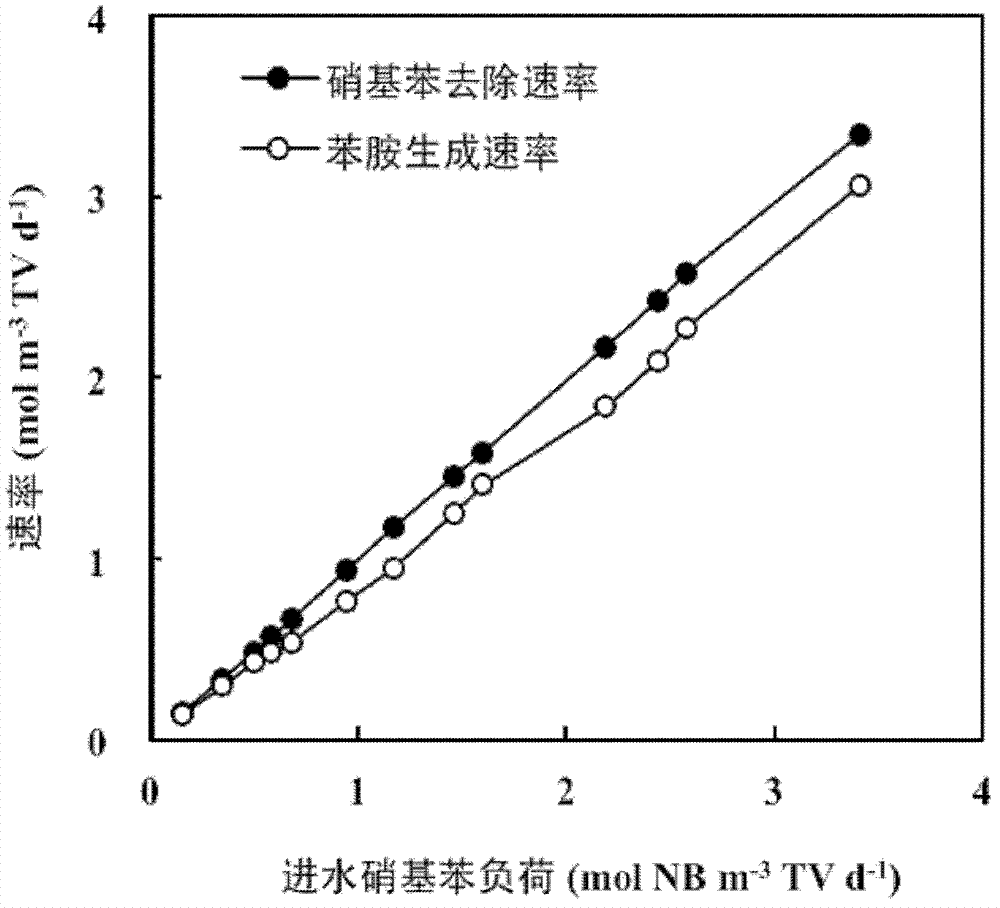
Method for strengthening anaerobic reduction of nitrobenzene by electrochemically regulating sulfur circulation
ActiveCN113003702APromote reductionEnhanced reduction conversionWater treatment parameter controlTreatment by combined electrochemical biological processesNitrobenzeneSulfide compound
The invention belongs to the technical field of industrial wastewater treatment, and discloses a method for strengthening anaerobic reduction of nitrobenzene by electrochemically regulating sulfur circulation. According to the invention, an electric field regulation and control technology is introduced into a traditional anaerobic reduction system, a diaphragm-free up-flow bioelectrochemical reactor is constructed, real-time conversion of sulfate reduction product sulfides is realized through regulation and control of cathode potential, electrons are synchronously released, reduction of nitrobenzene and sulfate in a cathode region is further promoted, the toxicity inhibition of H2S is effectively reduced, the consumption of an external carbon source is reduced, and the system stability is improved. Compared with an existing treatment process, the reduction conversion rate of NB is remarkably increased in a bioelectrochemical system with sulfur metabolism conversion, and the method has a wide application prospect in wastewater treatment.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
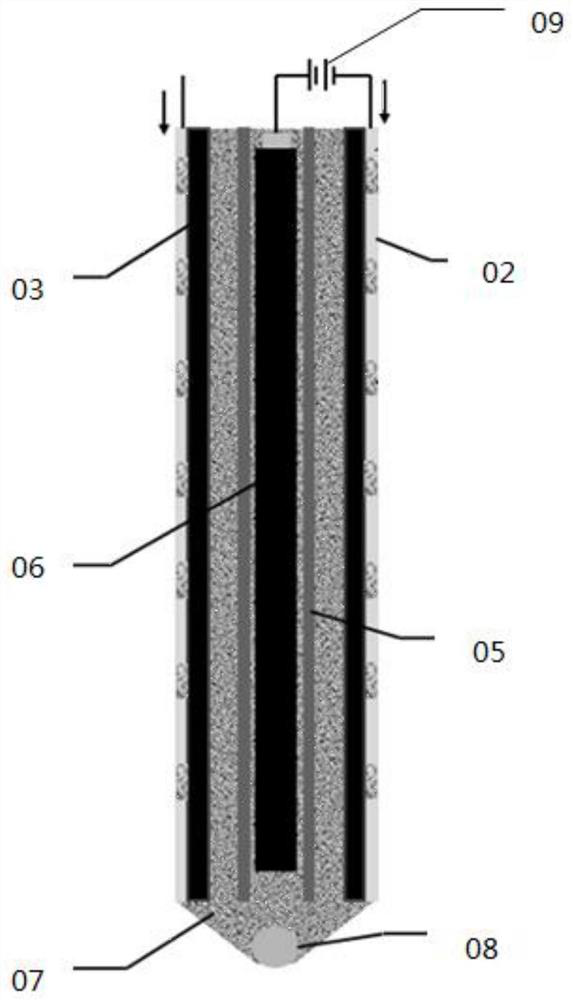
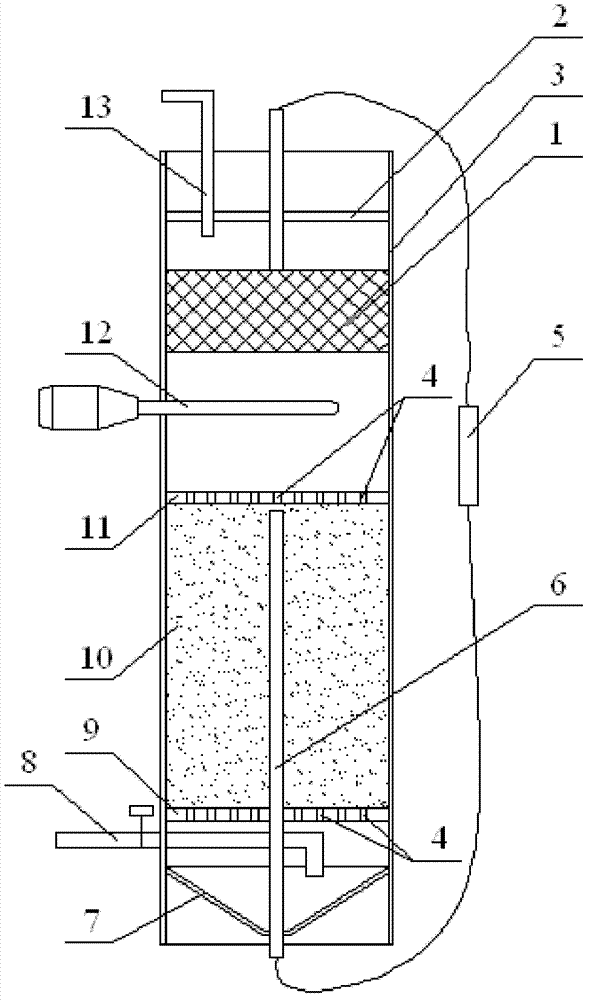
Sleeve type bioelectrochemical reactor for in-situ remediation of chlorinated hydrocarbon pollution of shallow groundwater
ActiveCN112661255ASimple and fast operationSuitable for complexityWater contaminantsWater/sewage treatment using germicide/oligodynamic-processHalohydrocarbonElectron donor
The invention relates to a sleeve type bioelectrochemical reactor for in-situ remediation of shallow groundwater polluted by chlorinated hydrocarbon, in particular to a bioelectrochemical reactor for in-situ remediation of shallow groundwater polluted by halogenated hydrocarbon. The bioelectrochemical dehalogenation technology is utilized, electrons are provided for dehalogenation breathing bacteria through the biological cathode, and completion of biological dehalogenation breathing is promoted, so that the problem that exogenous electron donors in underground water are insufficient is solved. A cathode of the reactor comprises a stainless steel cylinder with holes uniformly distributed in the surface and a carbon felt; the upper section of the bottom cylinder is of a straight cylinder structure, the lower section is of a conical cylinder structure, the upper edge of the bottom cylinder is connected with the stainless steel cylinder, and the check ball is located in the lower section of the bottom cylinder. The anode is located in the stainless steel cylinder, the PVC pipe is located between the anode and the cathode, and the anode and the cathode are electrically connected through an external direct-current power source. The device can be arranged in an in-situ monitoring well with a smaller caliber, is simple and convenient to operate, and is suitable for the characteristics of complex underground water environment and inconvenient operation conditions.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Purification and deodorization device for tail gas of capped sewage pool and deodorization method of device
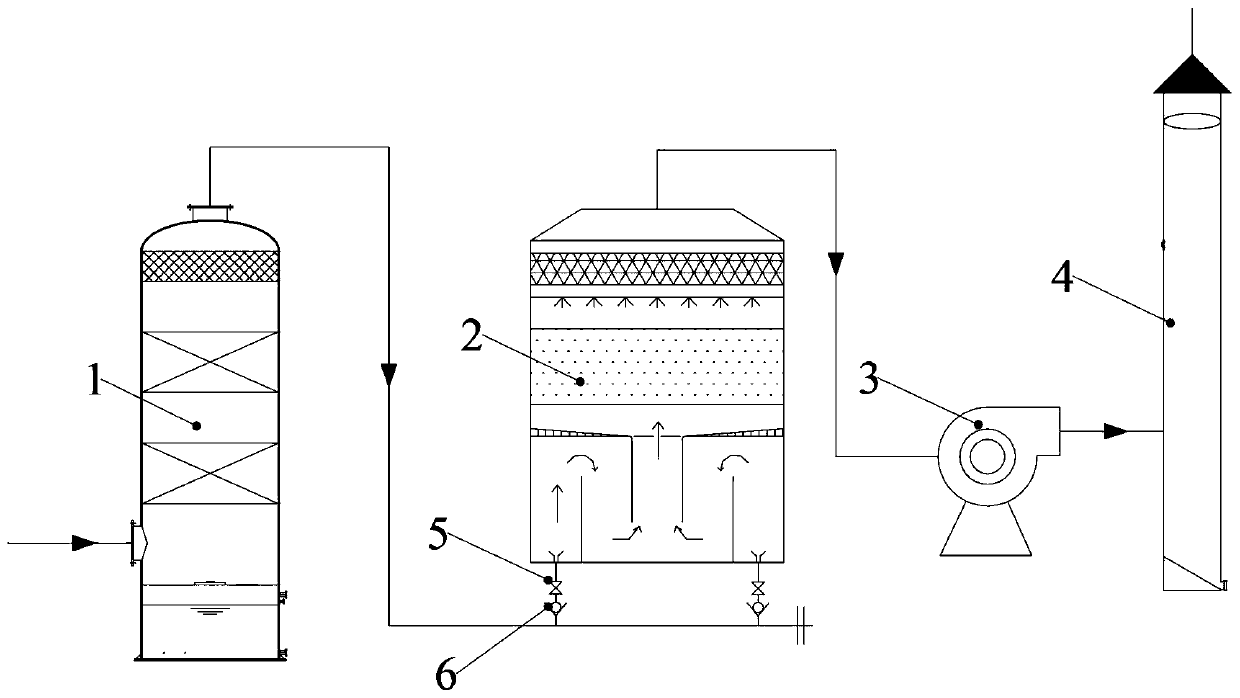
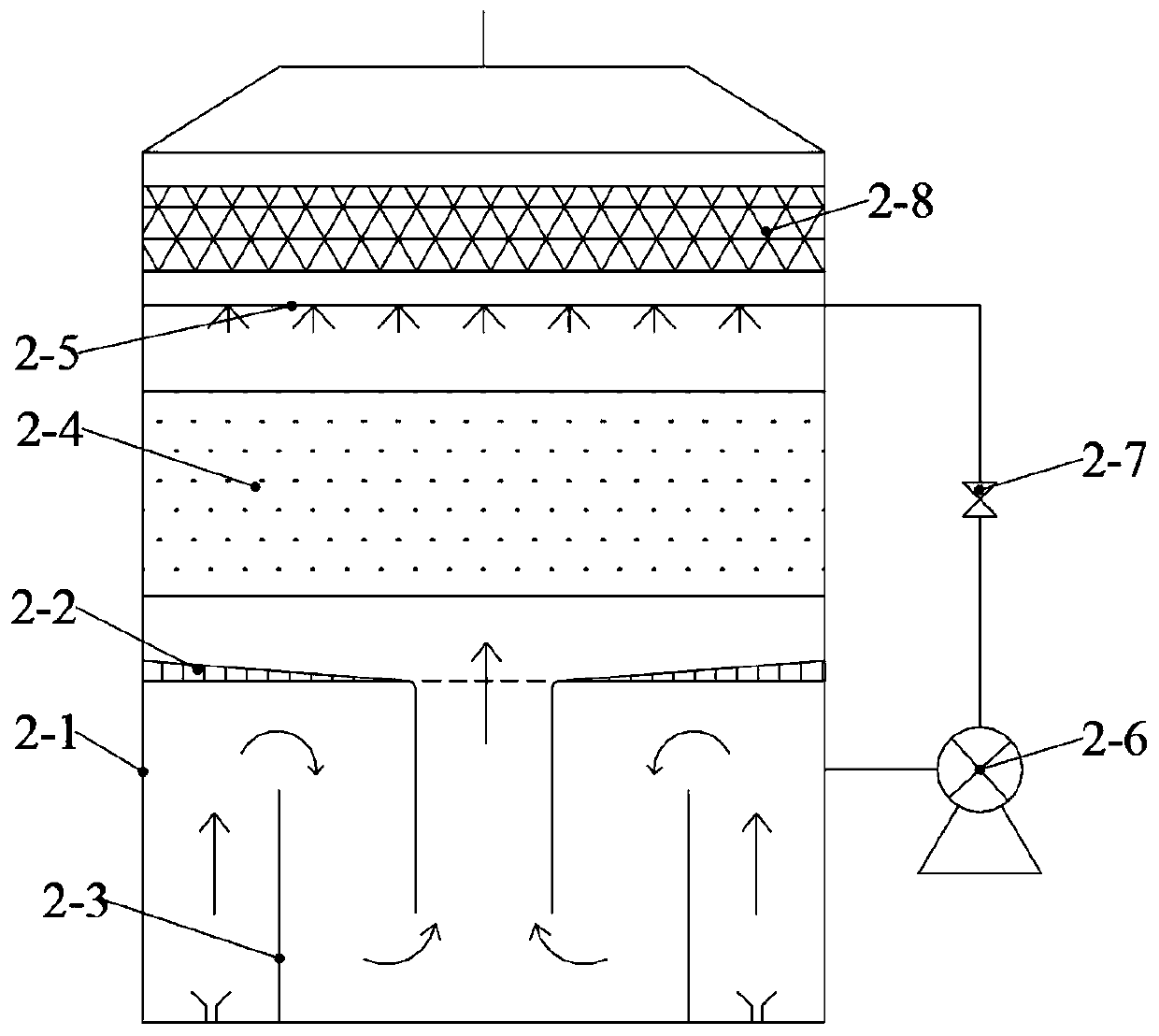
PendingCN110523247AGrowth inhibitionEasy transferDispersed particle separationAir quality improvementOdor sourceBiological filter
The invention discloses a purification and deodorization device for tail gas of a capped sewage pool and a deodorization method of the device. Odor related to capping of a sewage pool has the characteristics of complex components, a low concentration, a wide waste gas source, similar odor source strong components of all treatment units and the like, so that the difficulty of a subsequent deodorization process is increased. The purification and deodorization device for the tail gas of the capped sewage pool comprises an integrated electric-biological filter tank module; and the integrated electric-biological filter tank module comprises a filter tower body, a bioelectrochemical reaction unit, a biological filler circulation unit and a demister, an electrolyte solution is arranged in the filter tower body, the bioelectrochemical reactor comprises a positive electrode plate, a negative electrode plate, two flow guide plates and two partition plate groups, and the biological filler circulation unit comprises a biological medium filler, a spraying pipe and a circulation pump. An integrated electric-biological filter tower used in the invention can be used for screening dominant bacteriain a solution through an external electrode.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV +2
Non-diaphragm upflow type continuous flow bio-electrochemical apparatus for treating difficultly degraded waste water
ActiveCN102502973BBalance accumulationEconomical and efficient processingBiological water/sewage treatmentInternal resistanceContinuous flow
The invention discloses a non-diaphragm upflow type continuous flow bio-electrochemical apparatus for treating difficultly degraded waste water, which relates to an apparatus for treating waste water. The invention is used for solving the technical problems of high cost and low efficiency of BESs. A housing is fixedly connected with a base plate, a lower separator plate, a cathode, an upper separator plate, an anode and a top plate from the bottom to the top. According to the invention, present bio-electrochemical reactors are greatly improved, and according to the characteristics of waste water, the electrode positions are reasonably arranged, thereby pollutants which are difficult to be degraded in water are effectively detoxified at the cathode firstly, then the pollutants in water are further degraded by the effect of anodization, and the difficultly degraded waste water treatment efficiency is improved greatly. In addition, the invention employs a non-diaphragm design, thereby not only reducing internal resistance of the reactor, but also reducing cost, which are beneficial to the extension and engineering of the reactor.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
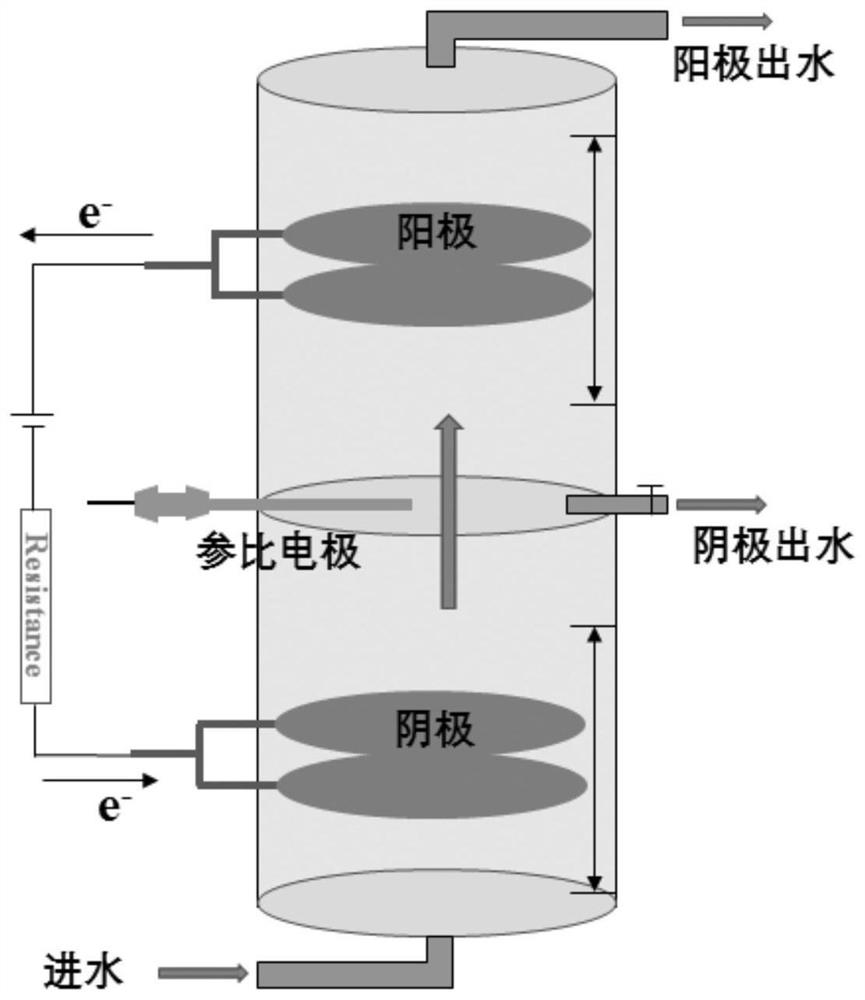
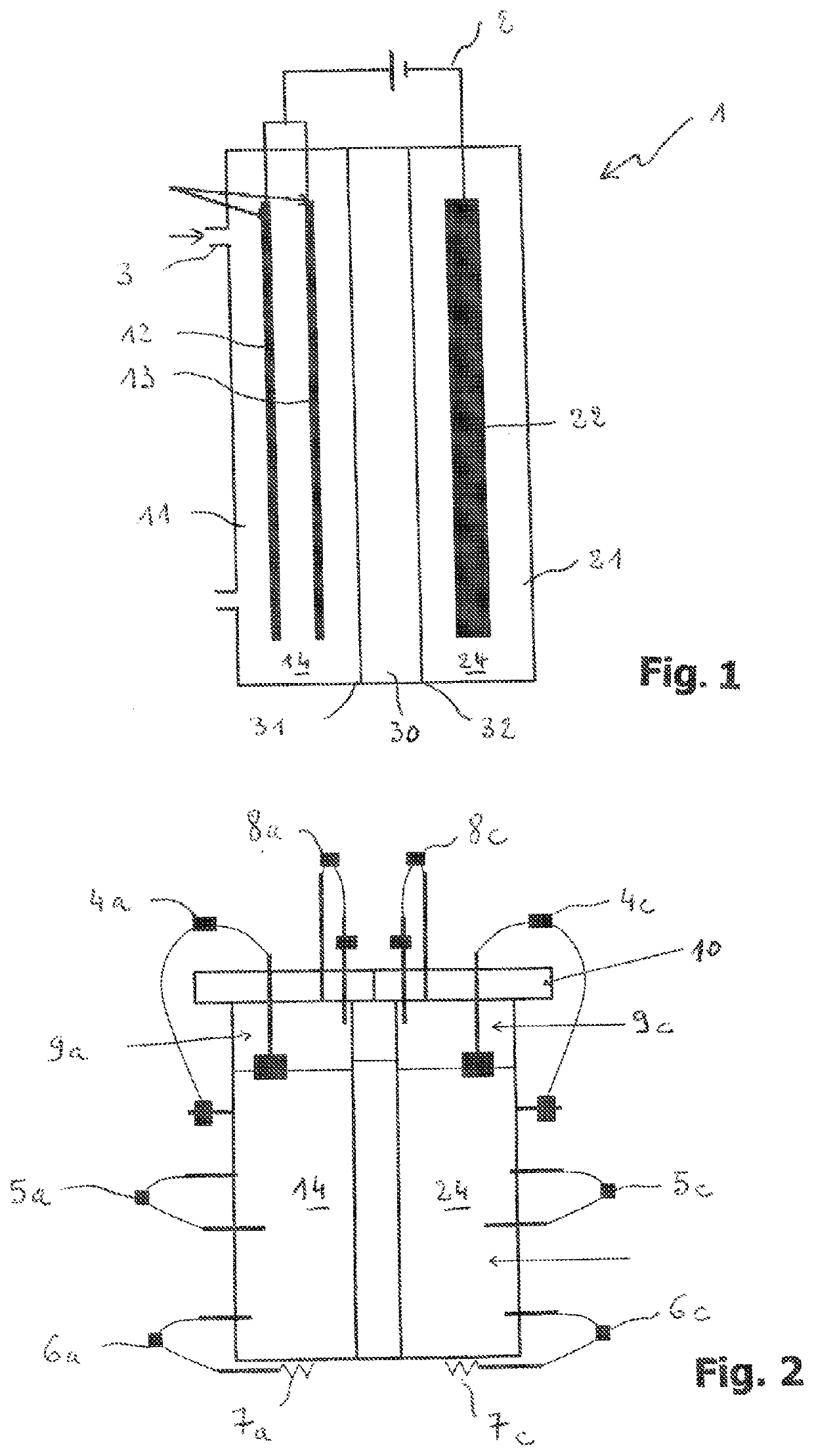
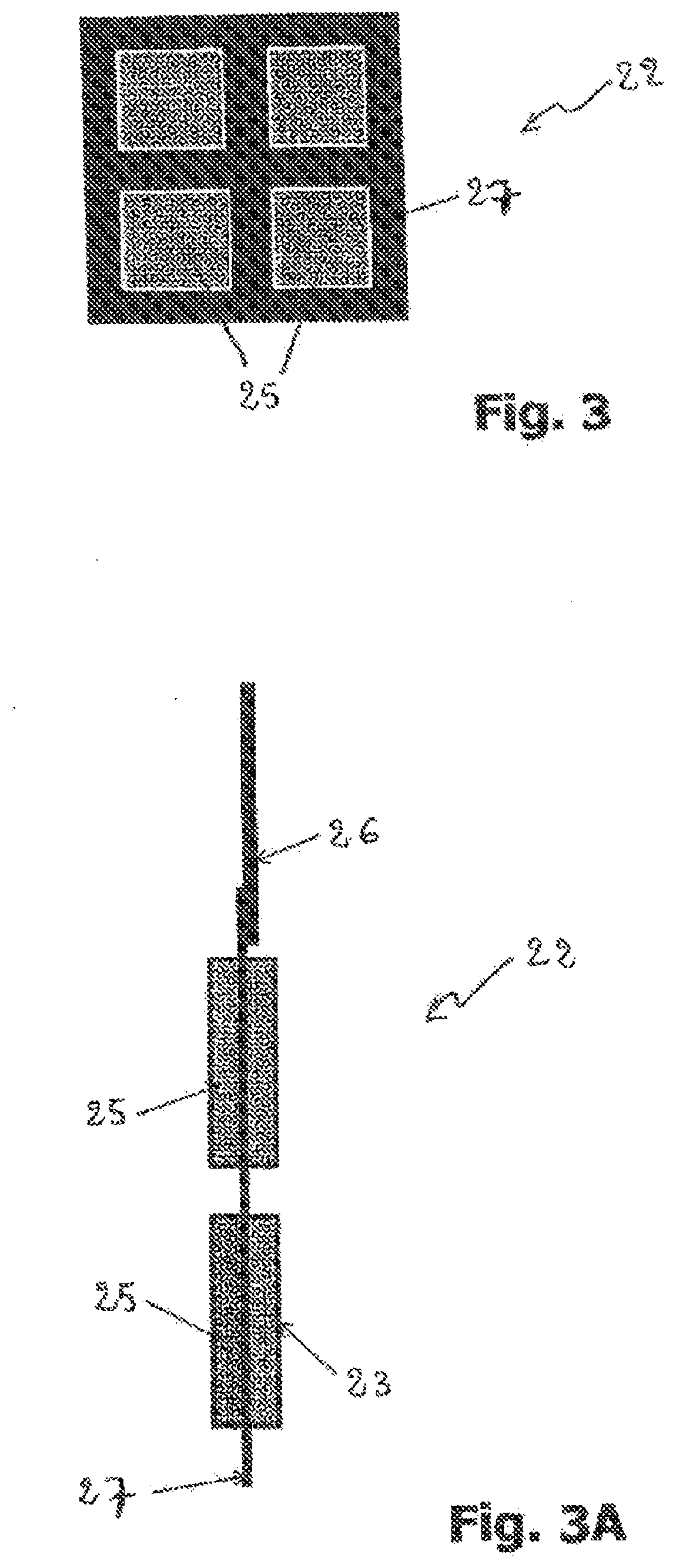
Bioelectrochemical reactor with double bioanode, method for anofic regeneration and use of the reactor for microbial electrosynthesis
PendingUS20210340039A1Increase inertiaImprove potential stabilityCellsWater treatment parameter controlElectrolytic agentMicroorganism
A bioelectrochemical reactor (1) has an anode chamber (11) having at least two bioanodes (12, 13), and an anodic electrolyte (14) with an anodic electroactive microorganisms,—a cathode chamber (21) with at least one biocathode (22), and a cathodic electrolyte (24) with a cathodic electroactive microorganisms. The anode chamber (11) is separated from the cathode chamber (21) by, running from the anode chamber to the cathode chamber, a cation exchange membrane (31) and an anion exchange membrane (32). The cation and anion exchange membranes are separated from each other by an inter-membrane chamber (30), and means for applying a potential difference between the interconnected bioanodes and the biocathode / biocathodes. The bioanodes and biocathode / biocathodes have active surfaces such that the total active surface of the biocathode / biocathodes (22) is greater than the total active surface of the two bioanodes (12, 13). The arrangement includes a method for regenerating the activity of the bioanodes of the reactor and to the use of said reactor for the electrosynthesis of organic acids and / or alcohols from organic waste.
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI +3
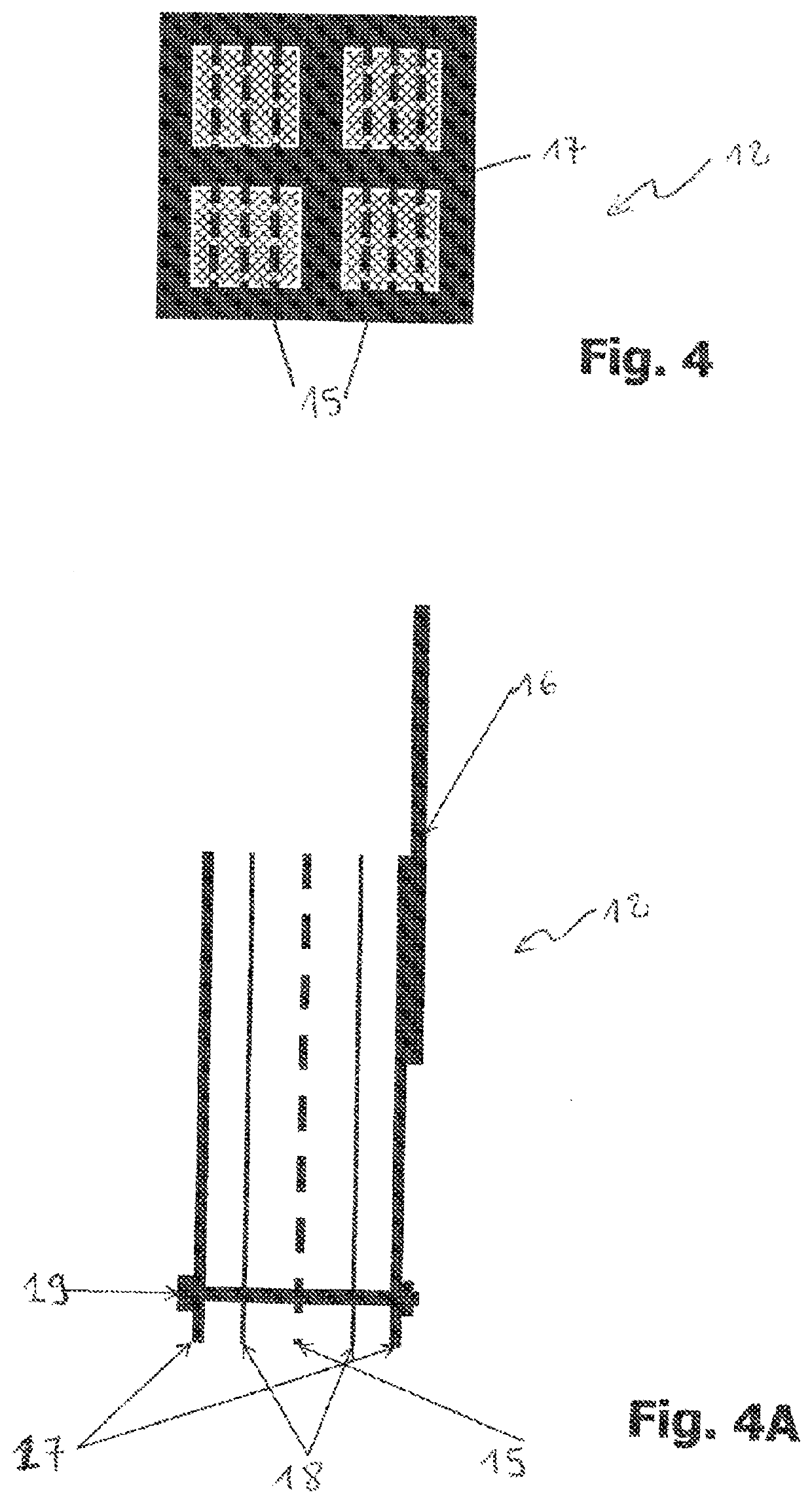
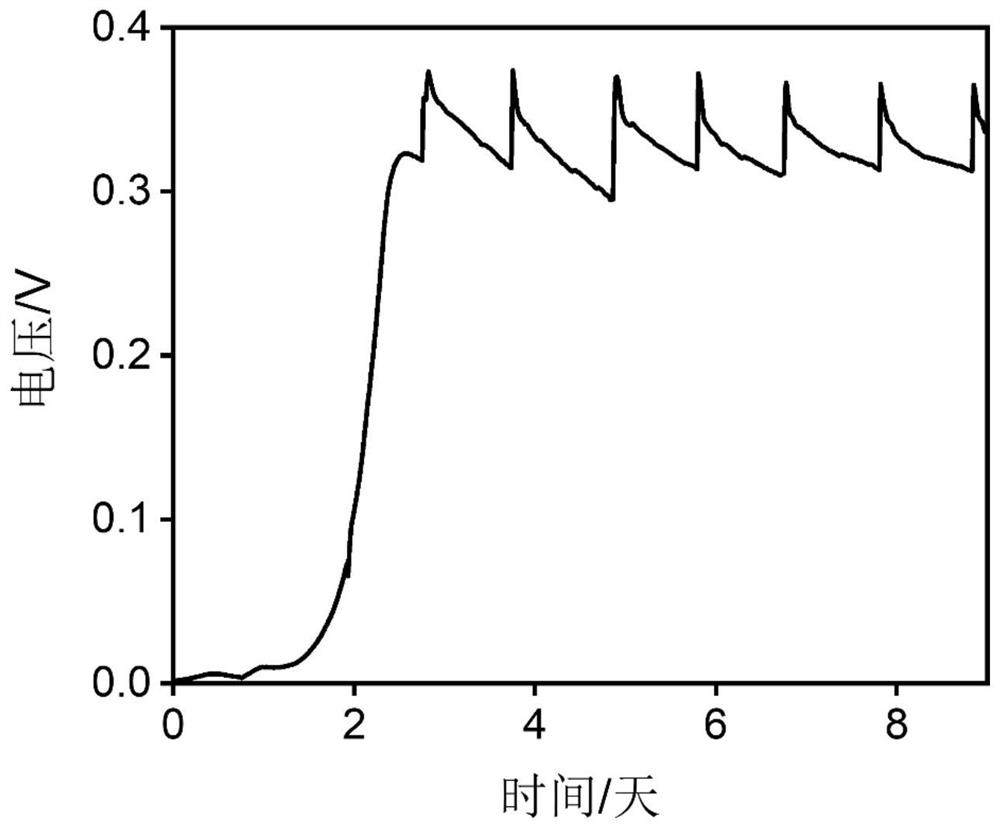
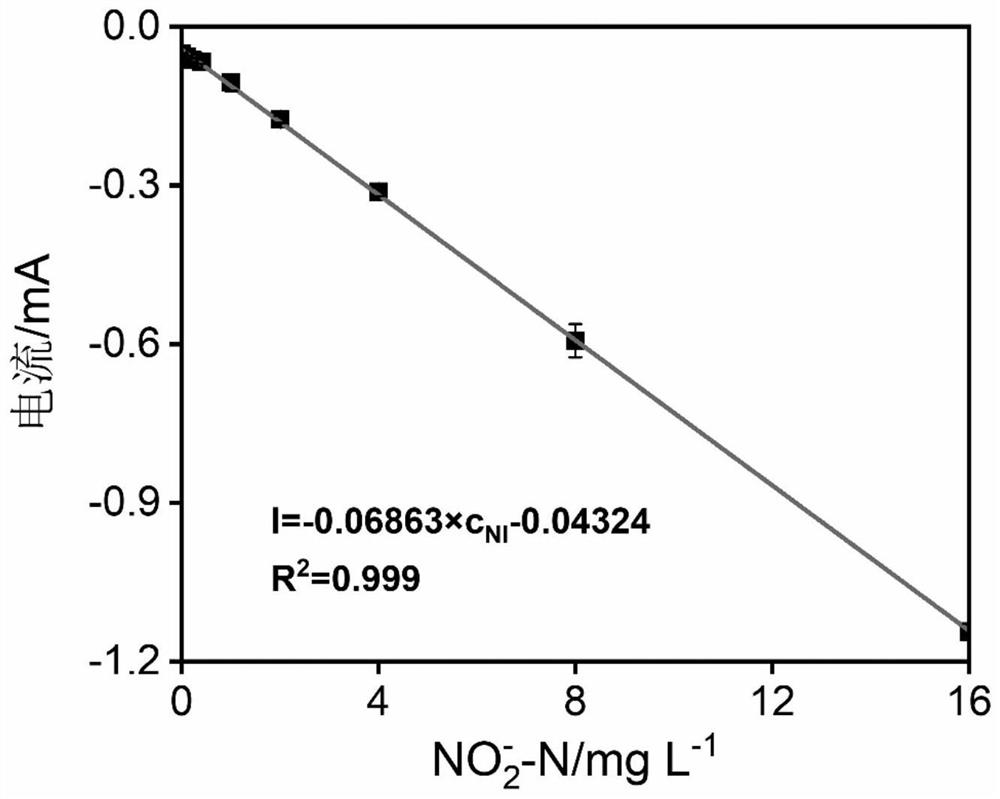
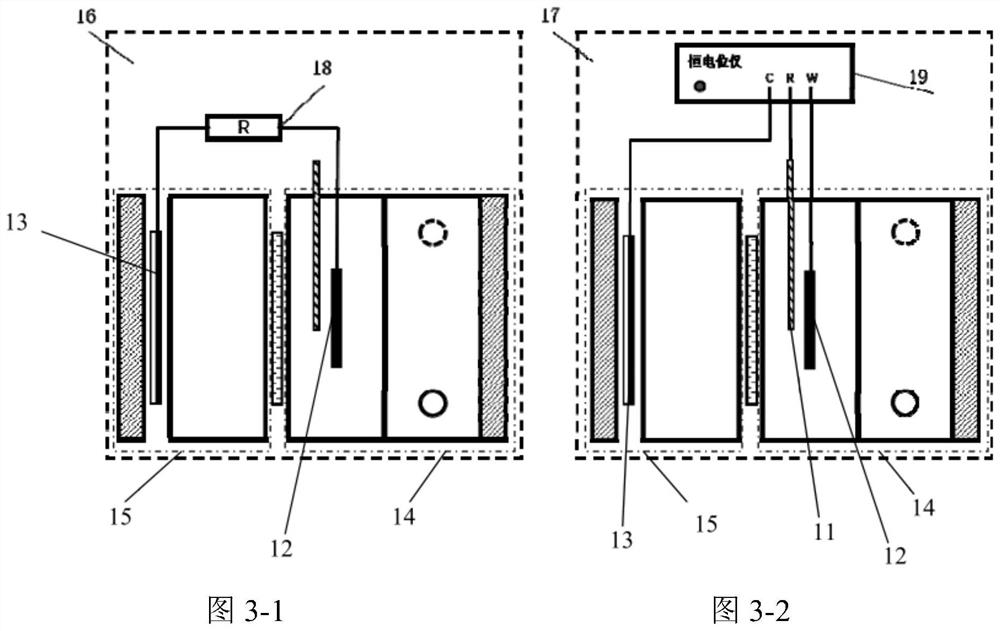
Bioelectrochemical method for real-time in-situ detection of nitrite in sewage
ActiveCN113504280AStabilized nitrite reduction electroactivityShort manufacturing timeMaterial electrochemical variablesMatrix solutionBiology
The invention discloses a bioelectrochemical method for real-time in-situ detection of nitrite in sewage, which comprises the steps of 1) taking a biological electrode as an anode and a non-biological electrode as a cathode, performing closed-circuit operation in an MFC mode, adding an inoculation solution into an anode chamber, continuing the inoculation process for five days, and replacing the inoculation solution every day; 2) culturing the biological electrode in a matrix solution, and replacing the matrix solution every day until an electrode biological membrane grows maturely; (3) connecting a bioelectrochemical reactor with a constant potential rectifier through a three-electrode system, putting the electrode biological membrane into solutions with different nitrite concentrations, carrying out linear voltammetry scanning analysis to obtain an electric response, and selecting an optimal electric response output potential; 4), obtaining a linear equation of the electrical response signal of the bioelectrochemical sensor and the nitrite concentration in solutions with different nitrite concentrations; and 5) obtaining the concentration of nitrite in the detected sewage according to the electric signal of the biological electrode in the detected sewage.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for removing azo dye mixed polluted wastewater by using bioelectrochemical reactor system
ActiveCN107082485BPromote reductionEasy to handleTreatment by combined electrochemical biological processesWater treatment compoundsElectrochemical responseReactor system
The invention relates to a processing method of azo dye mixed pollutant wastewater, in particular to a method for removing azo dye mixed pollutant wastewater through a bio-electrochemical reactor system. The technical problems that according to an existing anaerobic organism method, the azo dye wastewater processing speed is low, the efficiency is low, and the cost of physical and chemical methods is high are solved. The method comprises the steps of setting up the bio-electrochemical reactor system; 2, performing sludge cultivation and acclimation on the bio-electrochemical reactor system; 3, operating the bio-electrochemical reactor system. The removal rates of reactor outflow water COD, inorganic nitrogen and azo dyes can reach 89%, 75% and 92% respectively, the mixed pollutant wastewater containing azo dyes can be effectively removed, and the method can be used for sewage treatment projects.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
A method for constructing anode biofilm of microbial electrochemical system
ActiveCN106698682BShorten the time periodImprove Coulombic efficiencyTreatment by combined electrochemical biological processesWhole OrganismFiltration
The invention provides a construction method of a microorganism electrochemical system anode biological membrane and belongs to the technical field of construction methods of anode biological membranes. The construction method comprises the following steps: directionally expanding culture on electrochemical active bacteria, collecting a microorganism sample on an anode in a bio-electrochemical reactor running steadily as an inoculation bacterium source, inoculating into a culture medium, introducing nitrogen for creating an anaerobic environment, then sealing, and culturing on a shaking table under anaerobic condition; mixing and fixing conducting particles with electrochemical active bacteria, preparing conducting particle solution, carrying out ultrasonic dispersion, then sucking a certain amount of conducting particle solution into electrochemical active bacteria solution, shaking and standing; and carrying out a filtration fixation process on the surface of an anode by a composite structure biological film. The construction method provided by the invention has the advantages that starting time and starting cycle of a biological electrochemical system are successfully shortened by constructing a composite biological film of conducting particles, electricity generation performance is greatly improved, and coulombic efficiency of the whole biological electrochemical system is also improved.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
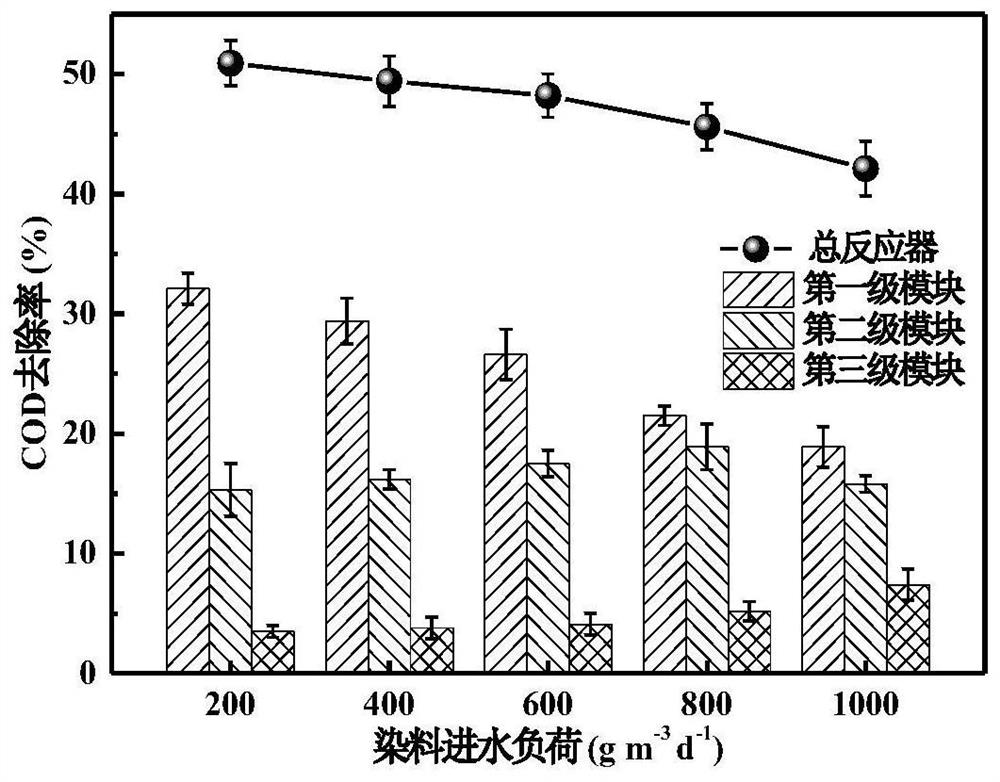
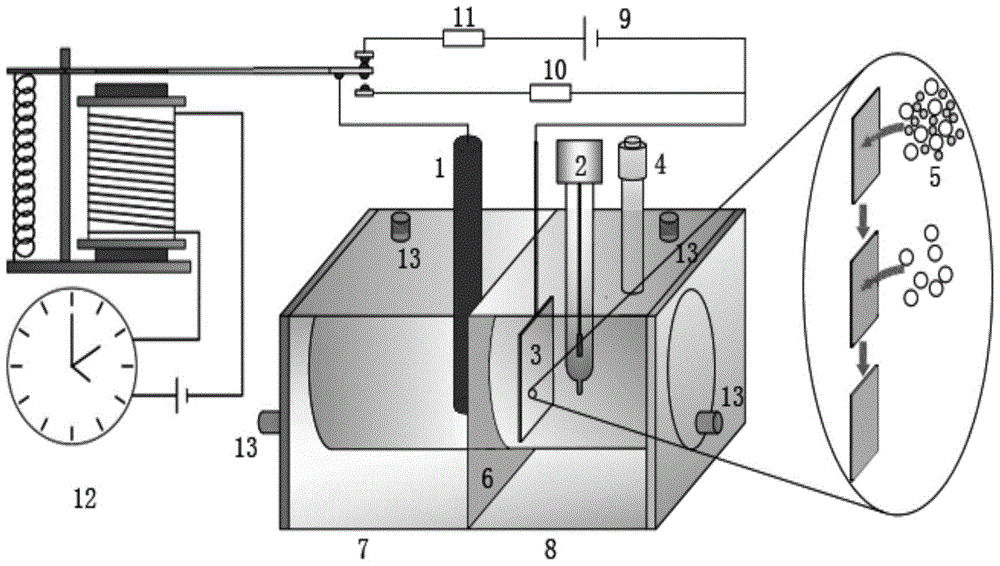
Bioelectrochemical wastewater treatment device with stacked and amplified functional modules and wastewater treatment method of device
InactiveCN112499751ARealize stacking amplificationRealize adjustable and controllable amplificationTreatment by combined electrochemical biological processesBiological treatment apparatusMicroorganismEngineering
The invention discloses a bioelectrochemical wastewater treatment device with stacked and amplified functional modules and a wastewater treatment method of the bioelectrochemical wastewater treatmentdevice, and belongs to the technical field of biological wastewater treatment. A bioelectrochemical reactor is constructed by stacking small bioelectrochemical modules, wastewater sequentially flows through all stages of modules, the pretreatment effect of biocatalysis and electrochemical catalysis on degradation-resistant wastewater can be achieved in a stage treatment and gradient removal mode,and toxicity reduction or toxicity removal of pollutants is achieved. The bioelectrochemical modules distributed by adopting surrounding type electrode arrangement has the advantages of being compactin structure and small in internal resistance, the relative distance of the electrodes is reduced, transfer of electrons and protons is facilitated, the electrodes are fully utilized, and then pollutant degradation is enhanced; and modular stacking is adopted, so that each module is a unit, gradient utilization and toxicity removal of pollutants can be achieved, microorganisms can form functionalflorae more easily, and the biodegradation effect is effectively achieved.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Method for electrochemical device to utilize corn cob hydrolysate
InactiveCN104531784AIncrease productionSimple methodMicroorganism based processesFermentationHydrolysateElectrochemistry
A method for an electrochemical device to utilize corn cob hydrolysate comprises the following steps that corn cobs are added into dilute sulphuric acid to be disinfected, and the corn cob hydrolysate is obtained after activated carbon decoloration, extraction filtration and rotary evaporation; a seed medium, catholyte, anolyte, seed washing liquid, an electron medium and DTT are prepared; disinfection is carried out on the prepared reagents, a bio-electrochemical reactor and a serum bottle; the disinfected serum bottle is fetched, the seed medium is added into the serum bottle, CO2 is led into the serum bottle, and actinobacillus succinogenes is added to be cultured to serve as a fermentative strain; centrifugation is carried out on the fermentative strain to remove the supernatant, a strain body is obtained after washing and secondary centrifugation and is added into the catholyte, then the electron medium and the corn cob hydrolysate are added into the catholyte to be mixed evenly and are connected to a cathode cavity of the bio-electrochemical reactor, and then the DTT is added into the anolyte to be mixed evenly and added into an anode cavity; chemical CO2 is led into the cathode cavity, and a product is obtained after fermentation at 37 DEG C. The method is simple, the yield is high, and the method is suitable for industrialized operation.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
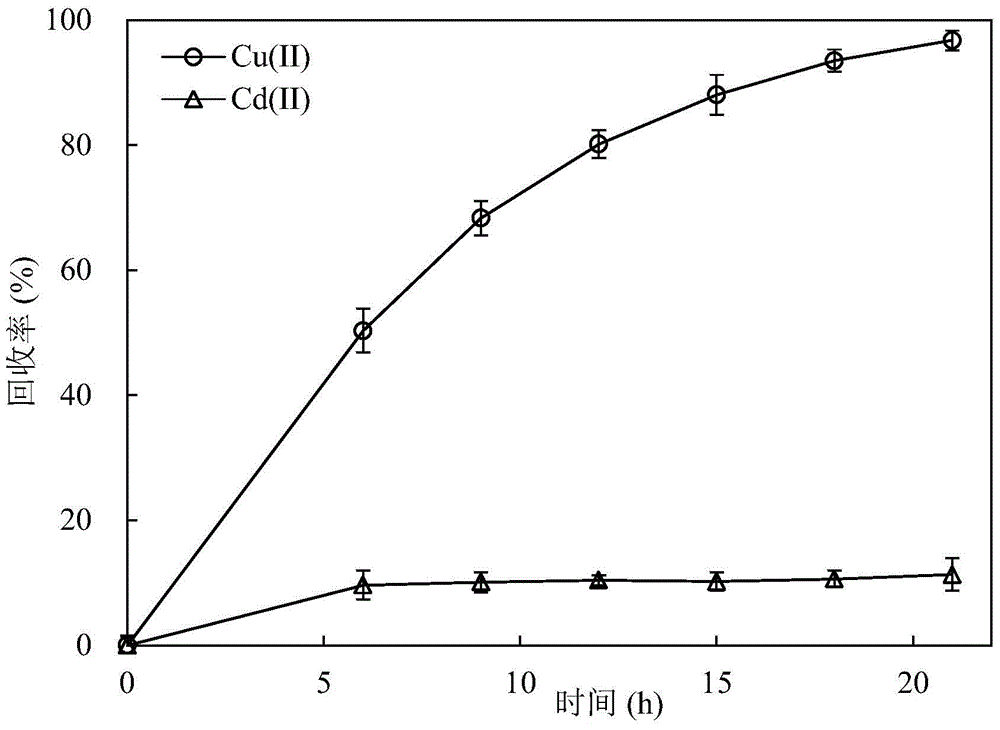
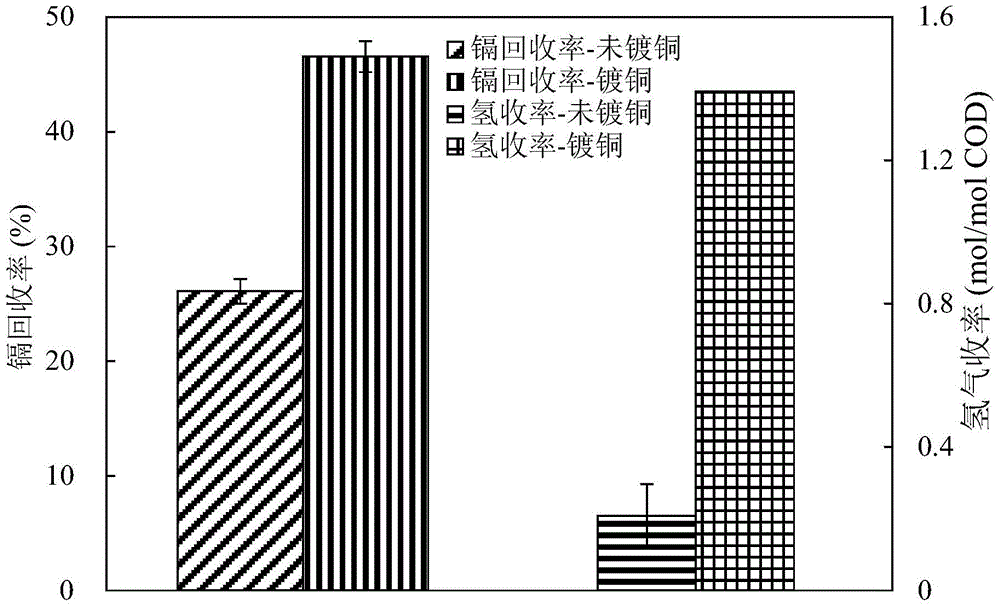
A method for recovering copper and cadmium and preparing cadmium bronze precursor in a compact bioelectrochemical reactor
InactiveCN104480493BHigh recovery rateEfficient recyclingPhotography auxillary processesBiochemical fuel cellsSludgeBioelectrochemical reactor
The invention provides a method for recycling copper and cadmium and preparing a cadmium bronze precursor employing a compact biological electrochemical reactor, and belongs to the technical field of bioelectrochemistry. A biological electrochemical reactor is switched into a mode of a microbial fuel cell or a microbial electrolysis cell through a relay switch; external resistors are connected in series in the mode of the microbial fuel cell; small resistors are connected in series in the mode of the microbial electrolysis cell; a power supply is externally connected; a mixed salt solution of Cu(II) and Cd(II) is enclosed into a cathode room of the reactor; a cathode and an anode of the reactor adopt conductive carbon materials; and the cathode room of the reactor is inoculated with sludge of a settling pond of a sewage treatment plant as electrochemical active microbes. The method is clean and efficient in process, compact in reactor, simple in structure and convenient to operate, and has a good application prospect in treatment of copper and cadmium wastewater treatment and preparation of the cadmium bronze precursor.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Reactors and methods for producing and recovering extracellular metal or metalloid nanoparticles
ActiveUS11008234B2Treatment by combined electrochemical biological processesWater contaminantsMetalloidBioelectrochemical reactor
Systems and methods for treating a metal or metalloid ion-contaminated liquid are provided. The method may include (i) feeding the metal or metalloid ion-contaminated liquid into a bioelectrochemical reactor containing a bacteria selected by the cathode to produce extracellular metal or metalloid nanoparticles; and (ii) operating the bioelectrochemical reactor anaerobically to reduce the metal or metalloid ions in the metal or metalloid ion-contaminated liquid to extracellular metal or metalloid nanoparticles. The method may further include separating the metal or metalloid nanoparticles from the bacteria with no energy input. A bioelectrochemical reactor system for production of extracellular metal and metalloid nanoparticles may include a bioelectrochemical reactor, a separation device, and a tangential flow filtration unit.
Owner:FLORIDA STATE UNIV RES FOUND INC
A membrane bioelectrochemical reactor device with high quality effluent and low membrane fouling
ActiveCN103241895BReduce pollutionRealize denitrificationWater contaminantsMultistage water/sewage treatmentPeristaltic pumpLow nitrogen
The invention relates to a membrane biological electrochemical reactor device with high-quality effluent and low membrane pollution, relates to the field of sewage treatment and is used for solving the problems of serious MBR (Membrane Bio-Reactor) membrane pollution, low nitrogen removal rate, poor treatment effect on sewage which is difficult to degrade and the like. The reactor device comprises a water box, a water-inflow peristaltic pump, an MFC (Microfunction Circuit) anode chamber, a stainless steel flat plate membrane, an MBR reactor, a conducting wire, an external resistor, an aeration head, an air flowmeter, an air compressor, a vacuum pressure gauge, a backflow peristaltic pump and an effluent peristaltic pump. As the reactor device is used, the sewage firstly enters the anaerobic MFC anode, and anaerobic electricity generating microorganisms perform hydrolytic acidification pretreatment; then the sewage enters the MBR, and the partial effluent are enabled to flow back into the anaerobic anode chamber, so that the denitrification of the sewage is further performed. Therefore, the energy source recovery and in-situ utilization of the electric energy performed by the MFC, the effective control of the membrane pollution and the efficient treatment of the sewage are realized. As a result, the reactor device is obvious in economic and environmental benefits. The reactor device provided by the invention is applied to the field of the sewage treatment.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Rapid starting method of biological electrochemistry technology for removing oxygen from oil field wastewater
ActiveCN109160596AStart fastRapid enrichmentWaste water treatment from quariesTreatment by combined electrochemical biological processesActivated sludgeElectrochemical response
The invention discloses a rapid starting method of a biological electrochemistry technology for removing oxygen from oil field wastewater. The method can realize effective rapid enrichment of electrogenesis microbes by controlling the culture medium ratio, inoculation sources, line connection, DO control and other conditions, and can realize the rapid starting of a bioelectrochemical reactor. A substrate for adjusting and starting the control conditions is the most applicable substrate for common dominant anode microbes, and meanwhile, activated sludge is adopted to improve the biological diversity of inoculums, the line connection is controlled to form high-voltage screening to functional microbes, the DO control properly matches with the demand on oxygen by facultative microbes in targetfunctional microbes, and meanwhile, the demand on oxygen by a cathode is balanced.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
A bioelectrochemical reactor and its application in degrading fluoronitrobenzene wastewater
ActiveCN104628090BImprove processing efficiencyEasy to operateTreatment by combined electrochemical biological processesWater contaminantsElectrochemical degradationNitrobenzene
The invention discloses a bio-electrochemical reactor and an application thereof in degrading fluoronitrobenzene wastewater. The bio-electrochemical reactor comprises a bed body, wherein an electrode is arranged in the bed body, the electrode is a spiral coil type electrode which is water-permeable in a radial direction, and a water distributor which is positioned on the periphery of the spiral coil type electrode and a water outlet device which is positioned at a central position of the spiral coil type electrode are also arranged in the bed body. According to the bio-electrochemical reactor disclosed by the invention, the spiral coil type electrode is formed by winding a cathode electrode and an anode electrode which are insulated from each other, and a cathode and an anode can be used for treating pollutants synchronously so as to ensure that the treatment efficiency can be improved, operation steps can also be simplified, and the treatment cost can be reduced. Meanwhile, the water distributor is arranged on the periphery of the spiral coil type electrode, the water outlet device is arranged at the central position of the spiral coil type electrode, wastewater can be permeated to the center from the periphery of the spiral coil type electrode, and a plurality of cathode-anode groups which can be used for treating the wastewater for a plurality of times are formed in the spiral coil type electrode, so that the wastewater treatment efficiency can be greatly improved; and aiming at the fluoronitrobenzene wastewater treated by using the bio-electrochemical reactor disclosed by the invention, the fluoronitrobenzene pollutant removal rate, defluorination rate and mineralization rate can basically reach more than 90% respectively.
Owner:ZHEJIANG GONGSHANG UNIVERSITY
Stacked circulatable microbial electrochemical reactor and degradation method of petroleum hydrocarbon contaminated soil
PendingUS20220219212A1Improve degradation efficiencyIncrease the scope of applicationContaminated soil reclamationWater/sewage treatment apparatusSoil scienceSoil remediation
A stacked circulatable microbial electrochemical reactor and a degradation method of petroleum hydrocarbon contaminated soil are provided, which belong to the field of microbial electrochemical soil remediation. The stacked circulatable microbial electrochemical reactor of the present disclosure expands influence range of anodes by a stacked microbial electrochemical system, accelerates the movement of the petroleum hydrocarbon molecules in the contaminated soil by a water circulation system, and improves the mass transfer capacity of soil, thereby increasing the degradation efficiency of petroleum hydrocarbon in the contaminated soil with microbial electrochemical technology from different aspects. The degradation method of petroleum hydrocarbon contaminated soil is provided. The degradation method of the present disclosure is simple in operation and has a high degradation efficiency of petroleum hydrocarbon in contaminated soil.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Bifunctional electrode with nitrification and denitrification activity, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN105140529BHigh removal rateEfficient recyclingCell electrodesBiochemical fuel cellsSludgeEnergy recovery
The invention provides a difunctional electrode with nitrification and denitrification activity and a preparing method and application thereof. A carbon-based material is used as a conducting skeleton of the electrode, an abiological catalyst is loaded on the surface of the electrode to catalyze an oxygen reduction reaction, the electrode is placed in a negative pole chamber inoculated with nitrification and denitrification activity sludge, a system is started and operates until a stable biological membrane is formed on the surface of the electrode, and therefore pollutants in sewage can be removed while electric energy is effectively recovered. The abiological catalyst is used under the oxygen condition to realize the efficient oxygen reduction reaction of the electrode, and meanwhile nitrogen in the microorganism catalyzed sewage is removed. The preparing method of the difunctional electrode is simple, the energy recovery rate of the difunctional electrode is obviously larger than that of a single biological electrode, organics and the nitrogen in the sewage are effectively removed, and the removal speed is higher than that of a single abiological electrode and the biological electrode; the electrode can be used in a microbial fuel cell or other bioelectrochemistry reactors.
Owner:重庆中科德馨环保科技有限公司
A bioelectrochemical method for real-time in situ detection of BOD in organic wastewater
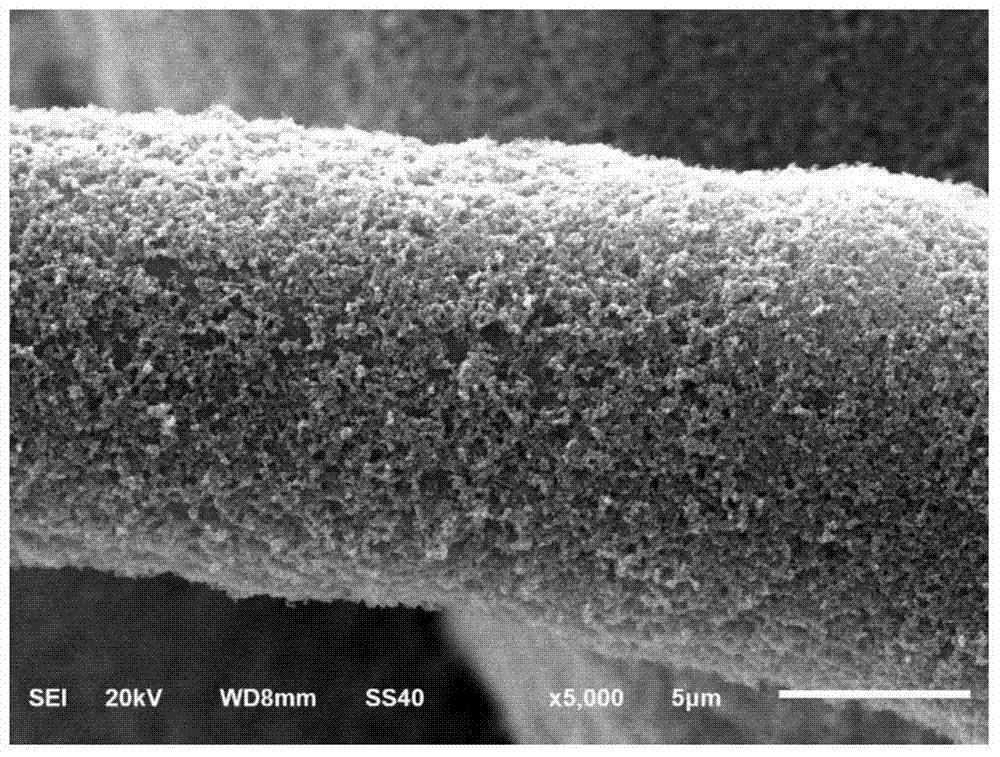
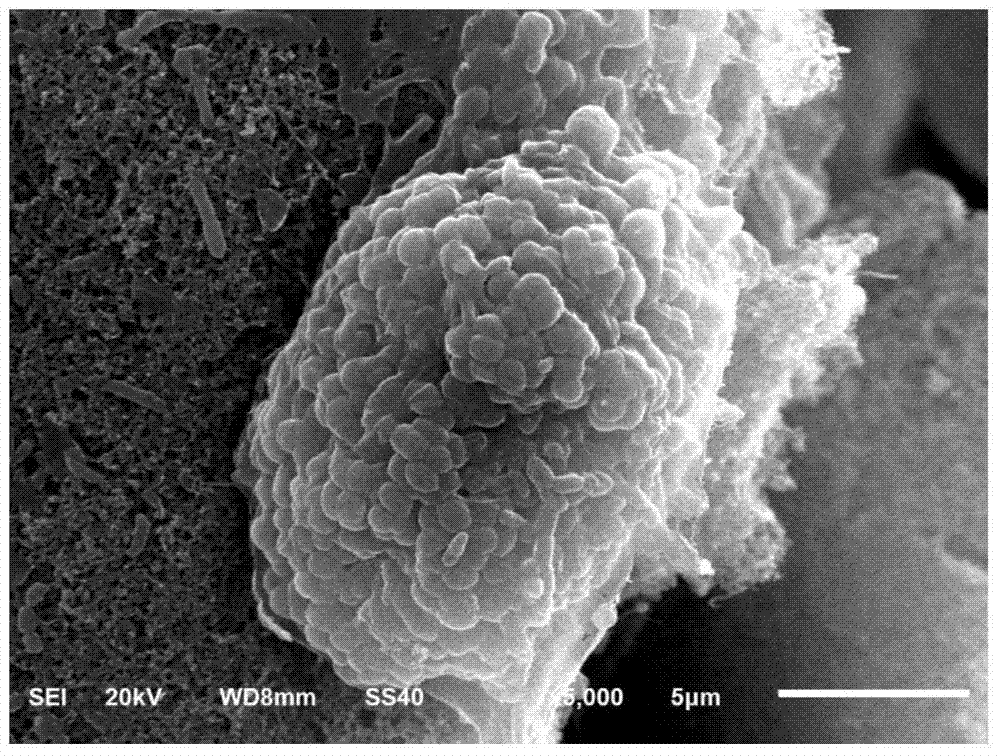
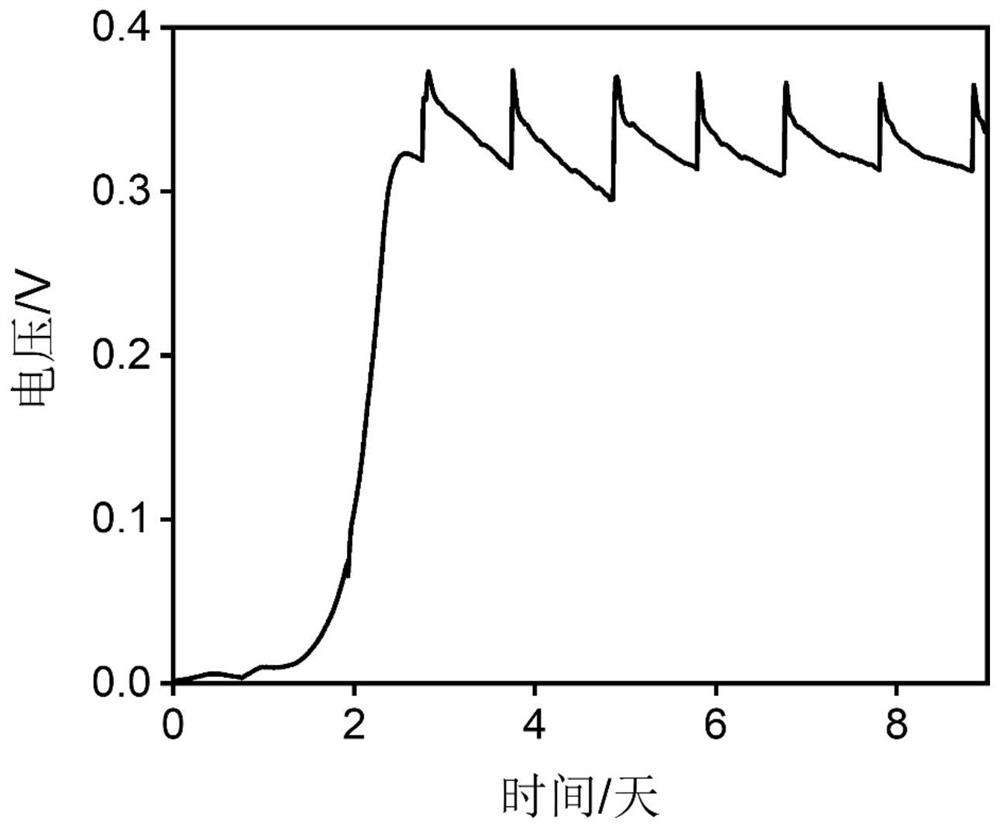
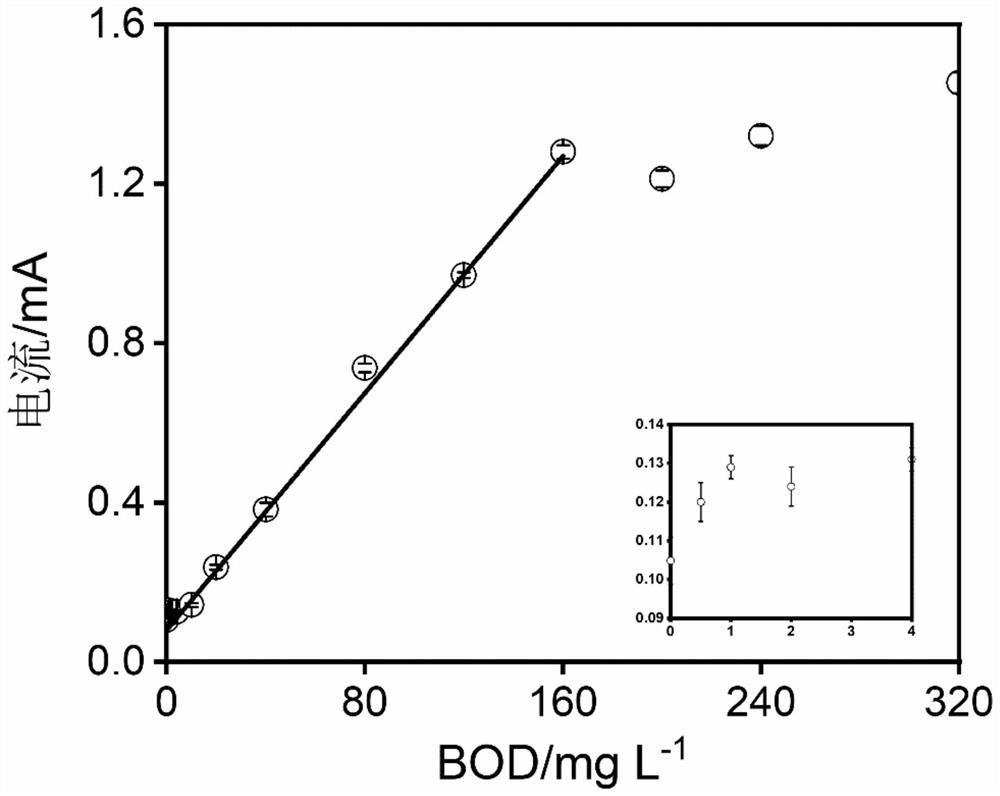
ActiveCN113484397BShorten test timeImprove test accuracyMaterial electrochemical variablesMatrix solutionBioelectrochemical reactor
The invention discloses a bioelectrochemical method for real-time and in-situ detection of BOD in organic wastewater, including 1): operating a bioelectrochemical reactor in a closed circuit in an MFC mode, and adding an inoculum solution to the anode chamber; 2): cultivating in a matrix solution Bioelectrode until the electrode biofilm matures; 3): The bioelectrochemical reactor is connected to a potentiostat to construct a bioelectrochemical sensor, and a linear voltammetry scan is performed, wherein the bioelectrode is placed in a single organic solution containing different BOD concentrations, Select the current at different potentials for fitting, determine the optimal signal output potential, and obtain the linear equation between the output current signal and the concentration of a single organic compound; 4): Obtain the linear equation between the output current signal and the concentration of each organic compound, and calculate the relative singleness of each organic compound Relative electricity production rate of organic matter; 5): Calculate the relative electricity production rate of organic wastewater, and the sensor outputs electrical signals in organic wastewater to obtain the BOD concentration of organic wastewater.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
A rapid start-up method for a bioelectrochemical process for deoxygenation of oilfield wastewater
ActiveCN109160596BStart fastRapid enrichmentWaste water treatment from quariesTreatment by combined electrochemical biological processesActivated sludgeElectrochemical response
The invention discloses a quick start-up method for a bioelectrochemical process for deoxygenation of oilfield wastewater. By controlling the culture medium ratio, inoculation source, line connection, DO control and other conditions during the start-up period, effective quick enrichment and high efficiency can be realized. Electrogenic microorganisms can achieve rapid start-up of bioelectrochemical reactors. The control conditions adjust the starting substrate to be the most suitable substrate for common dominant anode microorganisms. At the same time, the use of activated sludge improves the biodiversity of the inoculum, and the control line connection forms a high-pressure screening of functional microorganisms. The control of DO is very good. It matches the demand for oxygen of the facultative microorganisms in the target functional microorganisms, and balances the demand for oxygen of the cathode.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
A bioelectrochemical reactor for treating organic fluorine wastewater and a treatment method for organic fluorine wastewater
ActiveCN103787490BReduce processing costsEfficient coupling of degradation functionsWater contaminantsBiological water/sewage treatmentWastewaterFluoride
The invention discloses a bioelectrochemical reactor for treating organic fluoride-containing wastewater and a treatment method for the organic fluoride-containing wastewater. The bioelectrochemical reactor comprises a bed body, a partition plate, a conduit, a biological cathode, a biological anode, a power supply, a water inlet and a water outlet, wherein the partition plate is vertically arranged in the bed body, and divides the bed body into a cathode chamber and an anode chamber; the bottoms of the cathode chamber and the anode chamber are communicated through the conduit; the power supply is connected with the biological cathode and the biological anode; the water inlet is formed in the cathode chamber; the water outlet is formed in the anode chamber. According to the bioelectrochemical reactor and the treatment method, the organic fluoride-containing wastewater is treated in two stages under the catalysis action of cathode and anode microorganisms, so that the treatment efficiency of the organic fluoride-containing wastewater is improved, the overall treatment cost of the organic fluoride-containing wastewater is lowered, and the problem of difficulty in the biodegradation of the organic fluoride-containing wastewater is solved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG GONGSHANG UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com