Method for electrochemical device to utilize corn cob hydrolysate
A corn cob hydrolyzate, electrochemical technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, methods based on microorganisms, microorganisms, etc., can solve the problems of limiting the development of succinic acid, unsustainable development, and low production of succinic acid. Achieve the effect of easy operation, simple method and low pollution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
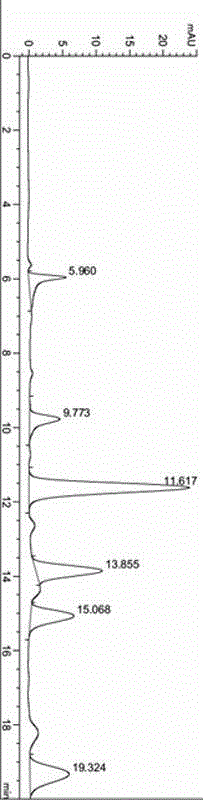
Image
Examples
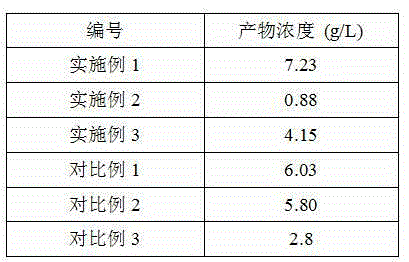
Embodiment 1
[0023] A method for utilizing corncob hydrolyzate in an electrochemical device, comprising the following steps:
[0024] Step 1, degrading corncob by dilute acid method: add 5mL dilute H with a volume fraction of 2% per gram of corncob 2 SO 4 , 121°C, sterilized for 20 minutes, decolorized with activated carbon, filtered with suction, and rotary steamed.
[0025] Step 2, prepare seed culture medium, catholyte, anolyte, seed washing liquid, wherein, seed culture medium (g·L -1 ) including glucose 10 (divided), yeast extract 5, corn steep liquor 5, NaHCO 3 10, NaH 2 PO 4 2H 2 O 9.6, K 2 HPO 4 ·3H 2 O 15.5; catholyte (g L -1 ) including yeast extract 5, NaH 2 PO 4 2H 2 O 8.5, Na 2 HPO 4 12H 2 O 31.51, NaHCO 3 10; neutral red (g L -1 ) 0.0288; anolyte (g L -1 ) including Na 2 HPO 4 12H 2 O 2.51, NaH 2 PO 4 2H 2 O 2.81, NaCl 1.45; DTT (g L -1 ) 0.2; seed lotion (g L -1 ) including Na 2 HPO 4 12H 2 O 5 , NaH 2 PO 4 2H 2 O 5.6, DTT 0.15.
[0026] ...
Embodiment 2
[0031] Step 1 to step 4 are the same as Example 1.
[0032] Step 5, first centrifuge the fermented bacteria at 10000rpm to remove the supernatant, wash 4 times with the seed washing solution and centrifuge, then insert the bacteria into the catholyte, then add 0.0288g / L neutral red and 10g / L corn cob The hydrolyzate is connected to the catholyte, mixed evenly, and finally connected to the cathode cavity of the bioelectrochemical reactor. Then 0.2g / L DTT was added to the anolyte, mixed evenly, and then connected to the anode cavity of the bioelectrochemical reactor.
[0033] Step 6, connect the bioelectrochemical reactor to electricity, keep the constant voltage at -0.8V, and pass CO into the cathode chamber 2 0.02 L / (min·L), the temperature was controlled at 37°C for 12 hours of fermentation.
Embodiment 3
[0035] Step 1 to step 4 are the same as Example 1.
[0036] Step 5, first centrifuge the fermented bacteria at 12000rpm to remove the supernatant, wash with the seed washing solution for 5 times and centrifuge, then insert the bacteria into the catholyte, then add 0.0288g / L neutral red and 15g / L corn cob The hydrolyzate is connected to the catholyte, mixed evenly, and finally connected to the cathode cavity of the bioelectrochemical reactor. Then 0.2g / L DTT was added to the anolyte, mixed evenly, and then connected to the anode cavity of the bioelectrochemical reactor.
[0037] Step 6, connect the bioelectrochemical reactor to electricity, keep the constant voltage at -1.2V, and pass CO into the cathode chamber 2 0.02 L / (min·L), the temperature was controlled at 37°C for 24 hours of fermentation.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com