Continuous flow process for synthesis of hydroxamic acid
A technology of hydroxamic acid and hydroxyl group, applied in the field of synthesizing hydroxamic acid, can solve the problems of slowing down the reaction speed and long reaction time, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
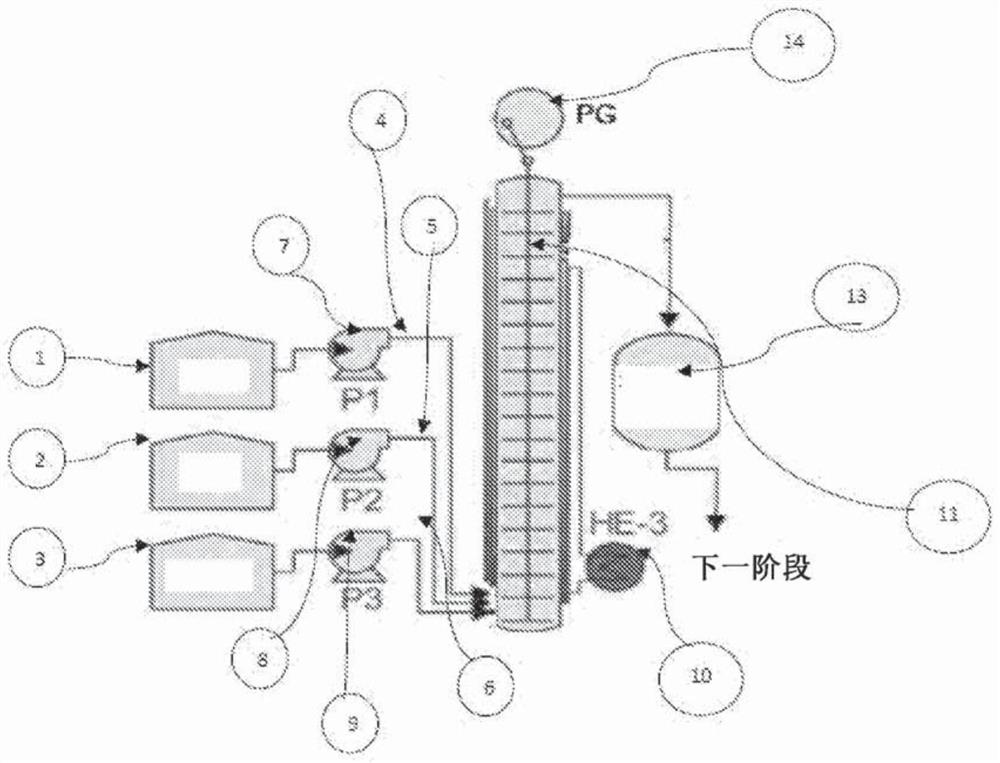
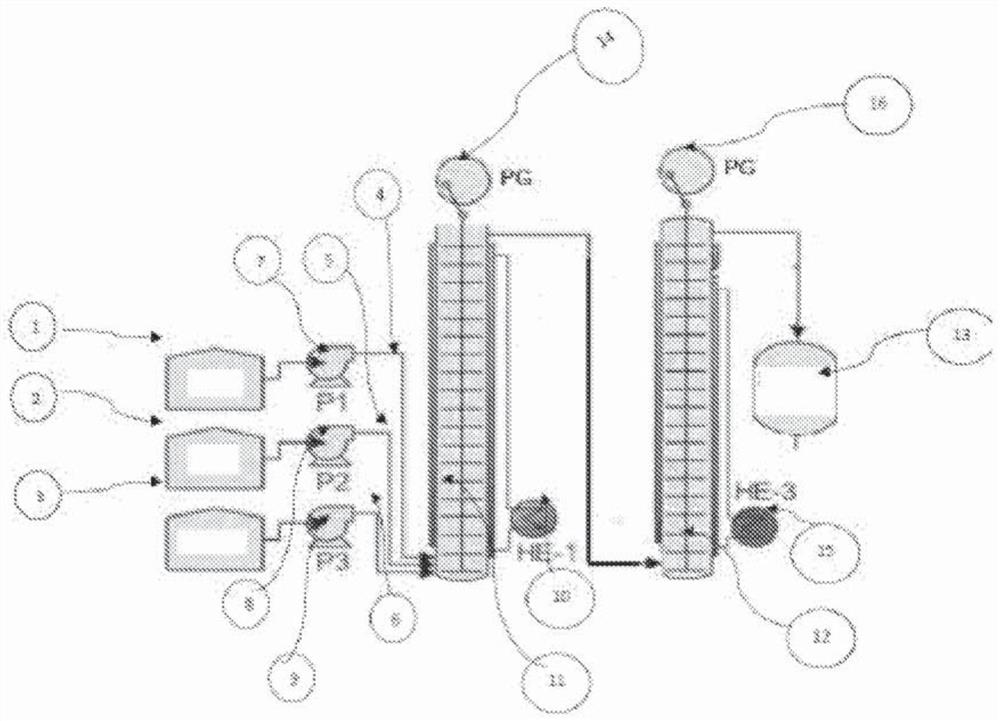
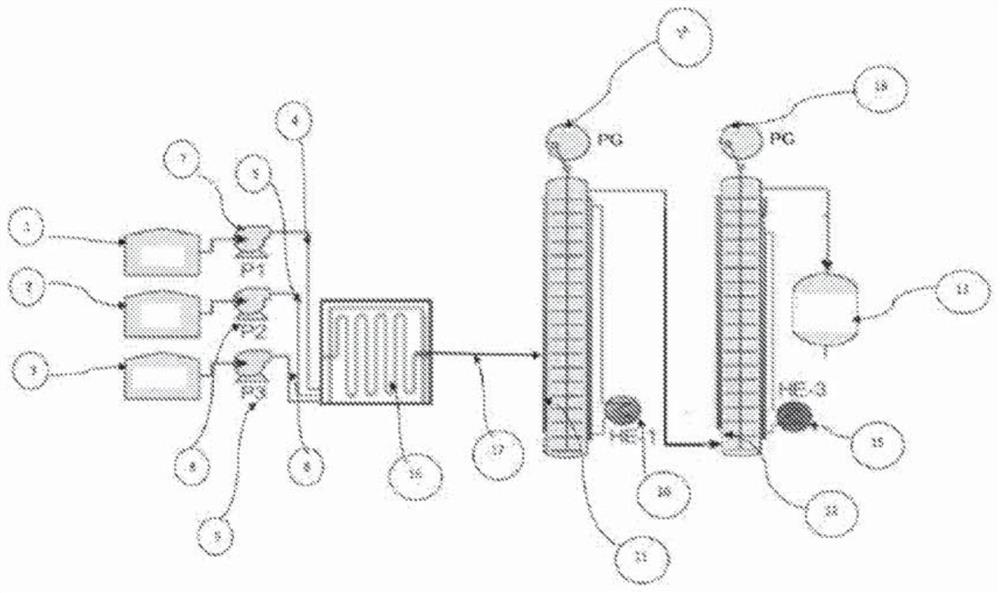
[0166] The continuous reaction was carried out using a three-line plug flow reactor (PFR). Ethyl acetate (88.11 g) was fed to the reactor at a rate of 7.61 ml / min through the first feed line, and a 30% hydroxylamine sulfate solution (169 gm hydroxylamine sulfate in 395 gm water) was passed through the second feed line at 16.5 ml. 30% NaOH solution (42 gm sodium hydroxide in 92.5 gm water) was fed to the reactor at a rate of 9.2 ml / min through the third line. The flow rate was adjusted to maintain a stoichiometric ratio of hydroxylamine sulfate:ethyl acetate:sodium hydroxide of approximately 1:2.15:2.6. All three feed lines discharged their contents into the reaction vessel, which was maintained at 90°C, to form acetohydroxamic acid with a residence time of 3 minutes. The results of the reaction setup are highlighted in Table 1. Samples were analyzed by HPLC (HPLC purity 97%).
Embodiment 2
[0168] The continuous reaction was carried out using a three-line PFR reactor. Ethyl acetate (88.11 g) was fed to the reactor at a rate of 7.0 ml / min through the first feed line, and a 30% hydroxylamine hydrochloride solution (71 gm hydroxylamine hydrochloride in 161 gm water) was passed through the second feed line at 12.64 ml 30% NaOH solution (42 gm sodium hydroxide in 92.5 gm water) was fed to the reactor at a rate of 13.42 ml / min through the third line. The flow rate was adjusted to maintain a 1:1.15:2.0 stoichiometric ratio of hydroxylamine hydrochloride:ethyl acetate:sodium hydroxide. All three feed lines drain their contents into the reaction vessel, which is maintained at 90°C. The desired product, acetohydroxamic acid, was formed within a residence time of 3 minutes without changing the existing conditions. The results of the reaction setup are highlighted in Table 1. The samples were analyzed by HPLC (HPLC purity 96%).
Embodiment 3
[0170] The continuous reaction was carried out using a three-line PFR. Ethyl acetate (88.11 gm) was fed to the reactor through the first feed line at a rate of 7.4 ml / min, and a 30% hydroxylamine sulfate solution (169 gm hydroxylamine sulfate in 395 gm water) was fed through the second feed line at 15.6 ml. 30% NaOH solution (42 gm sodium hydroxide in 92.5 gm water) was fed to the reactor at a rate of 10.38 ml / min through the third line. The flow rate was adjusted to maintain a 1:2.2:3 stoichiometric ratio of hydroxylamine sulfate:ethyl acetate:sodium hydroxide. All three feed lines drain their contents into the reaction vessel, which is maintained at 90°C. The desired product, acetohydroxamic acid, was formed within a residence time of 3 minutes without changing the existing conditions. The results of the reaction setup are highlighted in Table 1. The samples were analyzed by HPLC (98% purity by HPLC).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com