Heparin compositions that inhibit clot associated coagulation factors
A technology of heparin and factor, applied in the field of treatment of cardiovascular diseases, can solve the problems of short can not bridge thrombin and antithrombin, bad inhibitor, can not bridge thrombin and fibrin, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0109] Experimental observation
[0110] 1.1 Clinical limitations of currently available anticoagulants:
[0111] Heparin, LMWH and directed thrombin inhibitors have limitations in acute coronary syndrome. For patients with unstable angina, recurrent ischemic effects are central when treatment with these drugs is discontinued (Theroux, P., et al. (1992) N. Engl. J. Med. 327: 141-145; Granger, C. B., et al. (1996), Circulation 93: 870-888; Oldgren, J., et al. (1996), Circulation 94 (Suppl 1): 1-431). This is due to reactivation of coagulation, as there are elevated plasma levels of the associated prothrombin fragments F1.2 (F1.2) and fibrinopeptide A (FPA), reflecting increased thrombin generation and thrombin activity, respectively (Granger, C.B., et al. (1995), Circulation 91:1929-1935). In patients with acute myocardial infarction, induction of thrombosis with tissue plasminogen activator (tPA), streptokinase is characterized by increased levels of The prothrombin state o...
Embodiment 2
[0131] 2.0 Production of medium molecular weight heparins:
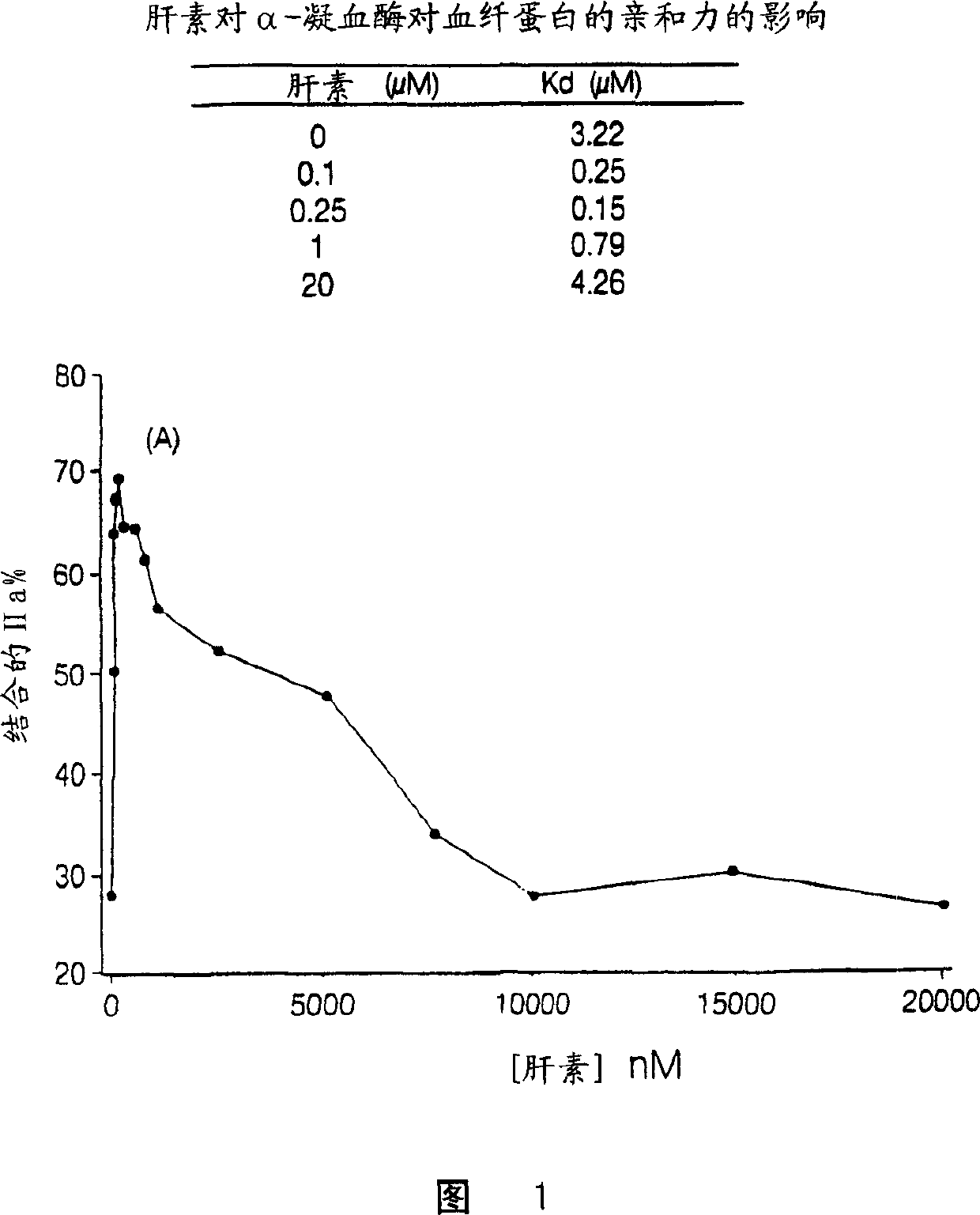
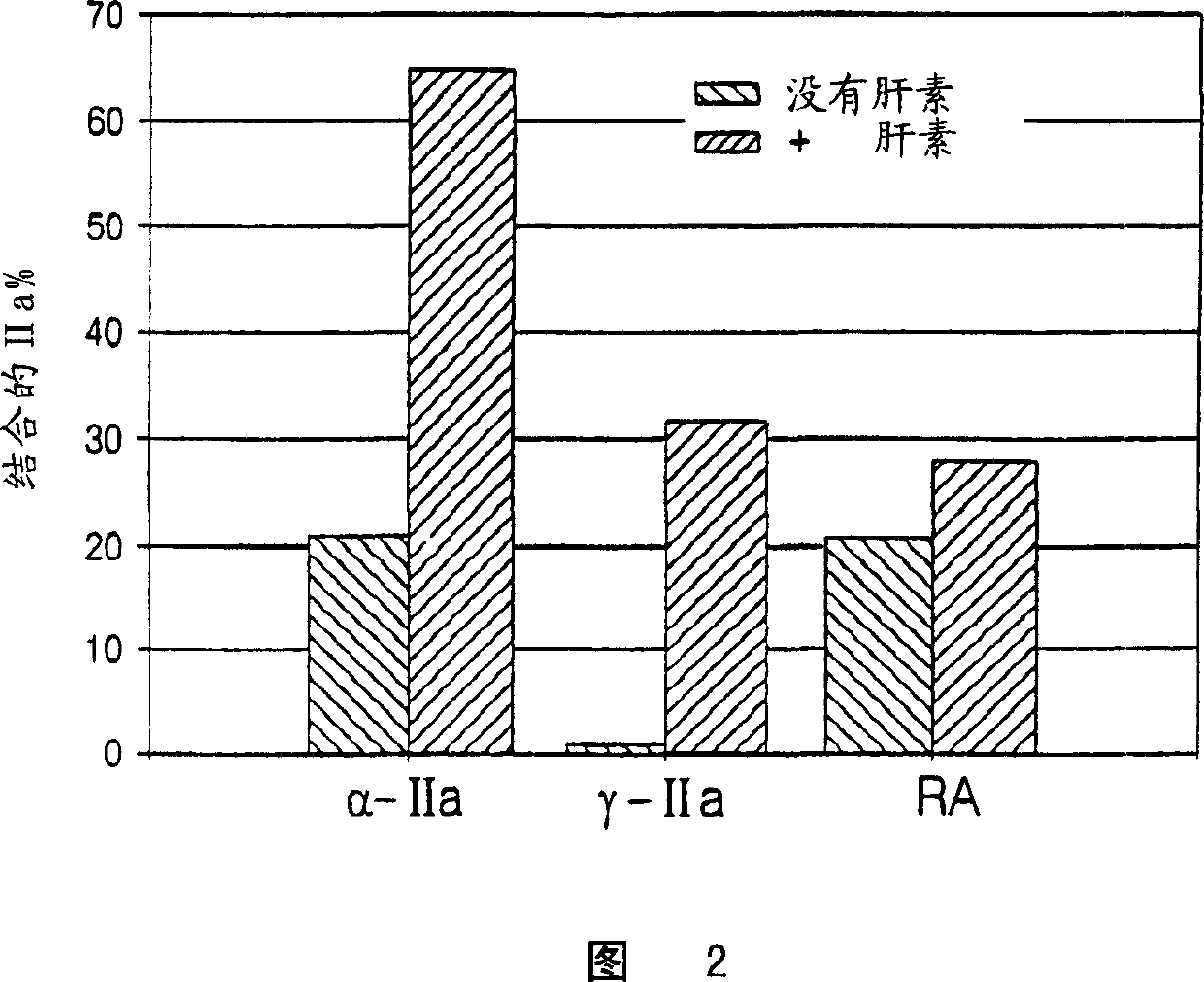
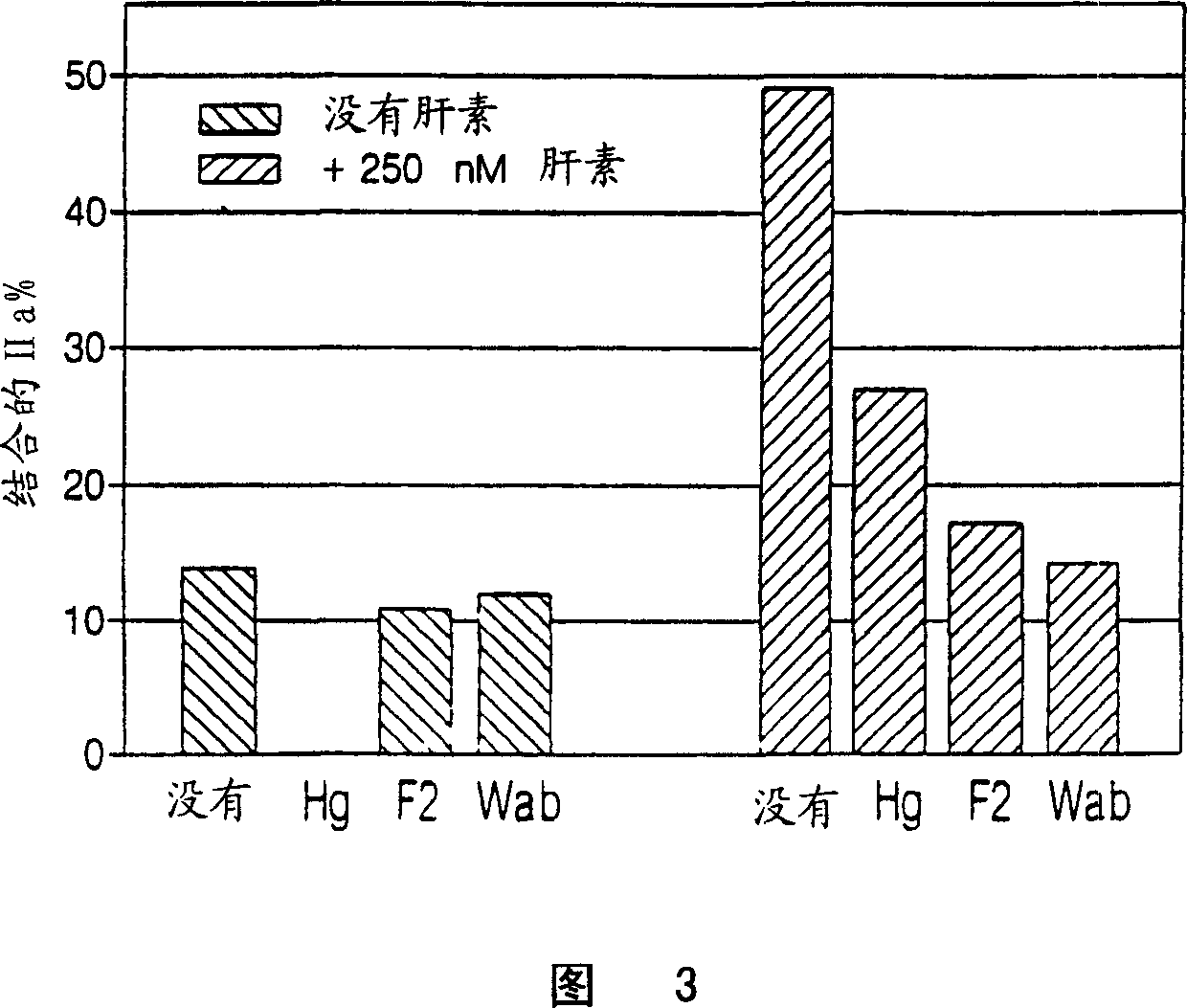
[0132] To catalyze thrombin inhibition, heparin bridges antithrombin and thrombin (Danielsson, A., et al. (1986), J. Biol. Chem. 261: 15467-15473). The premise is that the bridging function requires heparin chains with a minimum molecular weight of 5,400 (Jordan, R.E., et al. (1980), J. Biol. Chem. 225:10081-10090). Since most LMWH molecules are smaller than 5,400 Daltons, LMWHs have minimal antithrombin inhibitory activity (Jordan, R.E., et al. (1980), J. Biol. Chem. 225:10081-10090 ). Since heparin bridges thrombin and fibrin to form a ternary fibrin-thrombin-heparin complex, it was hypothesized that this function would also require heparin chains of minimum molecular mass. Furthermore, it is hypothesized that if this minimum molecular mass is not the same as that required to bridge antithrombin and thrombin, there may be cases where the heparin chain is too short to bridge thrombin and fibrin but long enough to ...
Embodiment 3
[0138] MMWH composition of the present invention compares with other known anticoagulant efficacy and safety
[0139] This example illustrates a study comparing the efficacy and safety of the MMWH component of the invention (indicated as V21 in the figure), LMWH, heparin and hirudin in a rabbit arterial thrombosis prevention model. The results show that the MMWH of the present invention is more effective than LMWH and heparin and safer than hirudin. Modification of the arterial thrombosis prevention model allows evaluation of both efficacy and safety in the same animals. Efficacy was evaluated by measuring the flow rate at 95% distal stenosis in the injured rabbit aorta over 90 minutes, and safety was evaluated by measuring blood loss over 30 minutes using a rabbit ear phantom. Four mixtures were compared at three dosage levels. Each mixture was administered as a bolus and infusion for 90 minutes. Doses listed in the graph below represent boluses and infusions / 60 minutes, a...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com