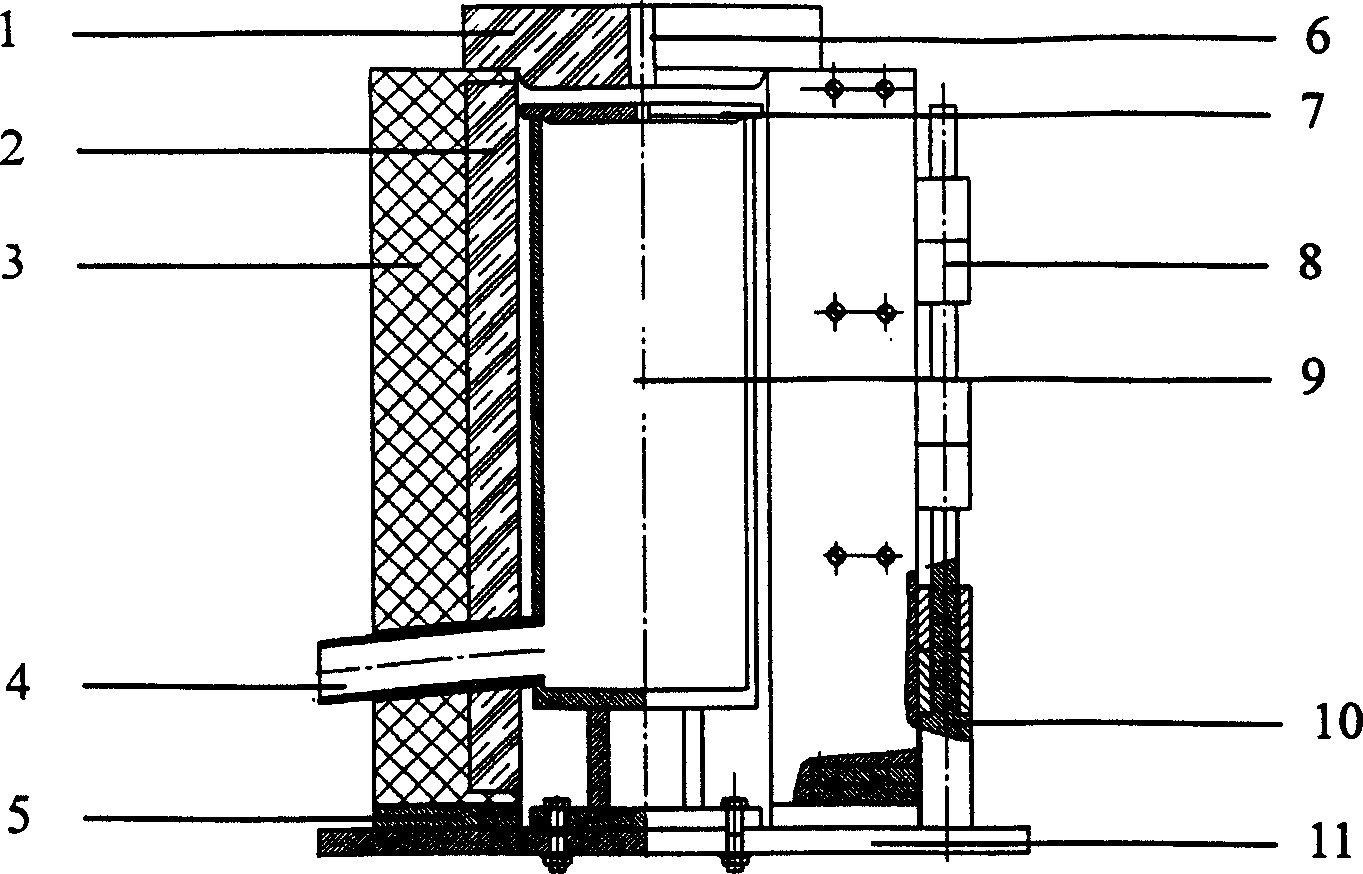
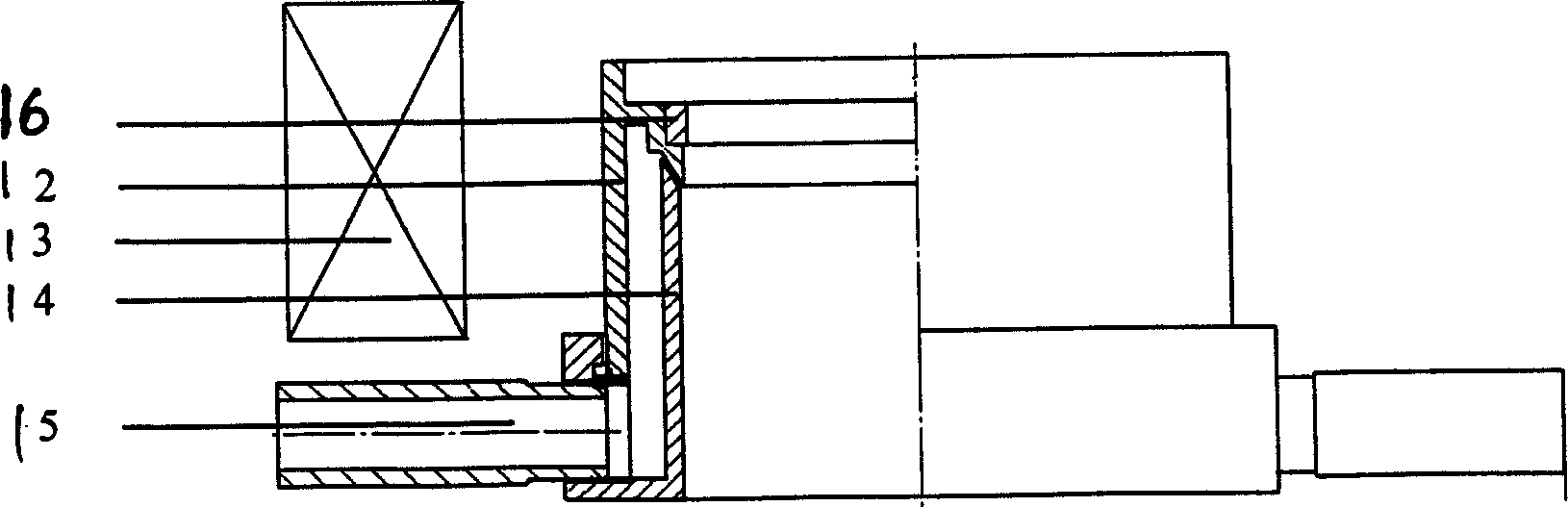
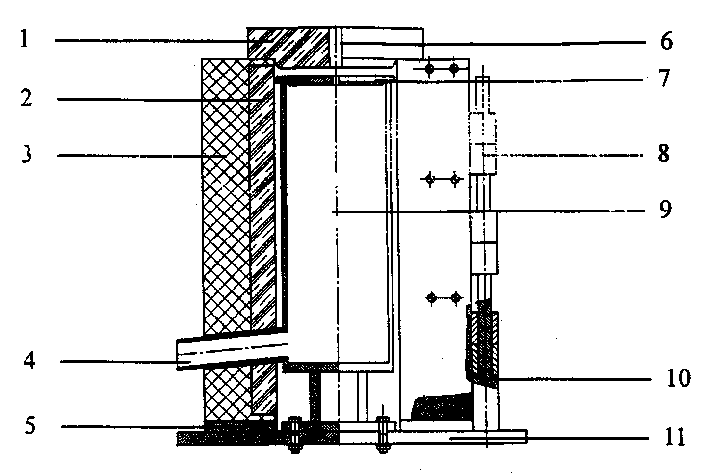
Magnesium alloy electromagnetic low-temperature semicontinuous casting method
A semi-continuous, magnesium alloy technology, applied in the field of magnesium alloy casting, can solve the problems of serious element segregation, long solidification time, low casting speed, etc., and achieve the effect of shortening the process flow, excellent surface quality, and increasing casting speed.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0039] Example 1 Electromagnetic semi-continuous casting of AZ91D magnesium alloy
[0040] A casting condition
[0041] Ingot size: Φ100, aluminum alloy dummy rod;
[0042] Electromagnetic field conditions: frequency 50HZ, ampere-turns 2400AN
[0043] B Process parameters and ingot quality comparison
[0044] comparison method
[0045] casting method
[0046] It can be seen that compared with the traditional semi-continuous casting, the electromagnetic low-temperature semi-continuous casting of AZ91D magnesium alloy reduces the height of the mold, reduces the casting temperature by about 100°C, and more than doubles the casting speed; It is rose crystal or fine dendrite, no inclusion or micro shrinkage cavity, greatly reduced Mn segregation, no crack or crack, smooth and smooth surface.
example 2
[0047] Example 2 Electromagnetic semi-continuous casting of ZK60 magnesium alloy
[0048] A casting condition
[0049] Ingot size: Φ100, aluminum alloy dummy rod;
[0050] Electromagnetic field conditions: frequency 30HZ, ampere-turns 3600AN
[0051] Comparison of BT Process Parameters and Ingot Quality
[0052] comparison method
[0053] casting method
[0054] It can be seen that compared with the traditional semi-continuous casting, the electromagnetic low-temperature semi-continuous casting of ZK60 magnesium alloy reduces the height of the mold, reduces the casting temperature by about 50°C, and increases the casting speed by more than 4 times; the grains are significantly refined, and the grains in the center and edge of the ingot The size difference is significantly reduced, no inclusions or micro-shrinkage cavities, no cracks or cracks, and the surface is smooth.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com