Reflector utilizing microimage to make exposure and its production method
A manufacturing method and mirror technology, applied in the field of reflective optical mirrors, can solve the problems of different values of etching rates on the surface of silicon oxide, and achieve the effect of good optical properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
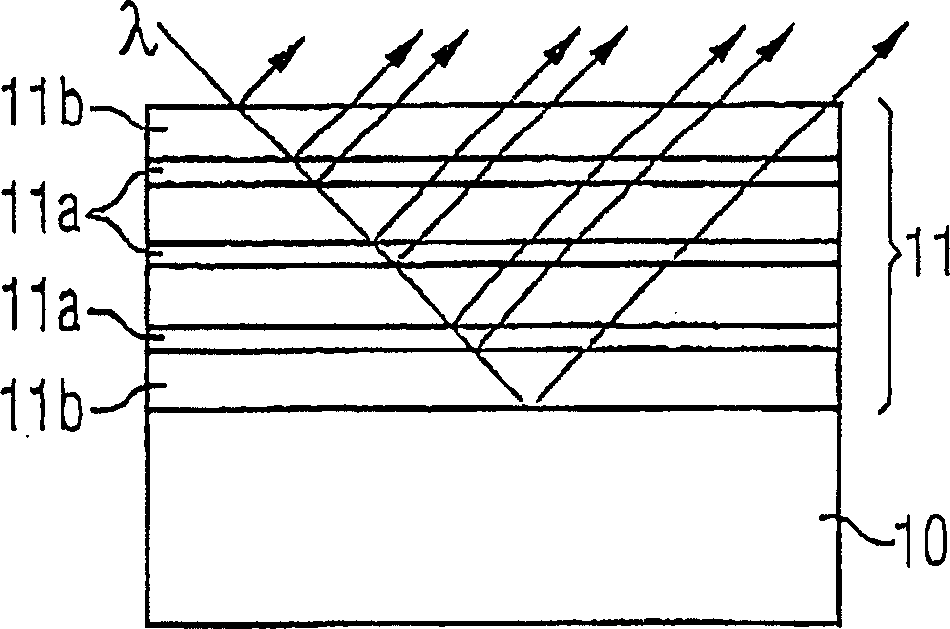
[0028] Figure 1A mirror is shown comprising a substrate 10 and a succession of thin layers 11a, 11b deposited one on top of the other. A semiconductor substrate or any other sufficiently thick and defined substrate can be used as the substrate 10. The layer thicknesses of the individual layers 11a and 11b are dimensioned such that the wavelength λ can be reflected at the layer interfaces adjacent to each other in such a way that the reflected partial light beams interfere structurally with each other; the highest possible light intensity of the total reflected radiation is at the semiconductor A short exposure time of the article is desired. The large angle of incidence of electromagnetic radiation having wavelength λ is shown in the figure, if Figure 1 Reflection at the non-non-interface is for illustration only; in practice, the reflection actually occurs perpendicular to the surface of the multilayer structure 11 .
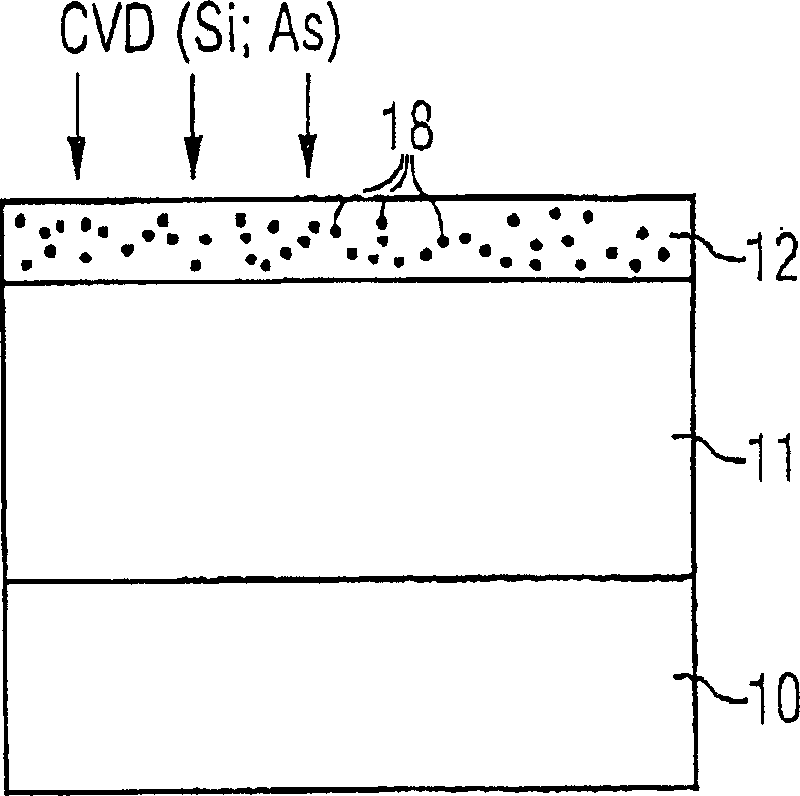
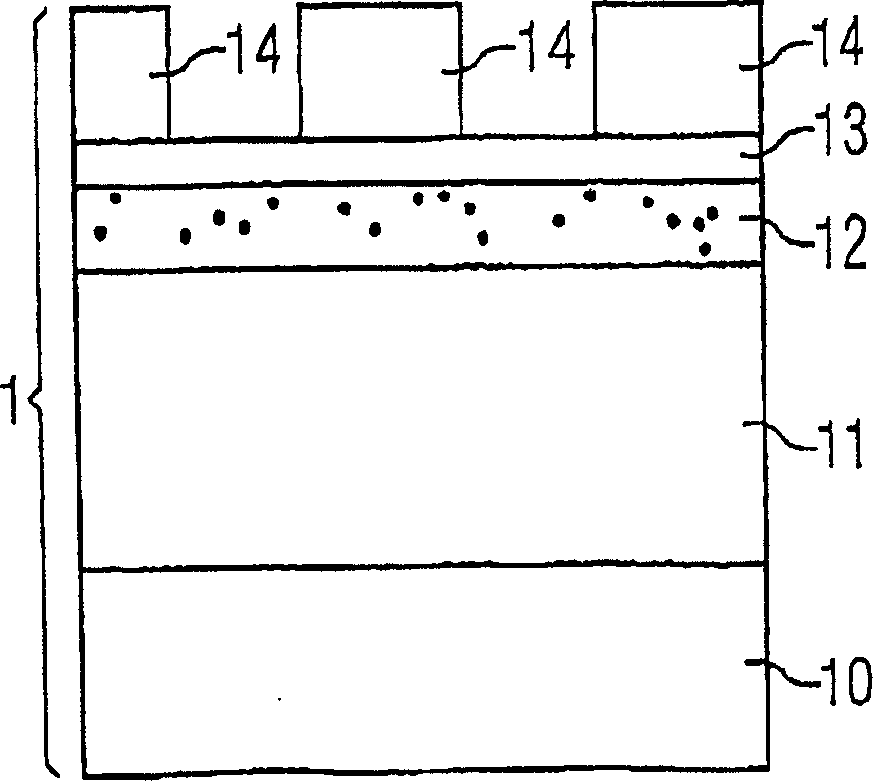
[0029] exist Figure 1 The layered sequence 11 is prod...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| coating thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com