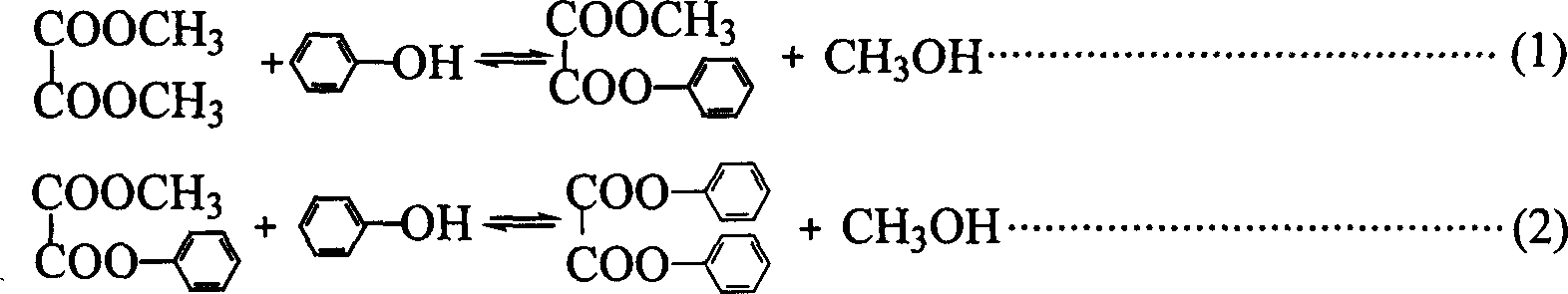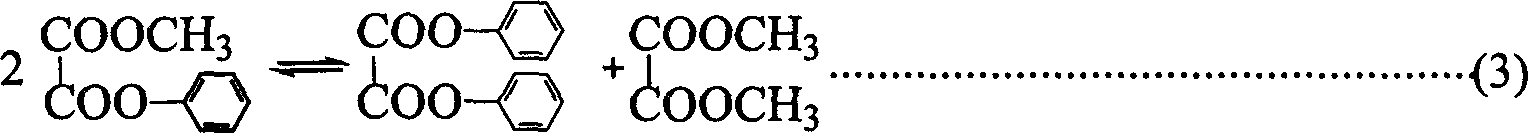Method for catalyzer synthesizing methyl-phenyl-oxalate and phenostal
A technology of methyl phenyl oxalate and diphenyl oxalate, which is applied in the field of catalytic synthesis of methyl phenyl oxalate and diphenyl oxalate to reduce production costs, improve selectivity, and save separation processes and equipment Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0015] In the present invention, under the condition of heterogeneous catalytic reaction, dimethyl oxalate and phenol are used as raw materials to prepare methyl phenyl oxalate and diphenyl oxalate process, which is carried out in a 250 ml three-necked flask. Electromagnetic stirring heating, equipped with a thermometer to display the temperature of the reaction system. The amount of industrial-grade DMO is 0.1 mole, the amount of chemically pure phenol is 0.5 mole, and the supported metal oxide catalyst MoO 3 / SiO 2 The consumption amount of is 1.8 grams, adds under normal pressure, wherein the load of metal molybdenum is 1% (weight, the same below). Stir and heat up, the reaction temperature is controlled at 180.0±2°C, and the reaction time is 2 hours. Reaction (1)-(3) The reaction equilibrium constants of each step are extremely small, in order to break the restriction of thermodynamic equilibrium and improve the conversion rate of raw materials, a constant temperature of...
Embodiment 2-9
[0021] Changing the Supported Metal Oxide Catalyst MoO 3 / SiO 2 The load of molybdenum in the middle is respectively 1%, 2%, 4%, 6%, 8%, 10%, 12%, 14%, 16%, under the situation that other conditions are completely identical with embodiment 1, carry out ester Exchange reaction, form embodiment 2-9 respectively, examine reaction result.
[0022] Table 1: MoO 3 / SiO 2 Series of catalysts catalyzed transesterification reaction results (weight percentage)
[0023] DMO selectivity, % yield, %
Embodiment 10-13
[0037] The catalyst was changed to SnO with a tin content of 4% 2 / SiO 2 Catalyst, MoO with 8% molybdenum 3 / MgO catalyst, MoO with 8% molybdenum content 3 / Al 2 o 3 Catalyst, MoO with 8% molybdenum 3 / ZrO 2 Catalyst, under the completely identical situation of other conditions and embodiment 1, carry out transesterification reaction, form embodiment 10-13 respectively, investigate reaction result.
[0038] Table 2: Transesterification results of different metals and different carrier catalysts (weight percentage)
[0039] DMO selectivity, % yield, %
[0040] Example Catalyst
[0041] Conversion rates%
[0042] Anisole MPO DPO MPO DPO
[0043] 10 SnO 3 / SiO 2 45.2 0.7 78.8 20.6 35.6 9.3
[0044] 11 M 3 / ZrO 2 53.7 0.7 85.9 8.4 46.1 4.5
[0045]12 M 3 / MgO 60.2 20.9 64.5 12.6 38.8 7.6
[0046] 13 MoO 3 / Al 2 o 3 62.7 35.4 53.9 5.9 33.7 3.7
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com