Method of prepn of ferrite from waste zinc-magnesium battery
A zinc-manganese battery and ferrite technology, which is applied in battery recycling, chemical instruments and methods, and solid waste removal, etc., can solve the problems of the limitation of zinc-shell battery preparation method, the difficulty of ferrite, and the unstable composition. Achieve high economic value and social value, easy implementation, and the effect of solving environmental pollution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
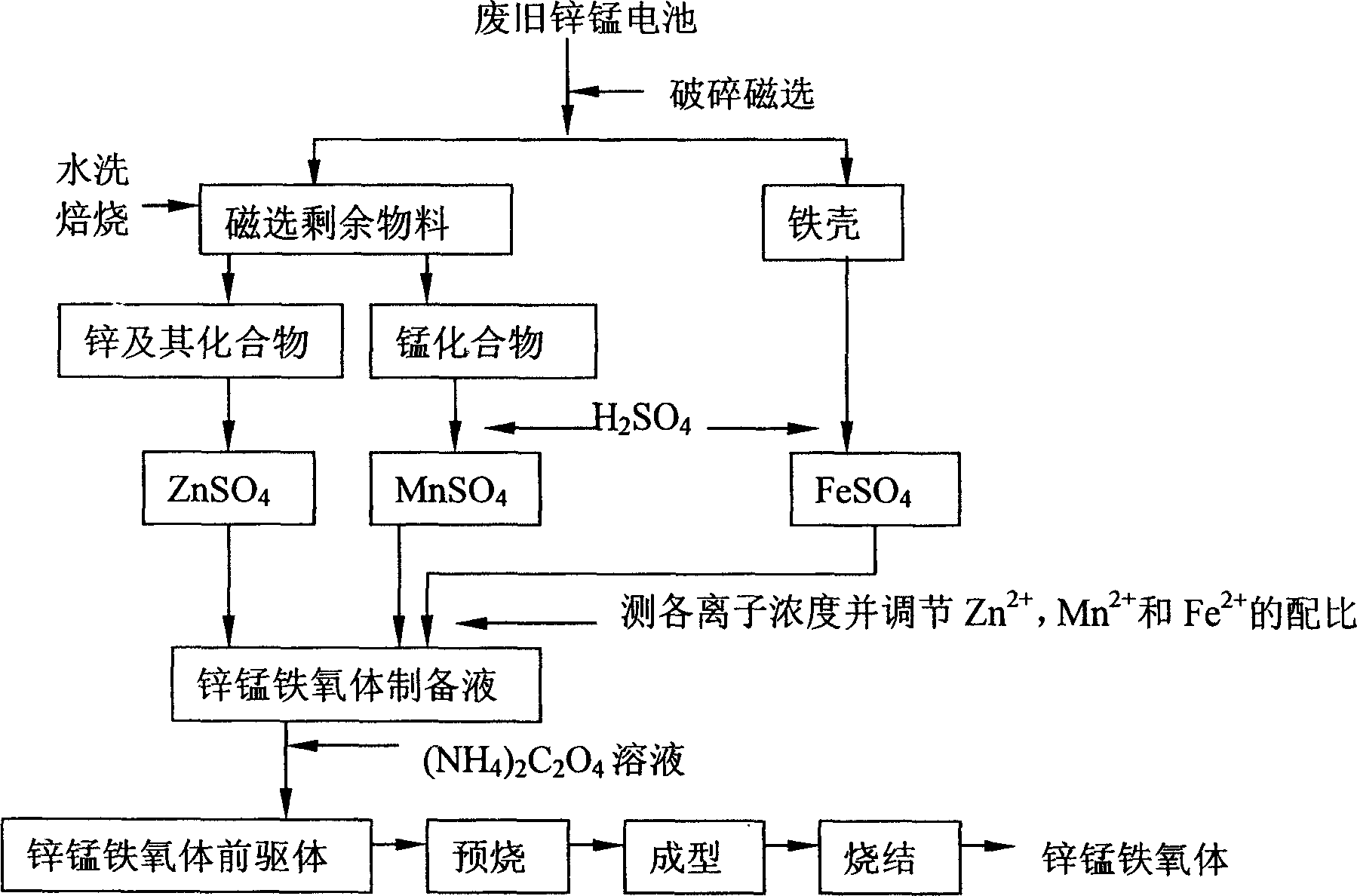
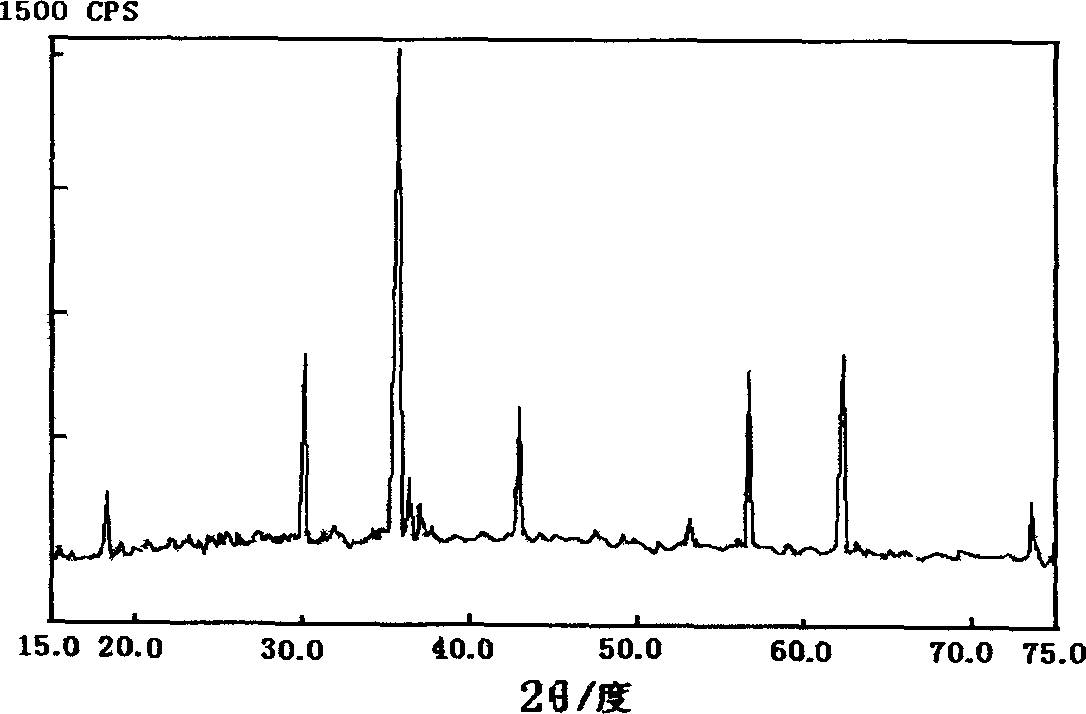
[0028] Attached below figure 1 And attached figure 2 An example of the present invention is described in detail, the used waste zinc-manganese battery (iron shell battery accounts for about 35%) is collected from the market, and the composition of the prepared ferrite is (MnO) 0.26 (ZnO) 0.23 (Fe 2 o 3 ) 0.1 .
[0029] The roasting furnace used for roasting the washed magnetic separation residue is self-made, the roasting temperature is 850°C, and the roasting time is 1h.
[0030] When using the iron shell separated by magnetic separation to prepare ferric sulfate, the reaction temperature condition is room temperature, and the H 2 SO 4 The concentration is 4mol / L, and the iron and sulfuric acid molar ratio is 1:1.5 for dissolution, and the final iron leaching rate can reach more than 93%. Obtained FeSO 4 Ni in solution 2+ The content is only Fe 2+ 2.5 / 10,000, the nickel impurity content meets the requirements, and no further impurity removal treatment is required....
Embodiment 2
[0036] Others are the same as Example 1, and the difference is that in step (1), the temperature of roasting through the magnetic separation residue washed with water is 800°C, the time is 5h, and the concentration of sulfuric acid that dissolves each species is 0.5mol / L, so The number of moles of sulfuric acid required is twice the number of moles of dissolved species. In the step (2), the precipitating agent is ammonia water, and the amount of the precipitating agent added is twice the total molar number of the three metal salt ions. The gas used to maintain the inert atmosphere in step (3) is nitrogen, the pre-calcination temperature is 700°C, and the pre-fire time is 3h; the high-temperature calcination temperature is 1050°C, and the calcination time is 2h. The specific saturation magnetization of the obtained sample was 67 emu / g.
Embodiment 3
[0038] Others are the same as Example 1, and the difference is that in step (1), the temperature of roasting the magnetic separation residue after washing is 950° C., the time is 0.5h, and the concentration of sulfuric acid that dissolves each species is 4mol / L, so The number of moles of sulfuric acid required is 1.1 times the number of moles of dissolved species. The precipitating agent in step (2) is ammonium oxalate, the amount of the precipitating agent added is 1.1 times of the total moles of the three metal salt ions, the temperature of the reaction solution is 40°C, and the reaction time is 0.5h. The gas used to maintain the inert atmosphere in step (3) is argon, the pre-firing temperature is 850°C, the pre-firing time is 1h, and the sintering temperature is 950°C for 3h. The specific saturation magnetization of the obtained sample is 58emu / g.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Specific saturation magnetization | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Specific saturation magnetization | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Specific saturation magnetization | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com