Controlling media particle size in slurried dense media separations
A particle size and density separation technology, applied in wet separation, solid separation, electrostatic effect separation, etc., to improve separation performance and reduce foam
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0077] Example 1: Effect of Media Particle Size on Plastic Surface Contamination
[0078] Magnetite with a particle size distribution in the range of 0.1 to 100 microns was placed in water and stirred. The slurry can settle for a few minutes and make-up fluid injected into the second container. This slurry is allowed to settle for a few minutes and then make-up fluid is injected into a third container. Each container holds a portion of coarse, intermediate, or fine medium size.
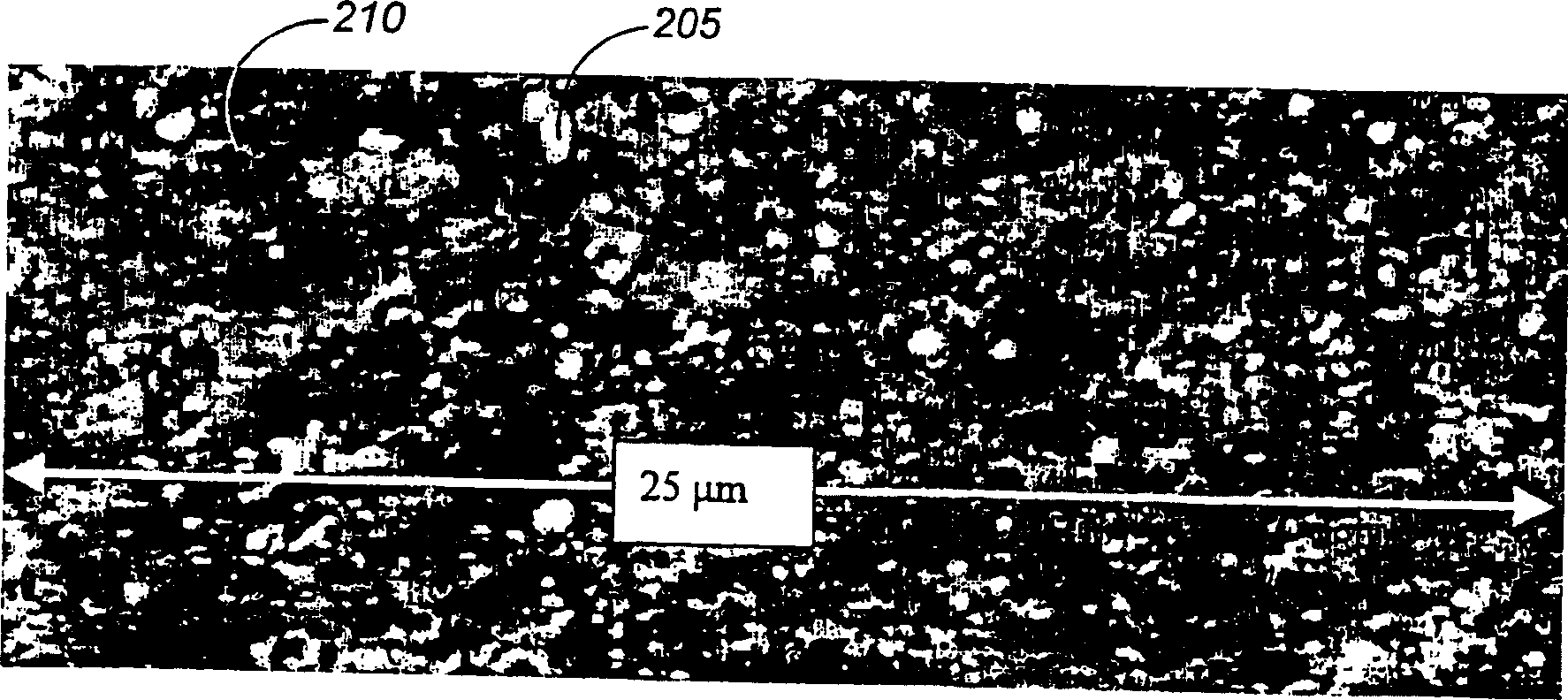
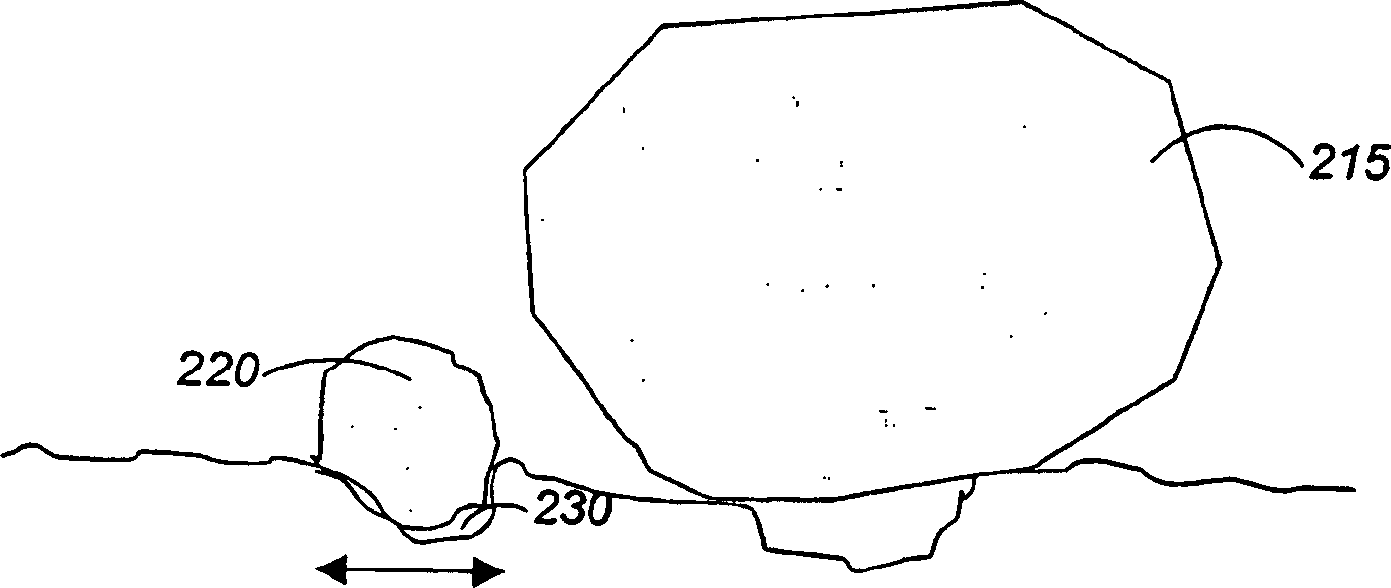
[0079] About 10 grams of polypropylene pellets were stirred in each of the three slurries for about 1 minute. The pellets are then removed, rinsed and oven dried. The pellets stirred with the fine particle slurry appeared significantly darker than the pellets stirred with the coarse or intermediate magnetite slurries.
[0080] The charge of the dried pellets was then measured after spinning in a polycarbonate container. Table 2 shows the charge per mass unit on spheroids of fine and coarse partic...
example 2
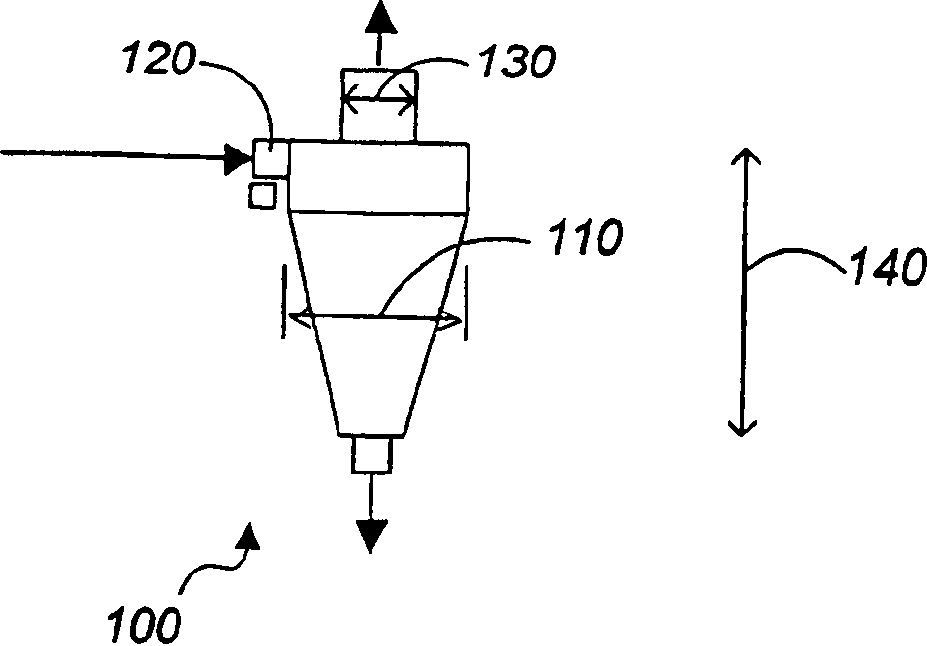
[0083] A 15-inch Model D15B hydrocyclone manufactured by Krebs Engineers, Tucson, Arizona, with a 6-inch vortex finder, an 11-square-inch inlet, and a 4.5-inch top supplies magnetite at about 7 psi and removes Particles above about 30 microns. Alternatively, by repeating the process or decreasing the separation cut point by increasing the feed rate, or changing another cyclone separation parameter, additional particles up to about 25 microns can be removed, yielding media of very close size 5-25 microns, as shown in Table 1 Show. The hydrocyclones were positioned at approximately 22 degrees from horizontal. The hydrocyclone distributes roughly half of the ~30 micron particles to the underflow, with a higher percentage of coarser particles to the underflow. About 30-40% of the total fluid is sent to the underflow, which will not effectively classify only 30-40% of the particles recovered to the underflow because it comes with the fluid and is not swirled. Streamer function. ...
example 3
[0085]Another example of selecting a media size is as follows. A model D4B-12 hydrocyclone manufactured by Krebs Engineers, with a 1.2 square inch inlet area, a 1.25 inch vortex finder, and a feed pressure of about 30 psi, expects about half of the 10 micron particle magnetite The slurry is recycled to the underflow. With a top diameter of 0.625, this cyclone sends about 10% of the total fluid to the underflow. As such, it concentrates particles coarser than 10 microns and may have very little ability to capture particles of 5 microns or smaller in the underflow. About 10% of all smaller particles are diverted to the underflow as they travel with the fluid reaching the underflow. In each pass, between 50 and 90% of all particles below 10 microns are removed from the media reaching the underflow. After passing through the cyclone 1-5 times, the magnetite recovered to the underflow will basically have no particles of 5 microns and below.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com