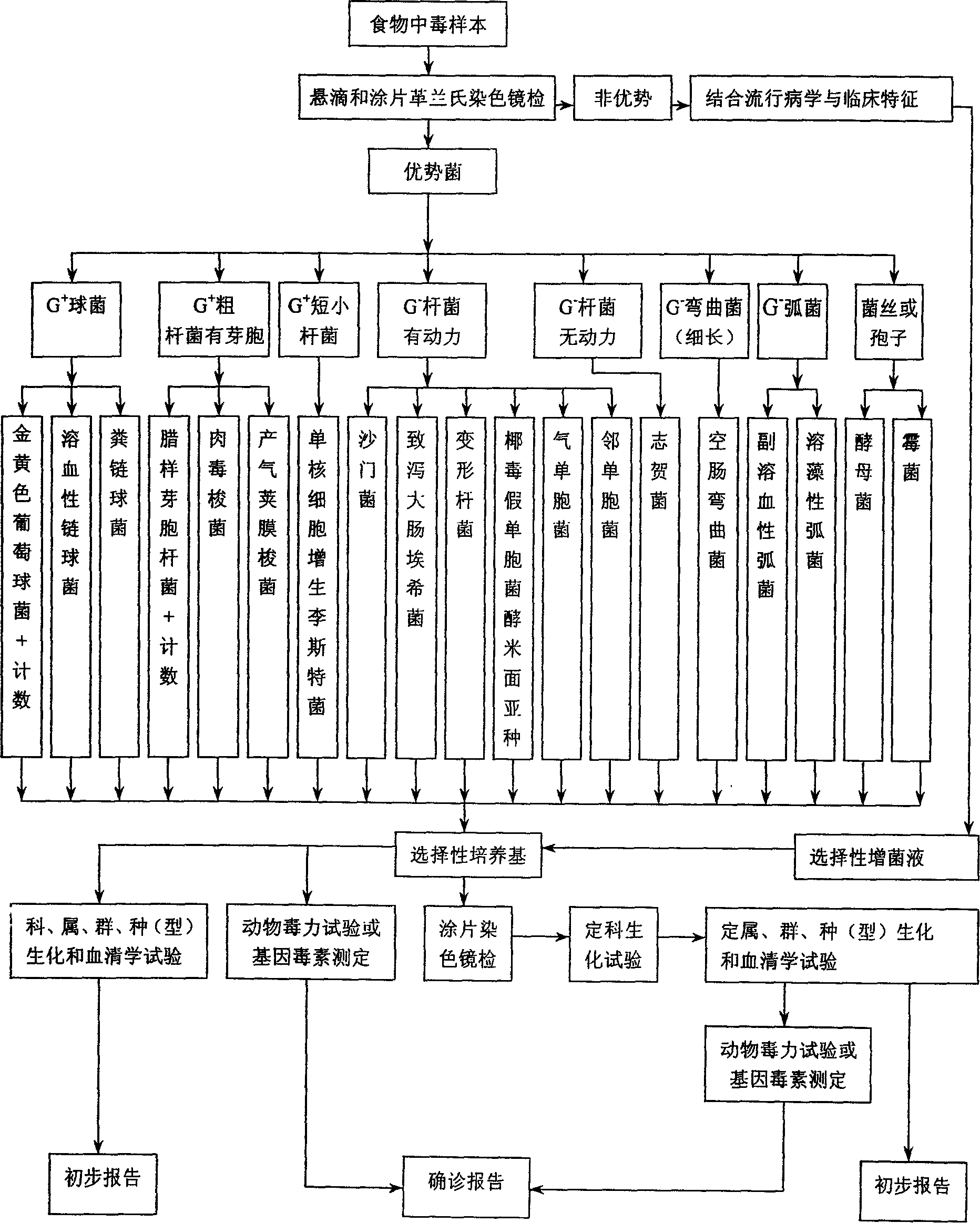
Dyeing indicating method used for detecting food poisoning pathogenic bacteria
A pathogenic bacteria detection and toxin technology, applied in the field of pathogenic bacteria detection, can solve the problems of long detection time, high blindness, low detection rate, etc., achieve the improvement of detection efficiency and accuracy, increase the positive detection rate, and shorten the detection time Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] Example 1: Detection results of 45 microbial food poisoning pathogens. Of the 45 cases of microbial food poisoning, 40 cases were detected with pathogenic bacteria, and the detection rate was 88.89%. Among them, 38 cases were bacterial (2 cases were caused by mixed infection of Staphylococcus aureus and Bacillus cereus), and 2 cases were fungal. A total of 42 strains and 13 strains were isolated from 40 cases of microbial food poisoning detected, including 40 bacterial strains, 7 strains of Bacillus cereus emetic; 6 strains of Staphylococcus aureus and 6 strains of Vibrio parahaemolyticus; 4 strains each of Bacillus cereus and Escherichia coli (ETEC); 3 strains each of Vibrio alginolyticus and Escherichia coli; 2 strains each of common, Proteus mirabilis, and Salmonella typhimurium; Escherichia coli 1 plant. Two fungal strains were Aspergillus versicolor and Penicillium arcuatus, which could not be detected by conventional methods.
Embodiment 2
[0021] Example 2: Detection results of dominant bacteria and non-dominant bacteria in 45 cases of microbial food poisoning. 45 cases of microbial food poisoning samples were directly stained with smears, 37 cases of dominant bacteria and 8 cases of non-dominant bacteria were found under microscope. 37 dominant bacteria were cultivated, and the pathogenic bacteria were identified by family, genus, group and species (type), and the detection rate was 100%. 8 cases of non-dominant bacteria were selectively enriched and cultured, and the pathogenic bacteria were identified by family, genus, group, species (type), and 3 cases of pathogenic bacteria were detected, with a detection rate of 37.50%.
Embodiment 3
[0022] Example 3: Relationship between 13 kinds of pathogenic bacteria and infection of food poisoning samples. 40 cases of microbial food poisoning were detected with pathogenic bacteria, and a total of 761 samples were collected, including 122 vomitus, 180 feces, 388 suspicious food residues, 47 tableware, 2 cutting boards, 2 kitchen knives, 14 rags, 6 copies of cook manure. As a result, there were 122 vomitus. 102 pathogenic bacteria were detected, accounting for 83.61%, among which the detection rates of Staphylococcus aureus and Bacillus cereus were 100% and 93.02%, respectively. Of 180 feces, 153 pathogenic bacteria were detected, accounting for 85.00%. Among them, the detection rates of Vibrio paralyticus, Bacillus cereus, Escherichia coli EIEC and Penicillium arcuatus were all 100%; Escherichia coli ETEC , Proteus mirabilis, Bacillus cereus, Escherichia coli EPEC, and Salmonella typhimurium were 93.10%, 88.89%, 83.33%, 82.14%, and 80.00%, respectively. Thirteen kind...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com