Formulation of albumin-free erythropoietin
An erythropoietin and preparation technology, which can be applied to peptide/protein components, medical preparations containing active ingredients, and extracellular fluid diseases, etc., can solve the problems of high manufacturing cost, increased physical and chemical problems and danger
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
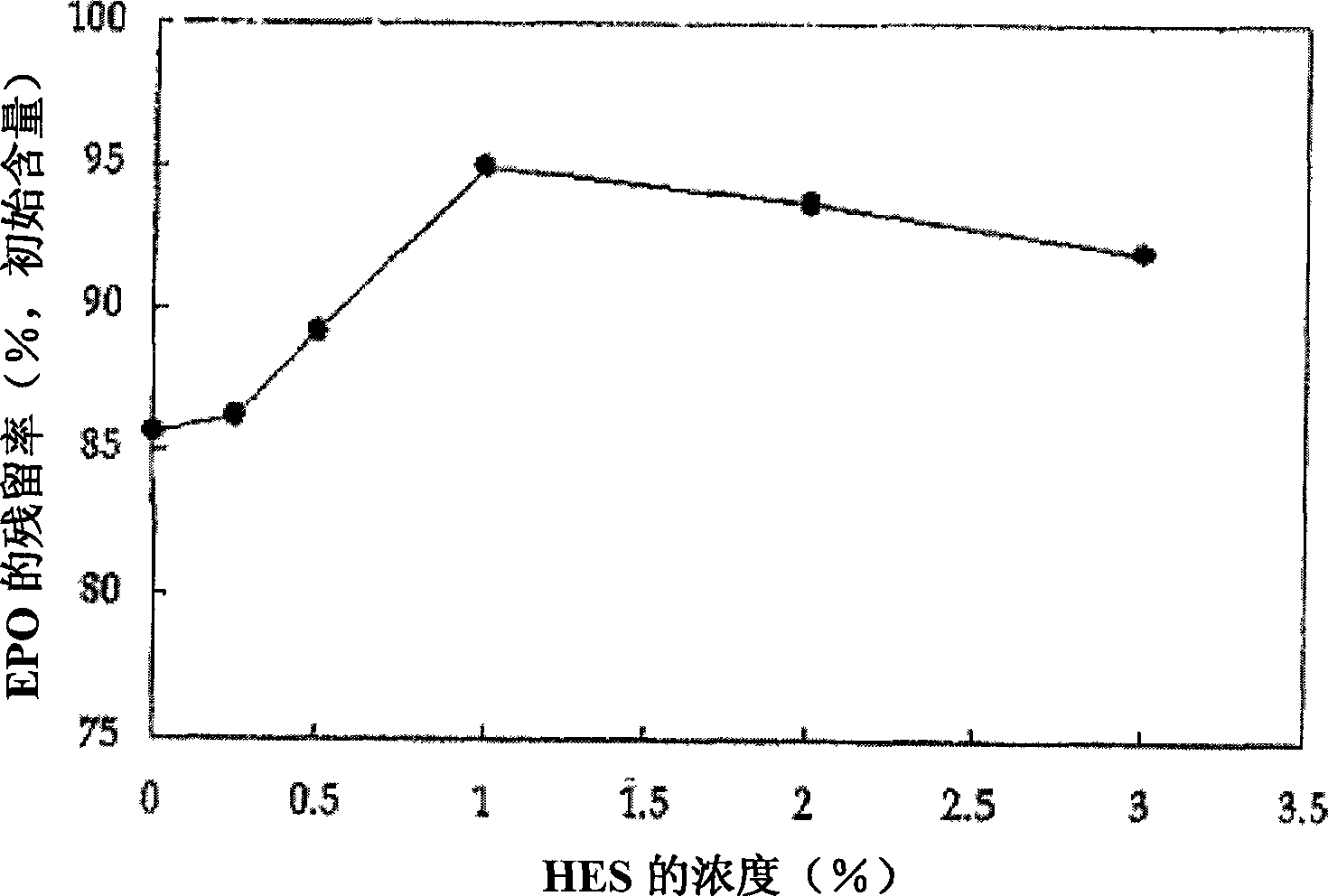
[0059] Example 1: Effects of various concentrations of HFS on the stability of FPO
[0060] To prepare an EPO solution containing 0-3% (0-30g / L) HES without adding specific amino acids, dissolve 0-3% HES in 0.9L water for injection and stir at 70±5°C for more than 20 minutes, Then cool to 35°C. To each cooled solution was added sodium chloride and polysorbate to dissolve them in solution. Additional water for injection was added to each solution to a final volume of 1 L. After stirring, each solution was individually adjusted to pH 6.9. Then, each solution was filtered through a 0.22-mm membrane and supplemented with a predetermined amount of EPO. The resulting solution was filled into Type I glass vials, thereby preparing stable samples. The dosage of EPO ranges from 2,000 to 10,000 IU.
[0061] The prepared stable samples were stored at 40°C for one week, and the residual rate of EPO was determined by RP-HPLC.
[0062] A suitable concentration of HES was found to have ...
Embodiment 2
[0066] Example 2: Effect of Isotonicity of Solutions Containing HES and Amino Acids on EPO Stability
[0067] According to the present invention, pure water is used to prepare injectable EPO solution formulations. In order to make these solution preparations isotonic, 0.5 to 10 g / L of sodium chloride, mannitol, sorbitol or other corresponding substances are added to each solution. These solution formulations were adjusted to pH 6.9 as in Example 1. In order to evaluate the effect of the isotonicity of the preparation on the stability of EPO, the EPO solution will be prepared according to the same method as in Example 1 below using a predetermined amount of HES and various amounts of sodium chloride, as shown in Table 2. The osmolality of each prepared sample was measured using a freezing point osmometer (Gonotec GmbH). These samples were stored at 40°C for two weeks, and then the residual EPO was determined by RP-HPLC. The results are shown in Table 2 below.
[0068] ...
Embodiment 3
[0071] Example 3: EPO Stability Evaluation in Solutions Containing HES and Glutamine
[0072] In order to study the stability of EPO in a solution containing HES and glutamic acid as stabilizers, an EPO solution was prepared in the same manner as in Example 1 using 1% HES and 8 mg / mL glutamine. The EPO solution was stored in an incubator at 40°C / RH75% for 2 weeks and in another incubator at 25°C / RH60% for 6 months. Then, the residual rate of EPO in the EPO solution was measured by the RP-HPLC method (Waters Company). The results are shown in Table 3 below.
[0073] table 3
[0074] Hydroxyethyl starch (HES)
[0075]As a result, when the compositions containing HES and glutamine were stored under stringent conditions at 40°C and 25°C, the residual rates of EPO were 95% and 91%, respectively, compared to the initial content of EPO.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com