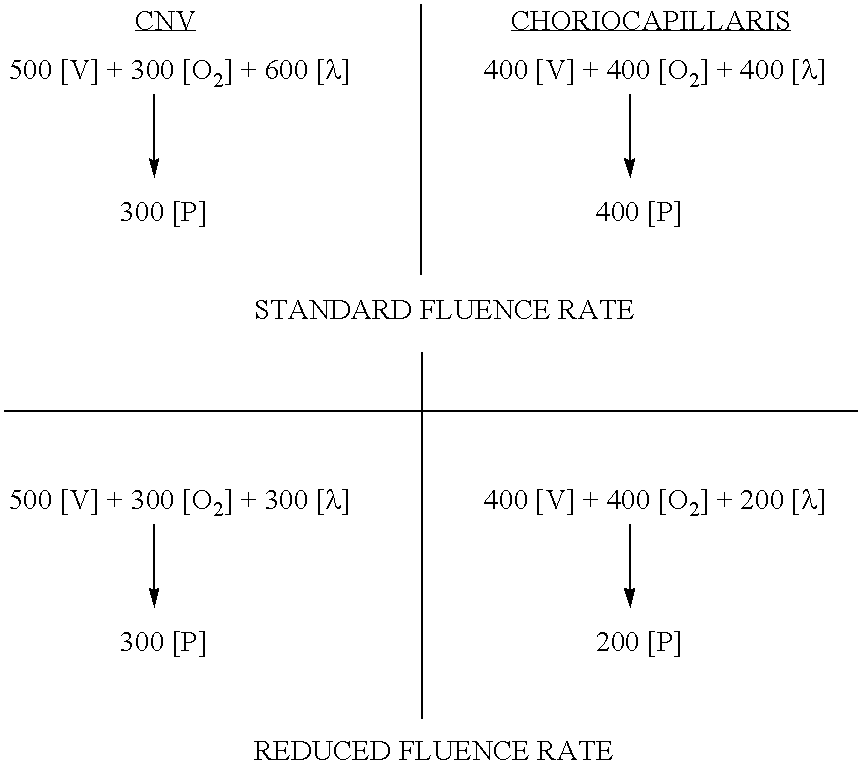Reduced fluence rate PDT
a fluence rate and photodynamic therapy technology, applied in the field of reducing the fluence rate photodynamic therapy, can solve the problems of inefficient irradiation beyond the necessary amount of ps to activate the photosensitizer (pdt), reducing the fluence rate, and reducing the amount of light.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Materials and Methods
[0081] Subjects will receive either VISUDYNE™ (verteporfin for injection) delivered as a two-step process: 1) a 10-minute intravenous infusion of VISUDYNE™ (6 mg / m2) and 2) light application 15 minutes after the start of the infusion using a light dose of 50 J / cm2 (600 mW / cm2) or 25 J / cm2 (300 mW / cm2).
[0082] Retreatment may be administered at 3-month intervals (±2 weeks) through Month 9, if evidence of CNV leakage is detected by fluorescein angiography. Subjects who have a severe vision decrease of vision of ≧20 letters within 7 days of treatment should not be retreated unless their vision completely returns to pretreatment levels.
[0083] Each vial of VISUDYNE™ will be reconstituted with 7 mL of Sterile Water for Injection to provide 7.5 mL containing a final concentration of 2 mg / mL. Reconstituted VISUDYNE™ is protected from light and used within 4 hours. Reconstituted VISUDYNE™ is an opaque dark green solution.
[0084] The volume of reconstituted VISUDYNE™ re...
example 2
Reduced Fluence Protocol
[0088] Subjects with minimally classic subfoveal CNV (a subtype of CNV) secondary to AMD will be treated with each of the protocols as shown below. [0089] 1. VISUDYNE therapy using a reduced light fluence rate of 300 mW / cm2, [0090] 2. VISUDYNE therapy using the standard light fluence rate of 600 mW / cm2,
[0091] At Week 1, fluorescein and ICG angiographic assessments will be evaluated compared to baseline for the first 10 evaluable subjects in each treatment group. Fluorescein angiography will be used to determine the area of CNV leakage. The Week 1 comparison will be conducted to look for a non-effect of the reduced light fluence rate group. The number of subjects with classic CNV leakage in the reduced light fluence (300 mW / cm2) group and the standard light fluence (600 mW / cm2) group will be compared at 1 week.
[0092] Fluorescein and ICG angiographic assessments will be performed at Week 6.
[0093] All patients will continue follow-up visits until the last su...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| wavelengths | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| wavelengths | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentrations | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com