Focused beam spectroscopic ellipsometry method and system
a spectroscopic ellipsometry and focused beam technology, applied in the direction of optical radiation measurement, instruments, polarisation-affecting properties, etc., can solve the problems of undetectable effects, undetectable effects, and unsuitable use of transmissive optics, so as to eliminate chromatic aberration in the focused beam, avoid aberration and other undesirable effects, and reduce off-axis aberration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0033] Throughout the specification, including in the claims, the phrase “incidence angle” of radiation at a surface denotes the angle between the normal to the surface and the propagation direction of the radiation. Thus, radiation with normal incidence at a sample surface has an incidence angle of zero degrees, and radiation with grazing incidence at such surface has an incidence angle substantially equal to 90°. Throughout the specification, including in the claims, the phrase “high incidence angle” denotes an incidence angle greater than 30°. Throughout the specification, including in the claims, the phrase “broadband radiation” denotes radiation whose frequency-amplitude spectrum includes two or more different frequency components. For example, broadband radiation may comprise a plurality of frequency components in the range from 230 nm to 850 nm, or a plurality of frequency components in the range from 400 nm to 700 nm.
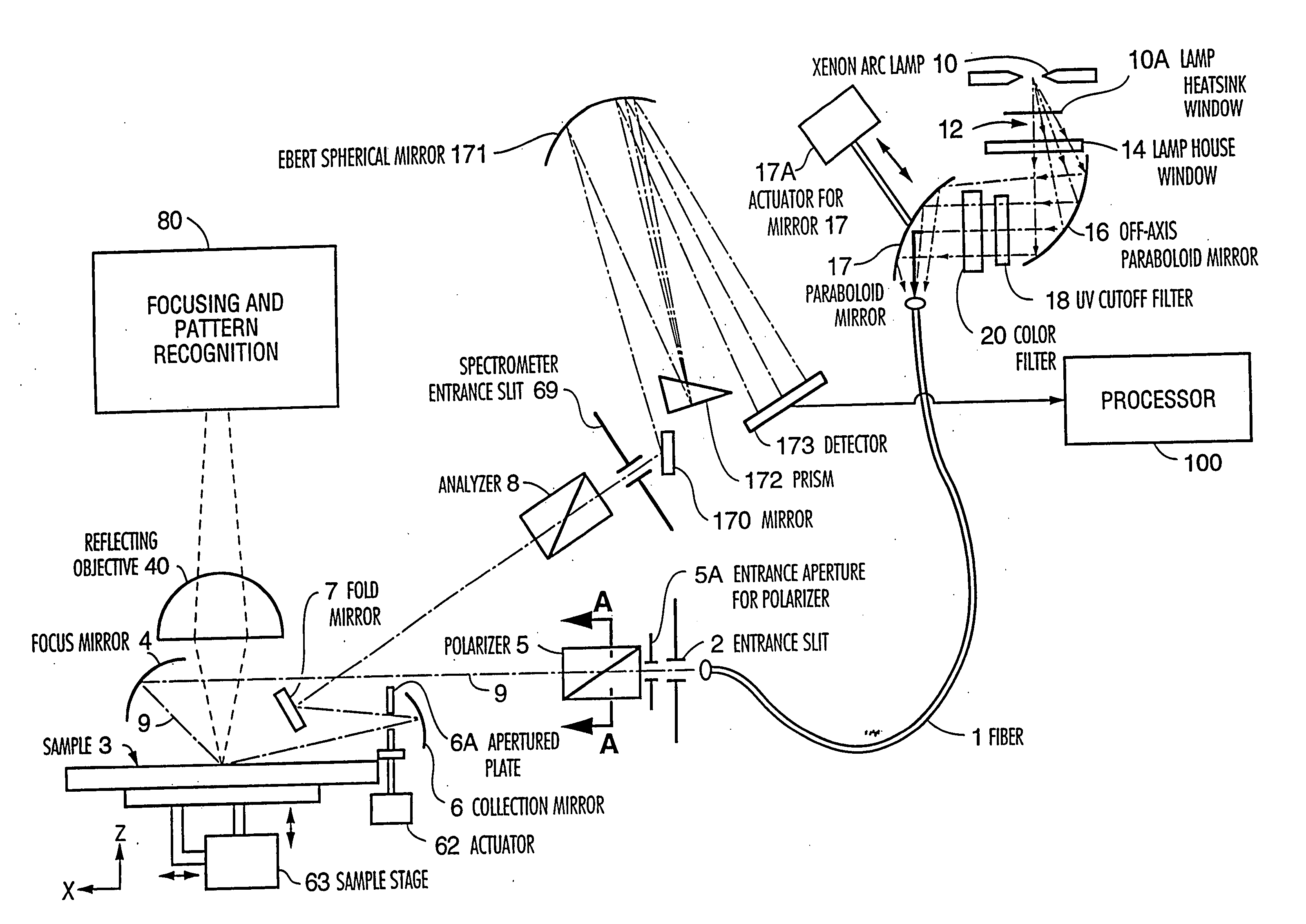
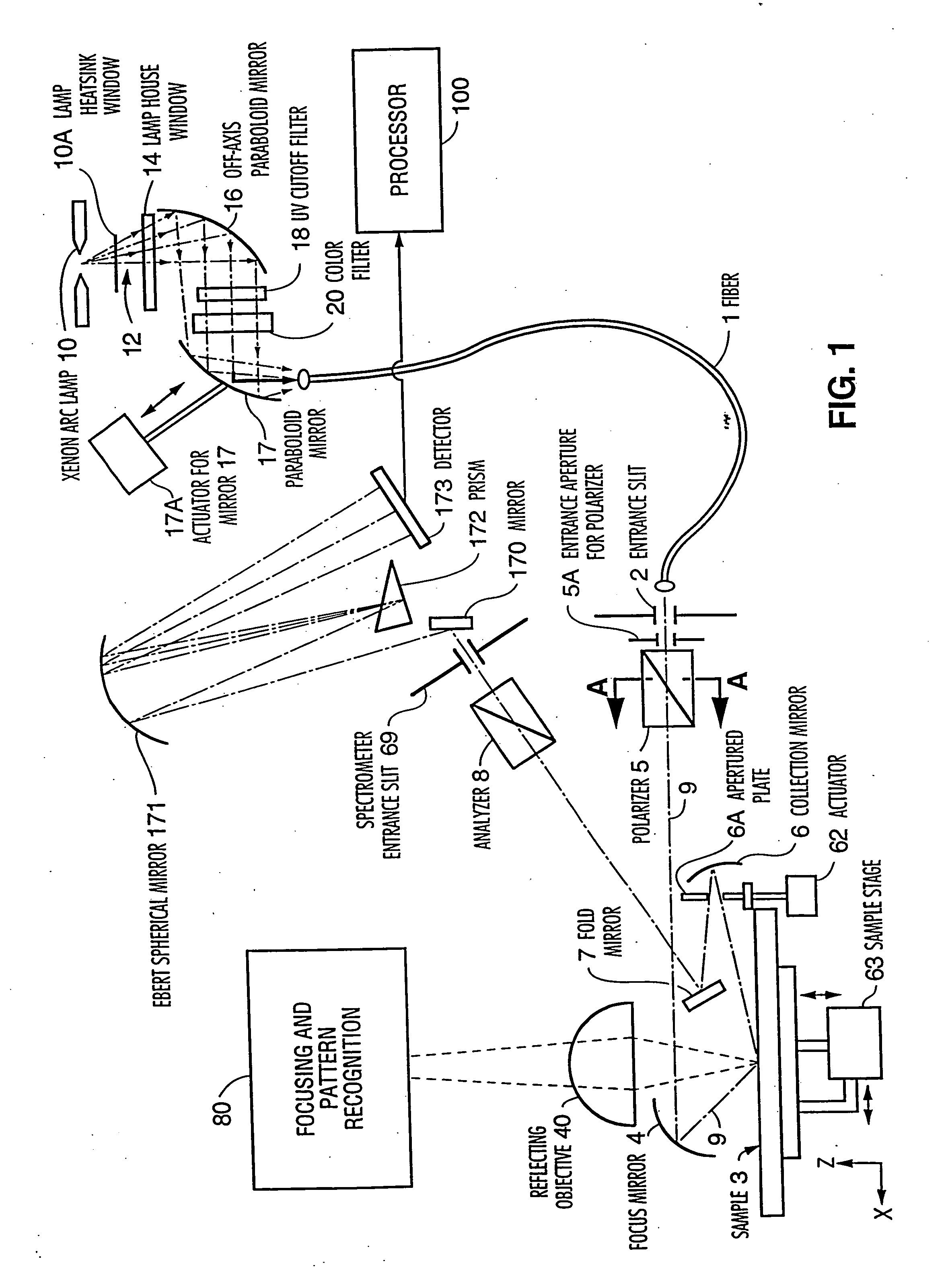
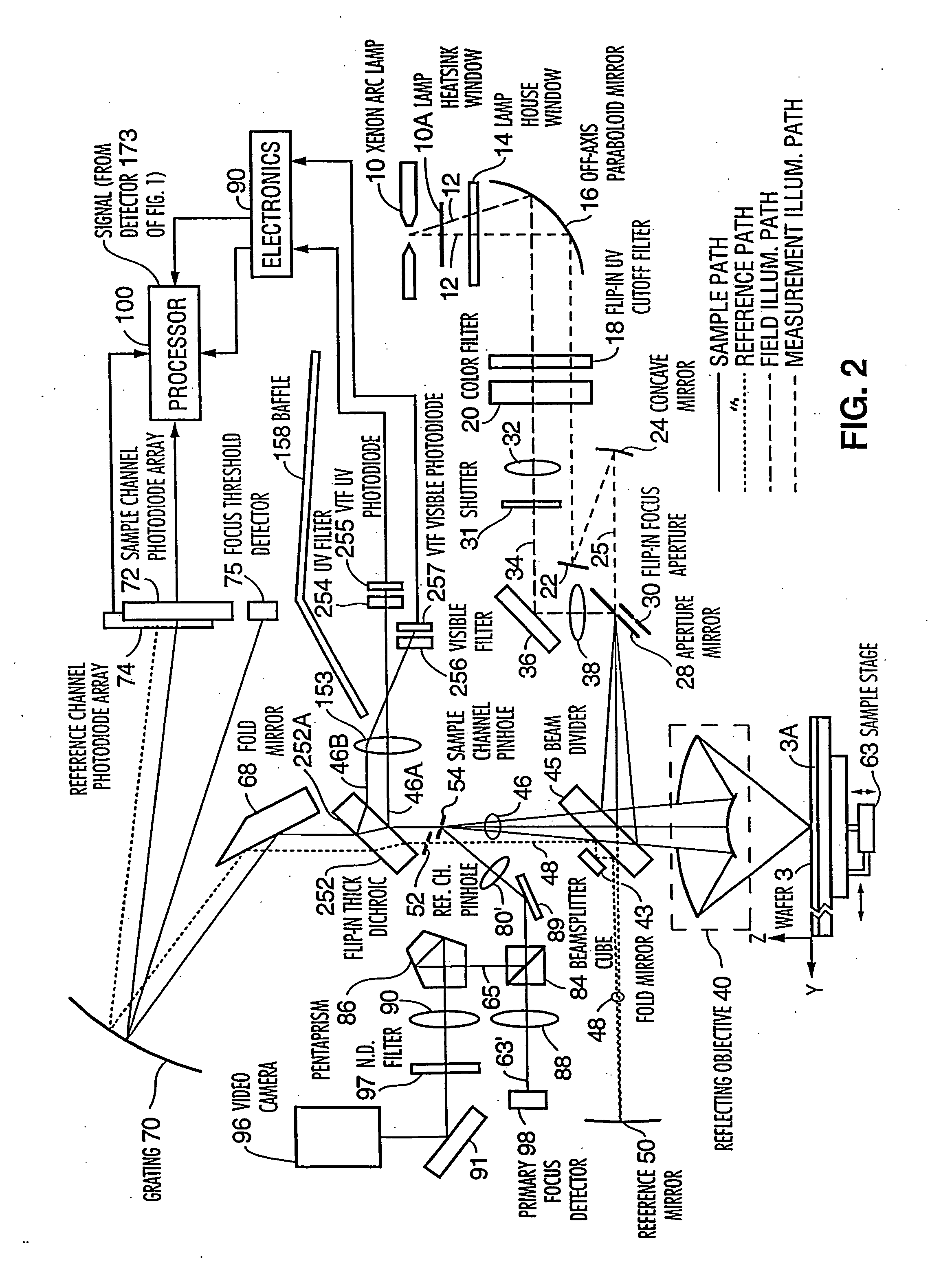
[0034] A preferred embodiment of the focused beam spectro...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com