Method for the preparation of phytosterols from tall oil pitch
a phytosterol and oil pitch technology, applied in the field of phytosterol preparation from tall oil pitch, can solve the problems of cumbersome procedures, complex solvent recovery systems, and complex adjustment of precise solvent compositions to maintain optimal operation for each processing stag
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
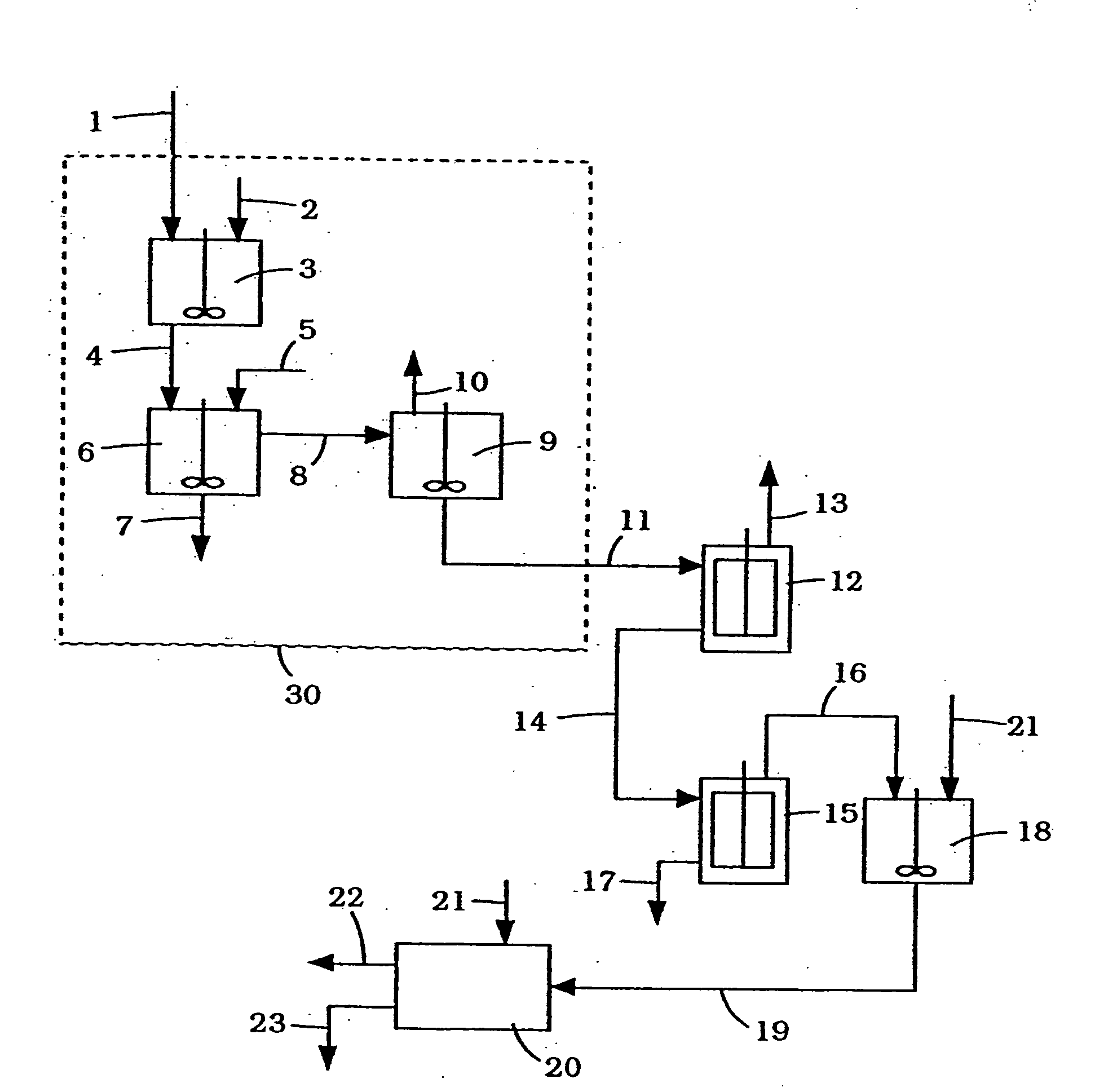
[0033] 9,598 kg of tall oil pitch were saponified with 1,325 kg NaOH at 12.0% concentration solution, at 146 deg. C. for 120 minutes, under vigorous mixing conditions. The weight ratio of sodium hydroxide (dry basis) to tall oil pitch was 0.138. The reacted mixture was then neutralized with 1,188 kg of 85% concentration phosphoric acid. After continued heating at 146 deg. C. and gentle stirring for 210 minutes, 6,600 kg of water was drawn off from the bottom of the reactor. The pH of the reactor bottom water was 6.4. The partially dewatered mixture containing about 37.5% water was transferred to a second reactor for vacuum stripping of residual moisture. The vacuum reactor was operated at 149 deg. C. at an average pressure of 300 mm Hg. The reaction was completed in 300 minutes. The dried, saponified and neutralized tall oil pitch had a moisture content of 0.4% by wt.
[0034] Table 1 summarizes the percentage of phytosterols present in free form at various stages in the procedure.
T...
example 2
[0036] A sample of tall oil pitch was saponified, neutralized and dewatered by the method described in Example 1. The modified tall oil pitch was found to have a composition of 141 mg free phytosterols / g and 164 mg total phytosterols / g. The modified tall oil pitch was preheated to about 100 deg. C. for feeding into a series of 0.1 square meter wiped evaporators (manufactured by UIC GmbH, Germany). The distillate from each evaporation stage was recovered for the analysis of free phytosterols by gas-liquid chromatography (GLC).
[0037] Table 2 summarizes free phytosterol production results for four tests runs (A1, A2, A3 and A4) under differing conditions of feed rate, temperature and pressure.
TABLE 2Test NumberA1A2A3A4Stage 1 EvaporationTall oil pitch feed, kg / hr15.515.611.515.6Temperature, deg. C.225225225220Pressure, mbar5.946.536.452.08Distillate yield, % by wt.1.90Free phytosterols in Stage 118181818distillate, mg / gStage 2 EvaporationFeed from above Stage 1 residue,15.615.611.51...
example 3
[0038] Samples of Stage 2 distillate from Example 2 were crystallized in laboratory jar tests by heating the distillate-solvent mixture to 65 deg. C. The mixtures were cooled to 30 to 35 deg. C. to yield a slurry containing the desired phytosterol crystals. The weight ratio of organic solvent to distillate was 15:1.0. The cooled slurry was then filtered through 50 micrometer filter paper, under vacuum. The filtered cake was then washed twice with solvent in an amount equal to 1.5 times the weight of distillate sample used for crystallization. The wash solvent had the same composition as that used for crystallization. Washing of the cake was conducted at ambient temperature. The washed cake was then dried at 90 deg. C. for 60 minutes prior to weighing and GLC analysis.
[0039] Table 3 comparatively summarizes crystal purities and crystal yields for test runs A1, A2, A3 and A4, firstly, utilizing methanol as the solvent and, secondly, utilizing a mixture of methanol and 2-propanol as t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com