Retrons for gene targeting
a technology of retrons and gene targets, applied in foreign genetic material cells, plant cells, enzymes, etc., can solve the problems of loss of wild-type genetic information at this locus, inability to accurately express transgenes which integrate at random sites in the genome, and inability to accurately analyze the effect of this transgen
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Genetic Assay and Test Alleles
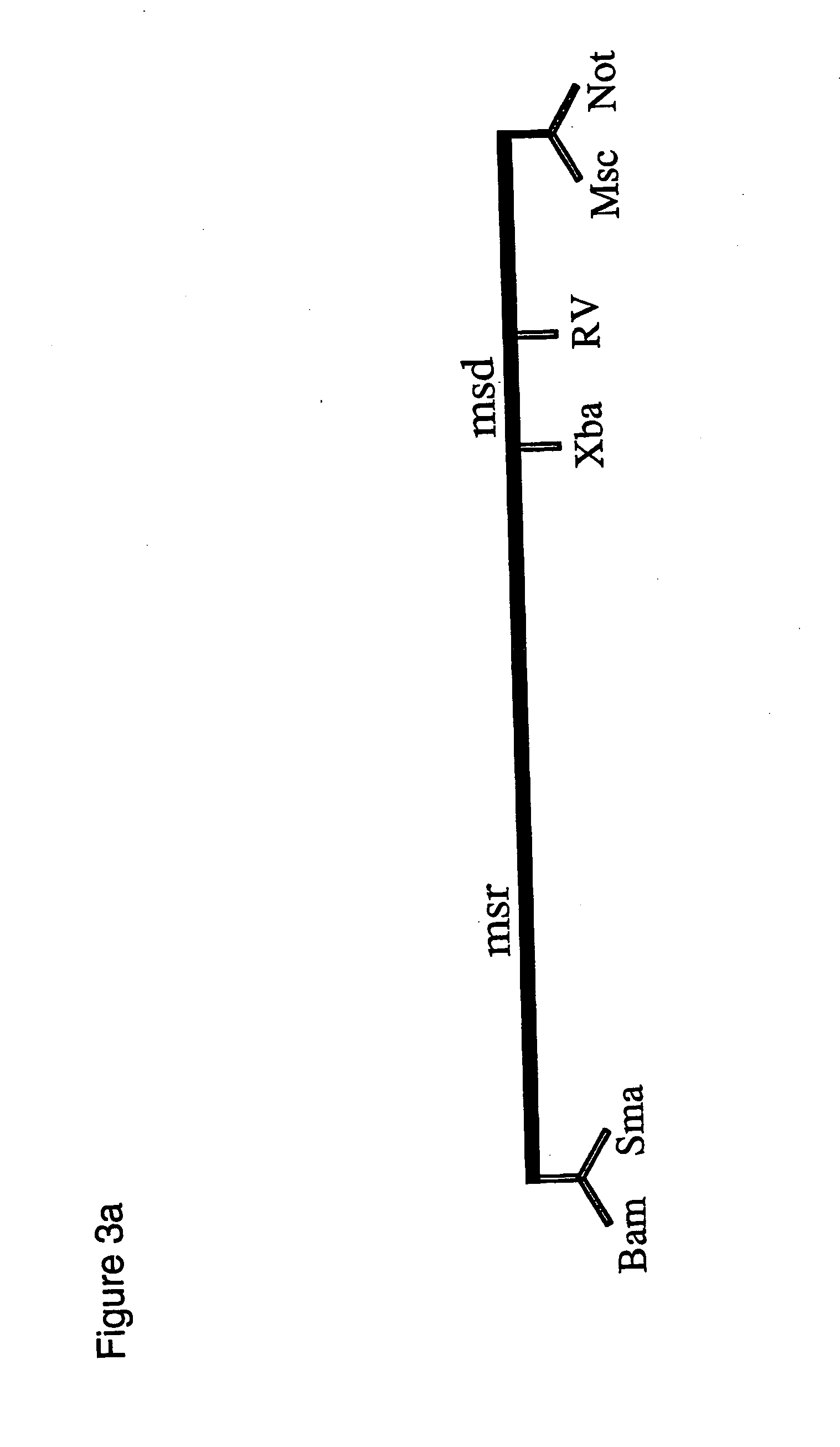
[0215] Several variations of gene targeting cassettes were developed and tested to demonstrate the potential of using reverse transcription to generate gene targeting substrates in vivo to facilitate genetic alteration of a chromosomal locus in eukaryotic cells. In some examples components of retro-elements (i.e. genetic elements which can convert the entire or partial region of an RNA molecule encoded by the genetic elements into a cDNA through the action of a reverse transcriptase) were used. One example of such an element is referred to as the retron, different versions of which are encoded by various bacterial species and strains. One example of a retron is denoted Ec86 from the E. coli strain HB8 [1685]. Another example of a retron is denoted Ec107 from E. coli strain ECOR70 [1657]. Functional elements from both Ec86 and Ec107 have been cloned (i.e. pMW3, pMW5, pMW4, pMW9; described later). Application of components encoded by Ec86 to facilitate g...
example 2
Wild Type Retron
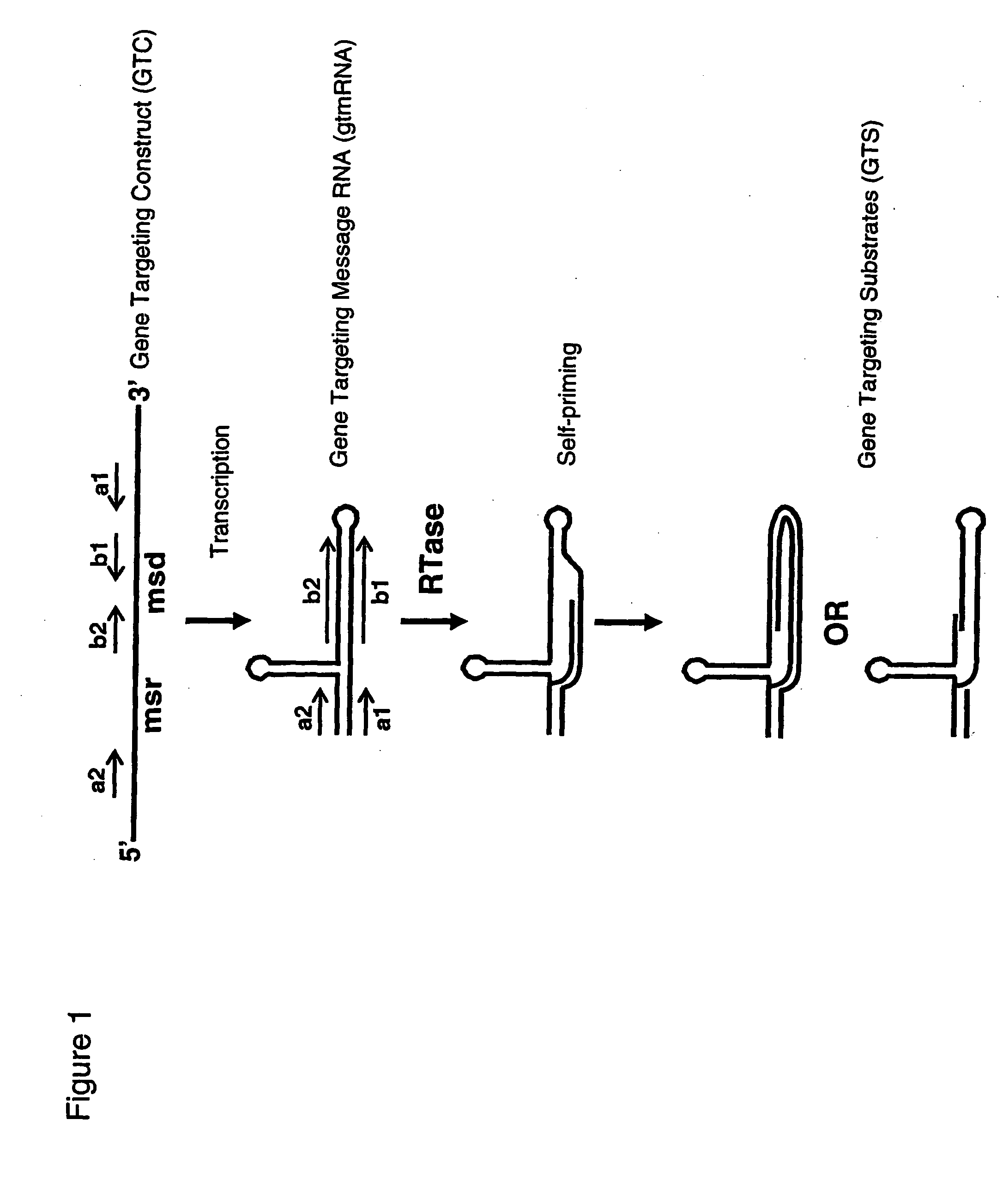
[0222]FIG. 1 summarises a current understanding of the reverse transcription process of at least some retron elements (as for example reviewed in [1648]). The principal components of a retron are the msr and msd elements flanked by the al and a2 inverted repeat sequences. In a RNA transcript of these elements, the a1 and a2 sequences base pair as do other inverted repeat sequences encoded within msr and msd, such as the b1 and b2 inverted repeat sequences within msd, to form stem and loop structures. The topology of stem and loop structures within the msr region of the folded RNA molecule enables recruitment of RTase. This protein-RNA interaction places the RTase in an appropriate context to be able to use the 2′-hydroxyl of a specific guanosine residue within the msr element to prime reverse transcription of the msd element. The reverse transcription proceeds through the msd sequence and terminates at a position at the boundary between the msd and msr sequences. In...
example 3
Modification of Reverse Transcriptase for Enhanced Functionality in Eukaryote Cells
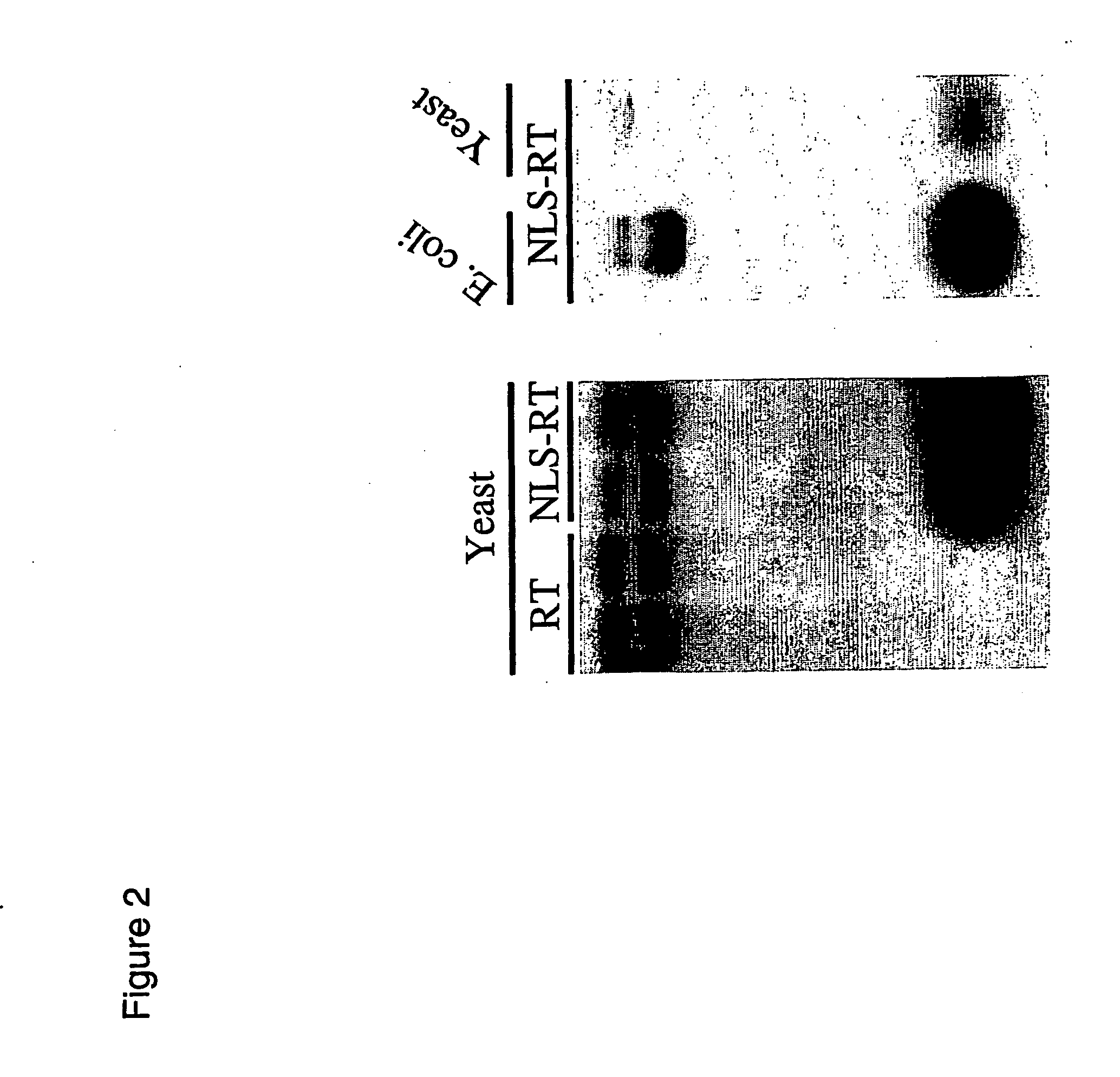
[0223] For effective gene targeting of chromosomal loci in eukaryote cells, the gene targeting substrate needs to be present in the nucleus. In some embodiments of the invention, reverse transcriptases are engineered to localize in the eukaryote host cell nucleus so that the enzyme can catalyse cDNA synthesis and production of the gene targeting substrate in the nucleus. One example to achieve this is to engineer the reverse transcriptase to encode a nuclear localization sequence. In one embodiment, the engineered reverse transcriptase may be of prokaryotic origin and thus may not possess an inherent nuclear localization sequence. One example is the Ec86 retron-derived reverse transcriptase which was engineered to encode the NLS from the SV40 T-antigen (i.e. pMW22). Another example is the Ec107 retron-derived reverse transcriptase which was engineered to encode the NLS from the SV40 T-antigen [109] (...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thermal melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| colony diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com