Single domain antibodies directed against tumor necrosis factor alpha and uses therefor
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Example of Camelidae Antibodies Against Human Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha
1) Immunization and Library Constructions
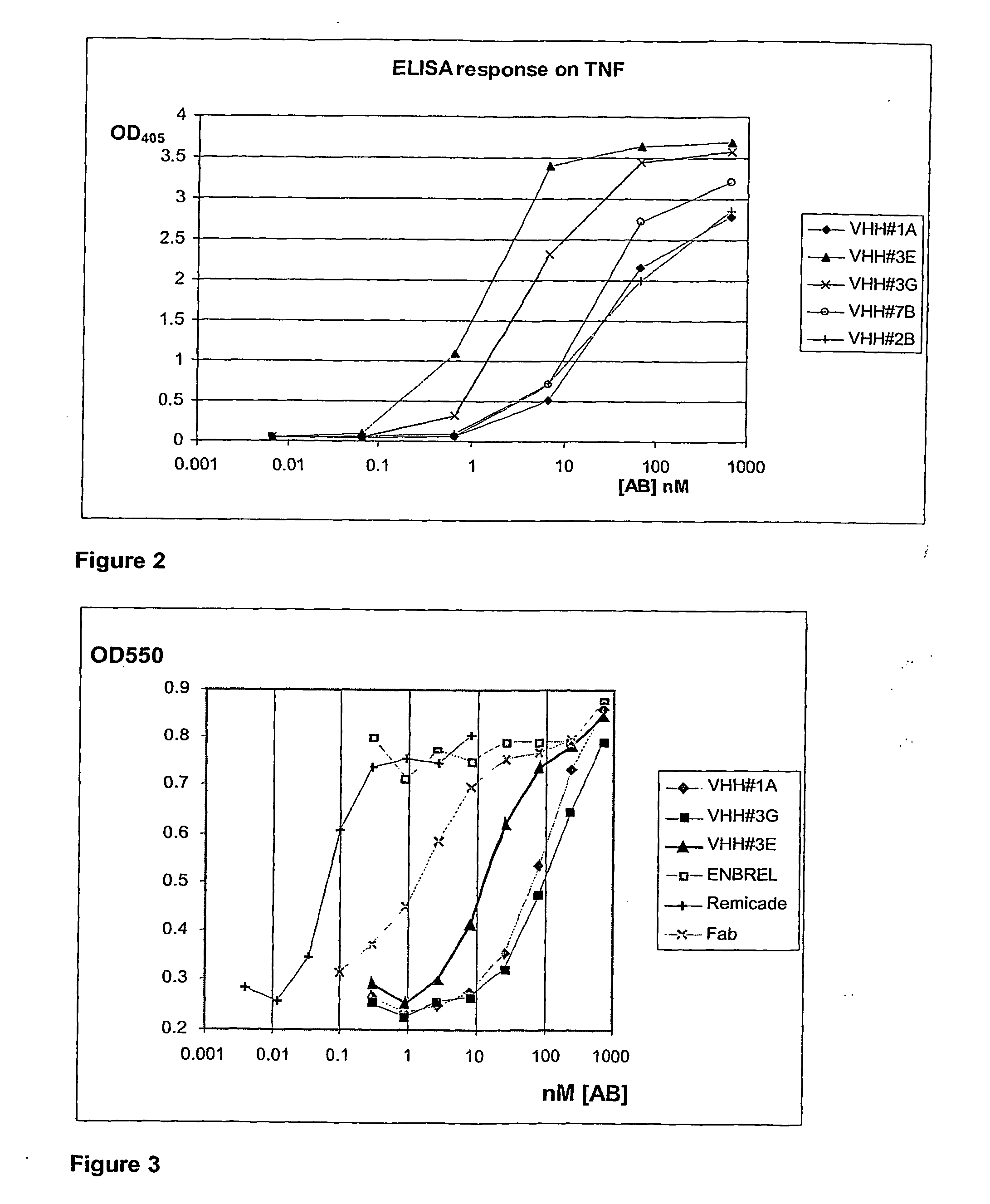
[0283] A llama (Llama glama) was immunized with human TNF-alpha. For immunization, the cytokine was formulated as an emulsion with an appropriate, animal-friendly adjuvant (Specoll, CEDI Diagnostics B.V.). The antigen cocktail was administered by double-spot injections intramuscularly in the neck. The animal received 6 injections of the emulsion, containing 100 μg of TNF-alpha at weekly intervals. At different time points during immunization, 10-ml blood samples were collected from the animal and sera were prepared. The induction of an antigen specific humoral immune response was verified using the serum samples in an ELISA experiment with TNF (data not shown). Five days after the last immunization, a blood sample of 150 ml was collected. From this sample, conventional and heavy-chain antibodies (HcAbs) were fractionated (Lauwereys et al. 1998) and used in an ELISA, w...
example 2
Humanization of VHH#12B and VHH#3E by Site Directed Mutagenesis
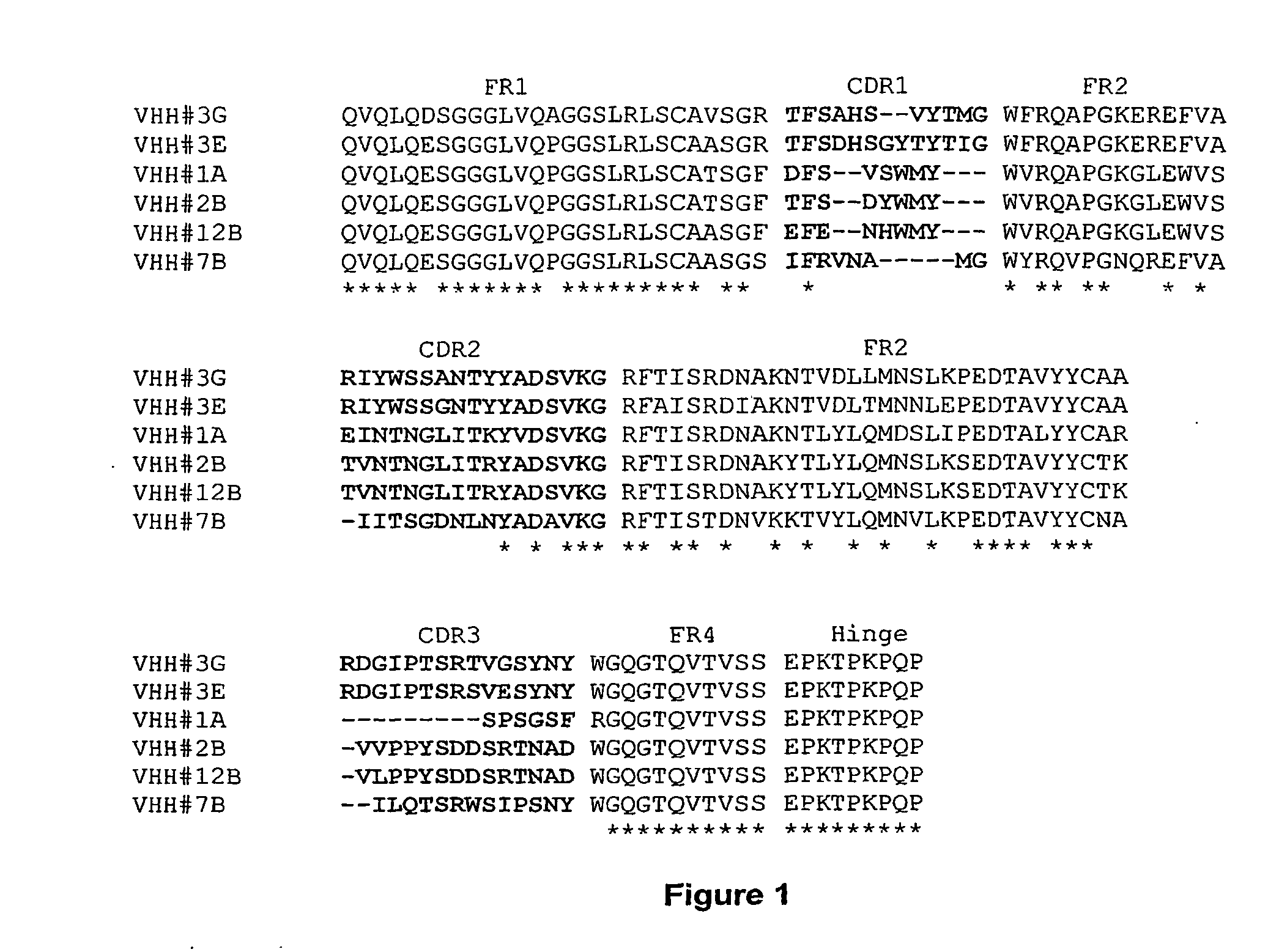
1) Homology Between VHH#3E / VHH#12B and Human Germline Heavy Chain V-Region DP-47
[0297] Alignment of VHH#12B and a human VH3 germline sequence (DP-47) revealed a high degree of homology: [0298] 4 AA changes in FR1 on position 1, 5, 28 and 30 [0299] 5 M changes in FR3 on position 74, 76, 83, 84 and 93 [0300] 1 AA change in FR4 on position 108
[0301] as represented in the following sequence alignment:
DP-47EVQLLESGGGLVQPGGSLRLSCAASGFTFS SYAMSWVRQAPGKGLEWVS AISGSGGSTYYVHH#12BQVQLQESGGGLVQPGGSLRLSCAASGFEFE NHWMYWVRQAPGKGLEWVS TVNTNGLITRYDP-47ADSVKG RFTISRDNSKNTLYLQMNSLRAEDTAVYYCAK------------- -----------VHH#12BADSVKG RFTISRDNAKYTLYLQMNSLKSEDTAVYYCTKVLPPYSDDSRTNAD WGQGTQVTVSS
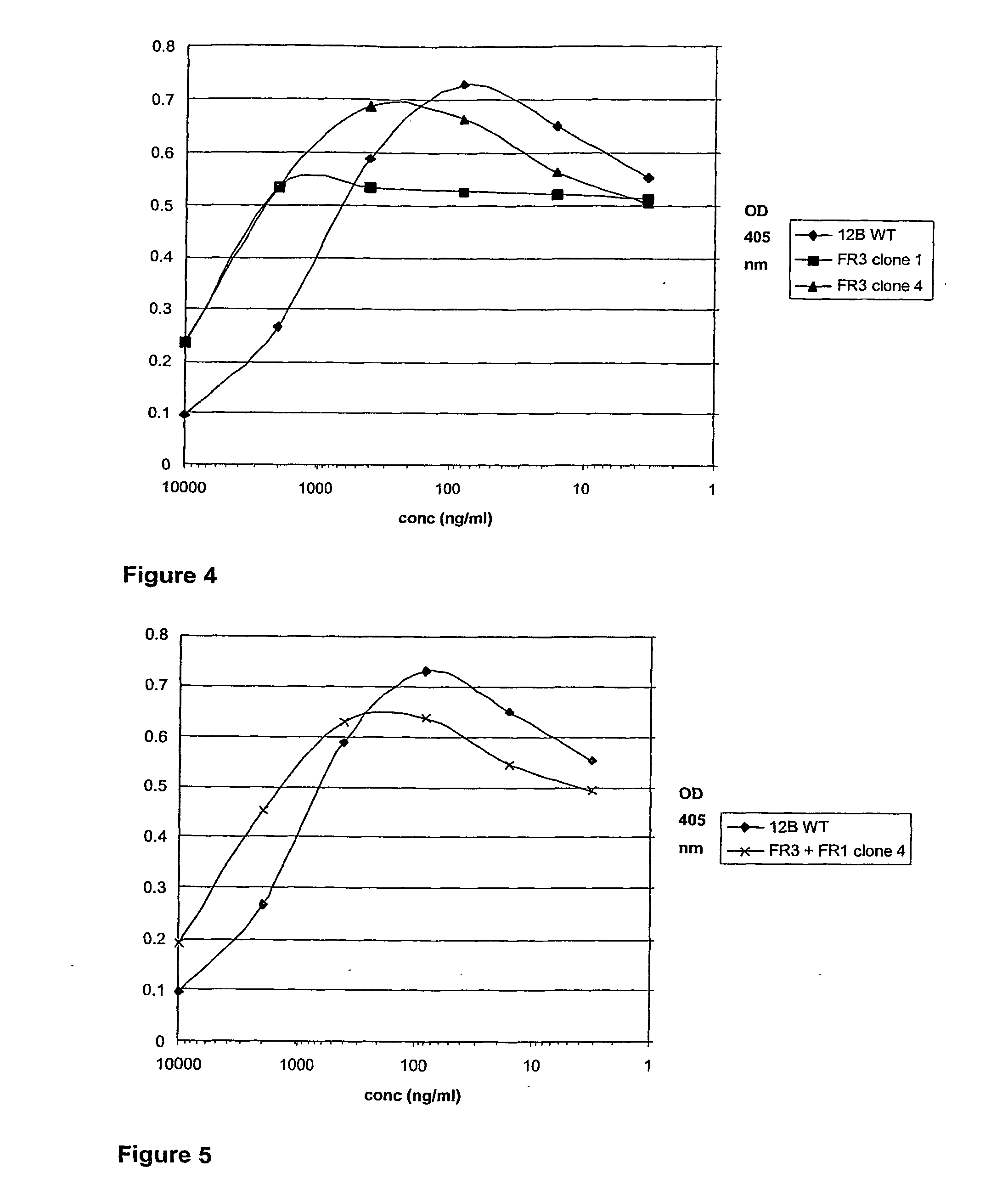
[0302] A specific inhibitor for the TNF-alpha cytokine, with high homology to the human germline gene DP47 was therefore an ideal candidate to further humanize and evaluate the influence of mutagenesis on inhibition capacity in ELISA.
[0303] Alignment...
example 3
Isolation of Antagonistic VHH Against Mouse TNF-Alpha
1) Selection of Anti-Mouse TNF-Alpha VHH
[0313] In order to perform efficacy studies in mouse models for IBD or Crohn's disease mouse TNF specific VHH were selected. Therefore a llama was immunized with mouse TNF-alpha as described in Example 1. RNA was extracted from PBL's sampled 4 and 10 days after the last immunization, as well as from a biopsy taken from a lymph node after day 4. Total RNA was converted in either random primed or oligo-dT primed cDNA and used as template for the amplification of the VHH encoding gene segments using Ig derived primers or a combination of oligo-dT primer and a single Ig primer (see example 1). With the Ig primers a library containing 8.5×107 clones was generated from the first PBL's, and a library with 7×106 clones for the second PBL sample and 5.8×108 clones for the lymph node. Using the combination of the oligo-dT primer and the Ig primer libraries from the first PBL sample were made contai...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com