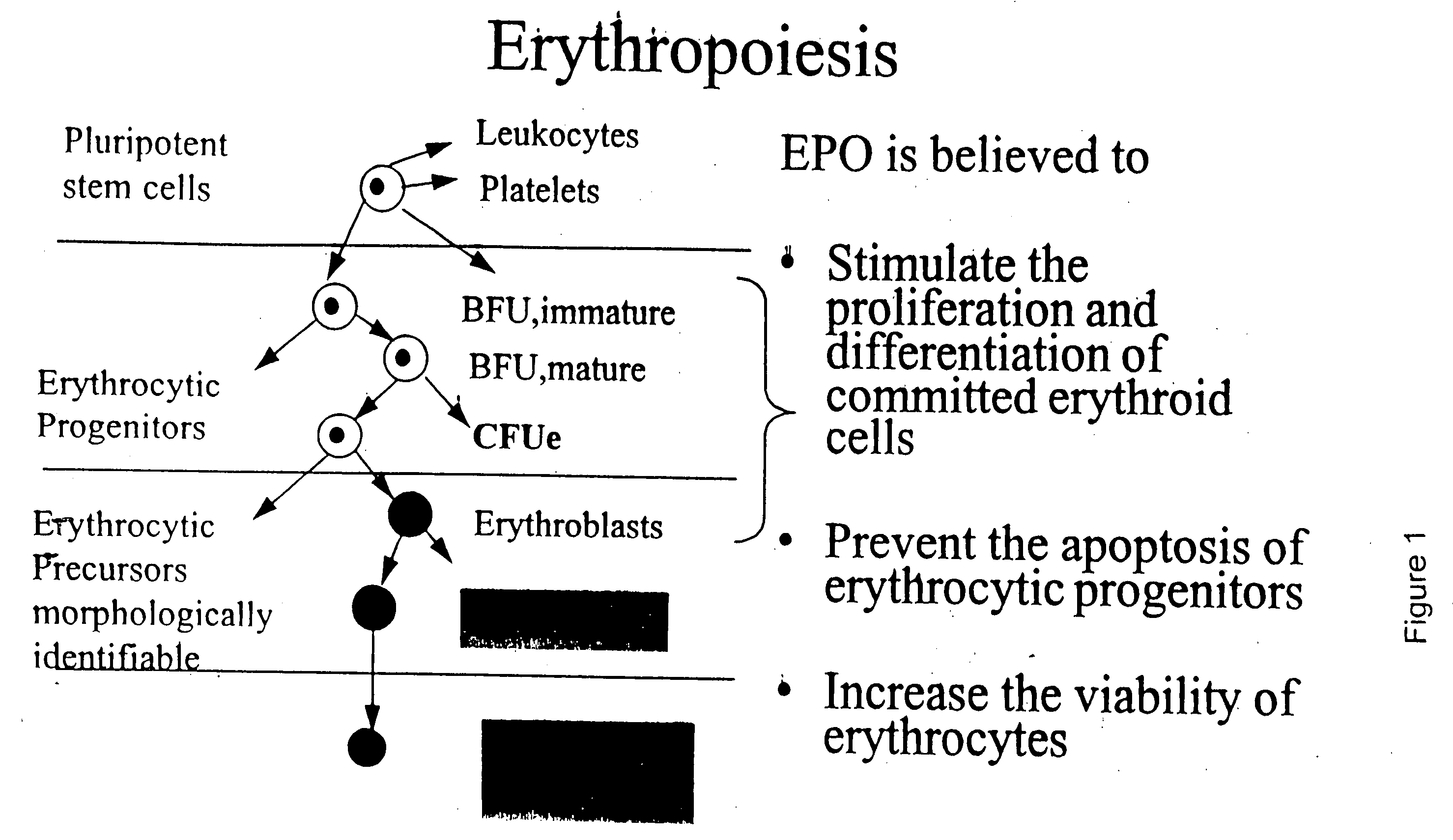
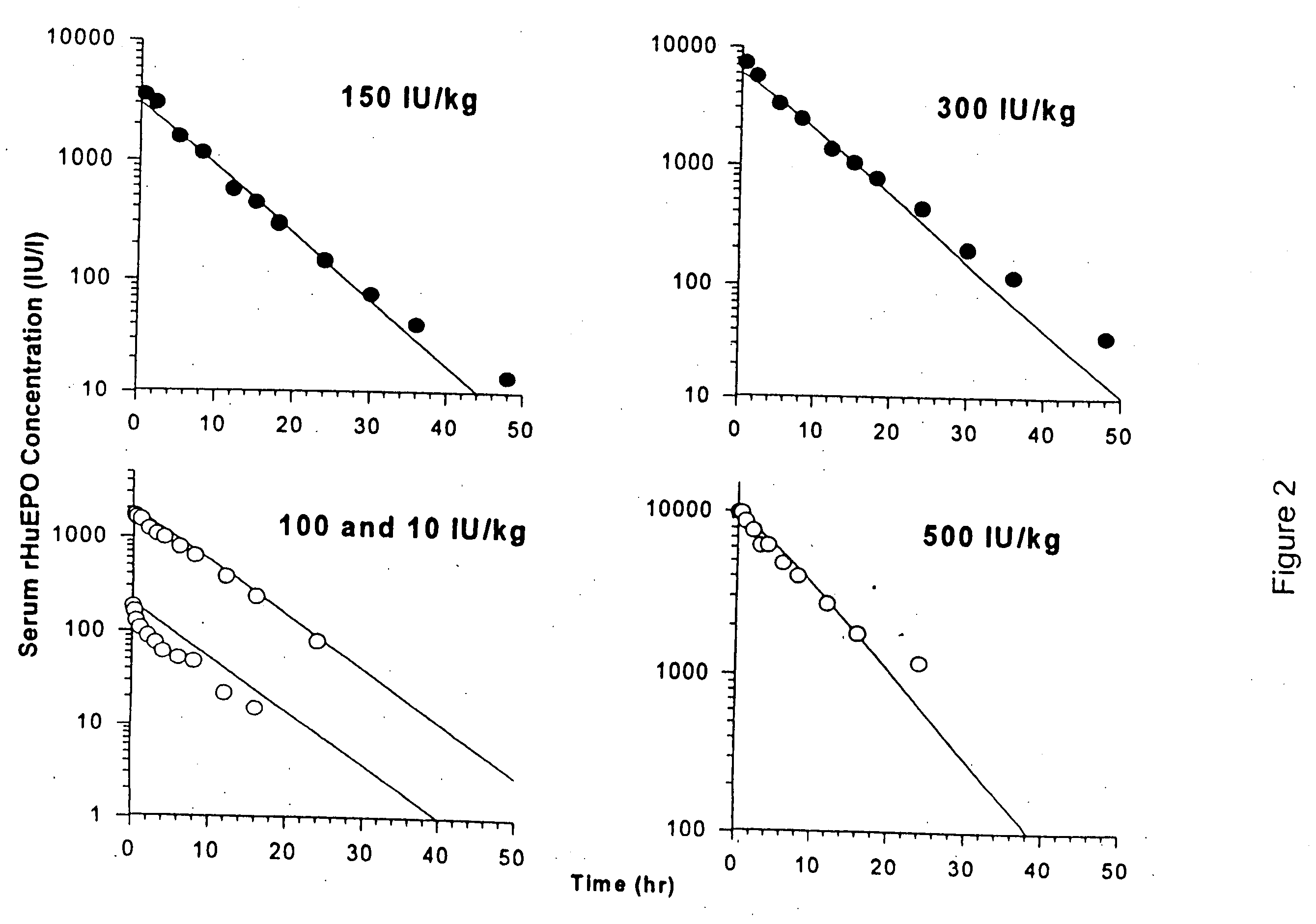
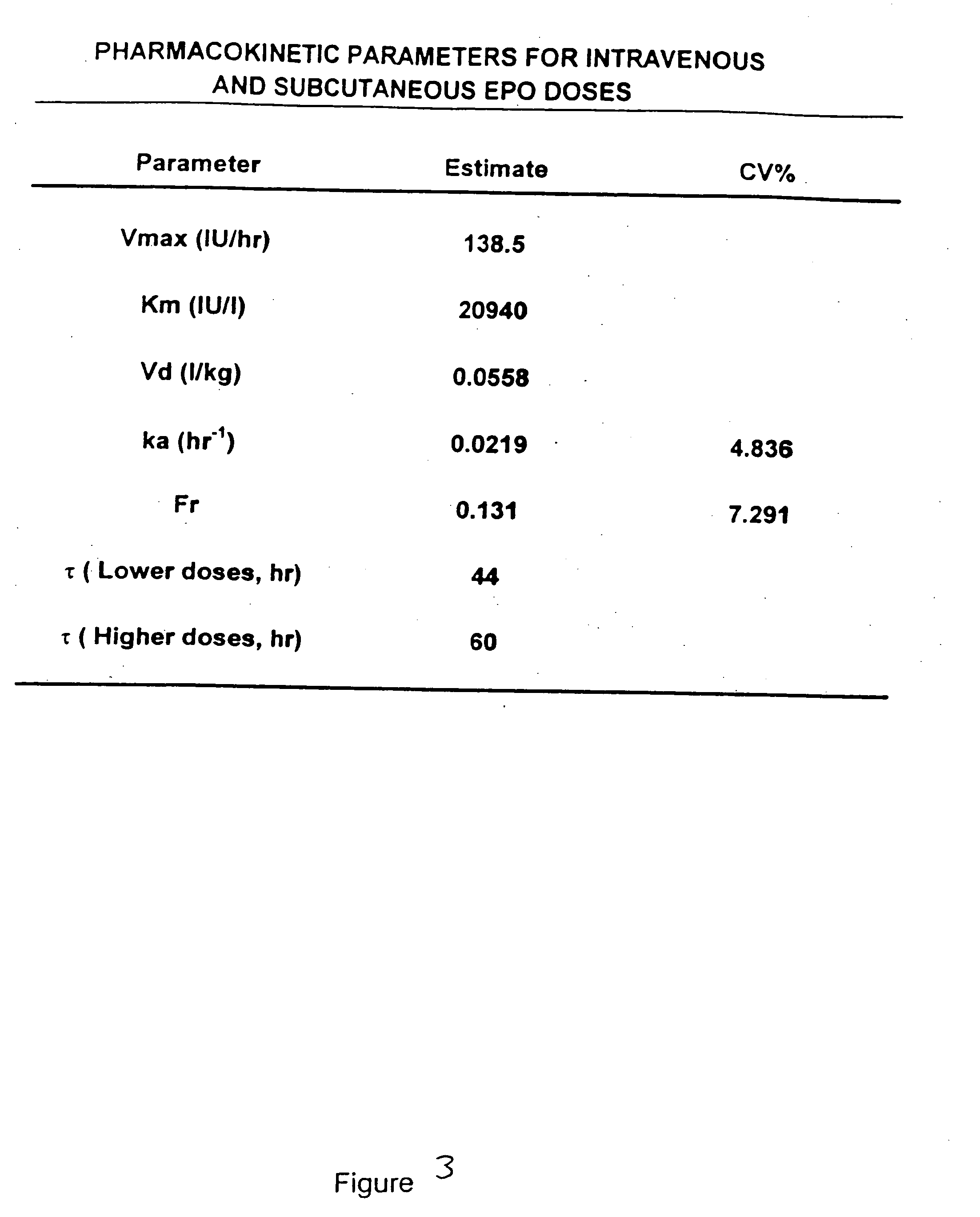
Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic modeling of erythropoietin administration
a technology of erythropoietin and erythropoietin, which is applied in the field of pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic modeling of erythropoietin administration, can solve the problems of large loss of blood, inconclusive data, and reduced oxygen availability in the tissues, and achieve the effect of facilitating the maturation of young red cells
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Human Pharmacokinetics and Bioavailability for EPO
[0249] The following example of the present invention provides a summary of the PK / PD data that support a 40,000-IU q.w. dosing regimen. The data are derived from both the literature and four clinical studies conducted by RWJPRI, Raritan, N.J. Three studies were conducted under Investigational New Drug BB-IND-2318, and one study was conducted in the UK. A brief overview of the studies is given in FIG. 17.
[0250] The clinical pharmacokinetic studies included in this technical summary are described FIG. 18A-18D, and the pharmacokinetic data from these studies are summarized in FIG. 19. The analytical methods used for the determination of EPO concentration in serum are summarized, infra, and FIG. 20.
[0251] Clinical Study EPO-PHI-373 (FIG. 17) provides the data to support the 40,000 IU once weekly dosing regimen. Clinical Study EPO-PHI-370 (FIG. 17), which has a similar design as Clinical Study EPO-PHI-373.
[0252] In Clinical Study EPO...
example 2
Evaluation of EPO PK / PD Profile After
Administration of 150 IU / kg t.i.w. and 40,000 IU q.w.
[0323] In specific indications, such as cancer, subjects are treated with 150 IU / kg epoetin alfa t.i.w. Thus, it remains an important goal to-change the currently approved dosing schedule to a more convenient (ie., once per week or once every two weeks) dosing schedule and regimen. A less frequent administration will improve user acceptance and convenience.
[0324] The pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties of the multiple dosing regimen of epoetin alfa have been defined in the previous example (EPO-PHI-358 and EPO-PHI-359). The data suggest that 150 IU / kg t.i.w. and 600 IU / kg / week dosing regimens have similar pharmacodynamic responses (e.g., a rise in hemoglobin). Therefore, epoetin alfa can potentially be administered as a weekly per kilogram dose. Since 600 IU / kg is equivalent to 42,000 IU / kg for a 70-kg person, the present study was conducted to demonstrate that a fixed dosing reg...
example 3
Comparison of PK / PD Parameters after Administration of EPREX® and PROLEASE®
[0417]FIG. 62 is a schematic representation of the model for erythropoiesis stimulating effects of rHuEpo. This model was used to estimate the kinetic and dynamic parameters for rHuEpo responses after administration of 8 single doses of EPREX® as well as the kinetic parameters after single dose PROLEASE® administration.
[0418] The pharmacokinetics of 600 IU / kg / wk EPREX® administered for 4 weeks was simulated using parameters obtained from the simultaneous fitting of the eight single doses. Only the Tau and Fr values were estimated. For the INT-57 cancer regimen of 150 IU / kg / t.i.w, the F, Tau, and Vd values were fixed as indicated in FIG. 63 based on previous estimations from the earlier study (EPO-358 / 359). The pharmacokinetics for single dose PROLEASE® (2400 IU / kg) were estimated and these parameters were used to simulate the multiple dose regimen of 1800 IU / kg / month. The same sets of kinet...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| percent reticulocyte-time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| body weights | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| body weights | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com