Inspection apparatus for inspecting patterns of a substrate
a technology of substrate and inspection apparatus, which is applied in the direction of image analysis, image enhancement, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of difficult to obtain high-resolution images, defects in wiring patterns in stairs, and defects in silicon oxide films or photosensitive photoresist materials through which light is transmitted on the surface cannot be detected, so as to improve inspection efficiency and improve throughput
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
second embodiment
[0143] the invention will now be described with reference to the drawings.
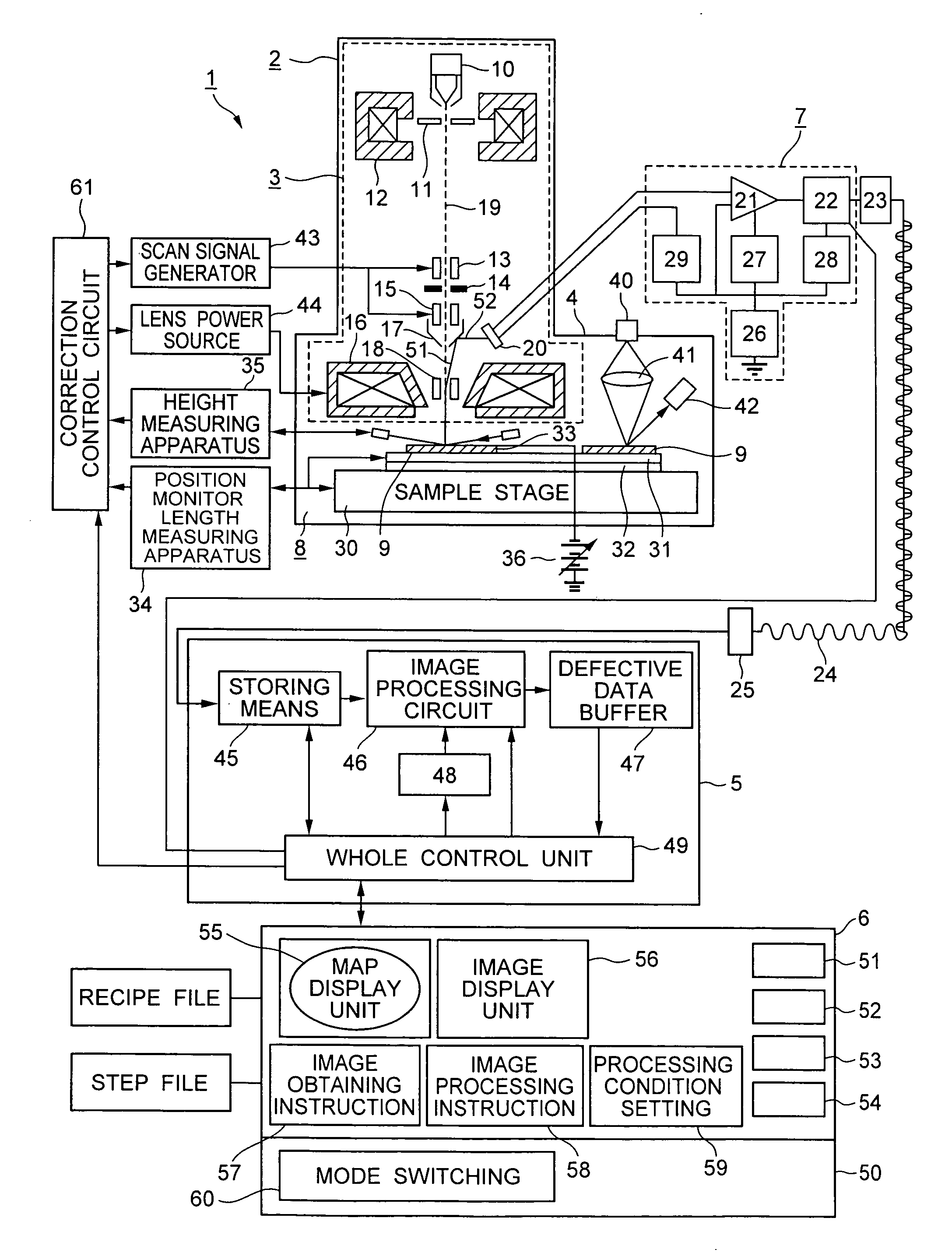
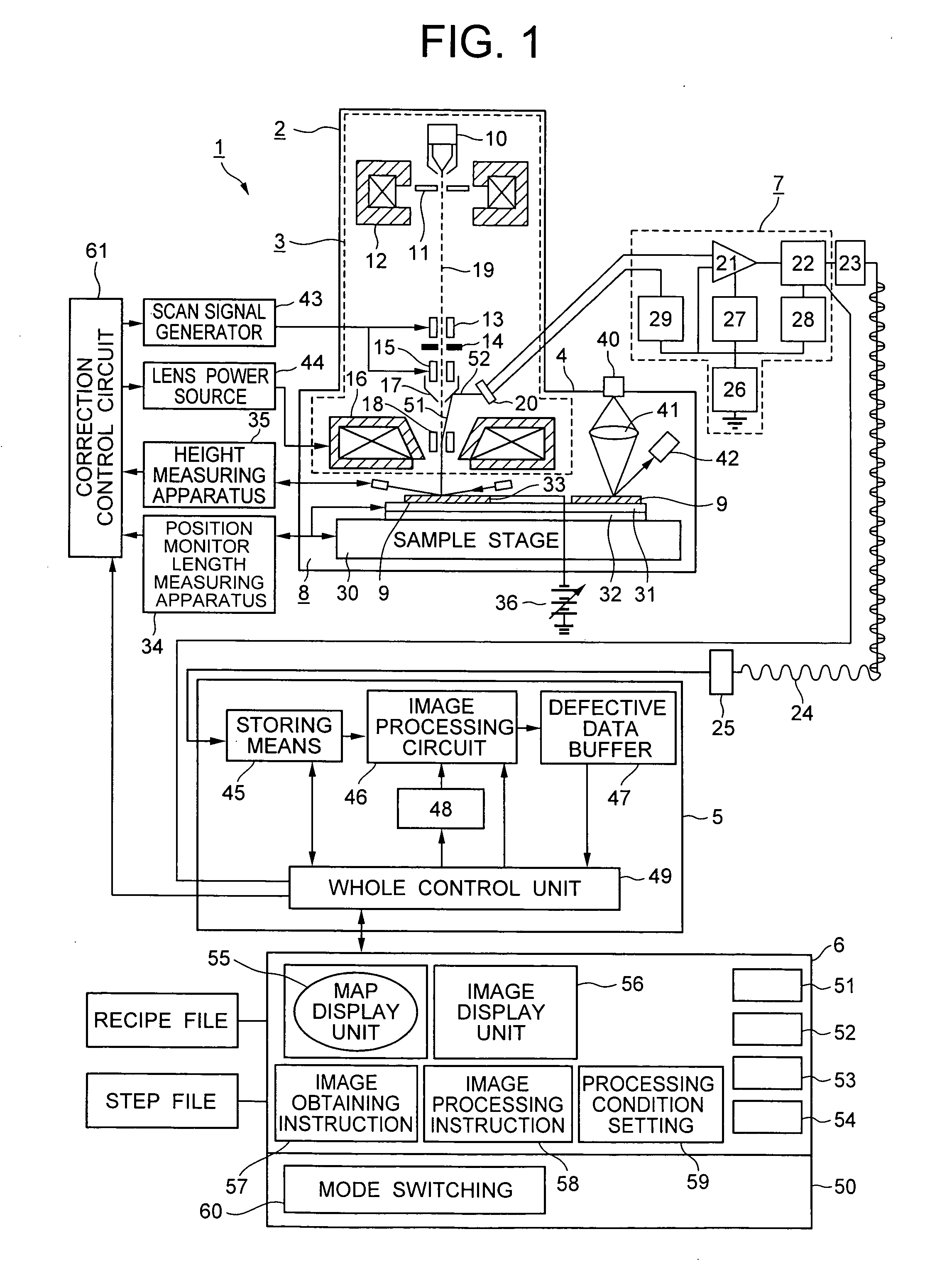
[0144]FIG. 11 is a functional block diagram of an external appearance inspection apparatus of a semiconductor wafer according to the invention. An external appearance of a semiconductor wafer 1100 as an inspection object is photographed by a sensor 1101. The photographed image is converted into digital image data by an A / D converter 1102 and the digital image data is stored into the image memory 1105 of an image processing unit 1103. As functions constructing the image processing unit 1103, besides the image memory 1105, there are the following component elements: a positional deviation detecting unit 1106 to calculate a positional deviation amount between the two image data to be compared; a defect discriminating unit 1107 to obtain a differential image between the two images by using the positional deviation amount calculated by the positional deviation detecting unit and extract defect candidates from the d...
third embodiment
[0175] the invention will now be described.
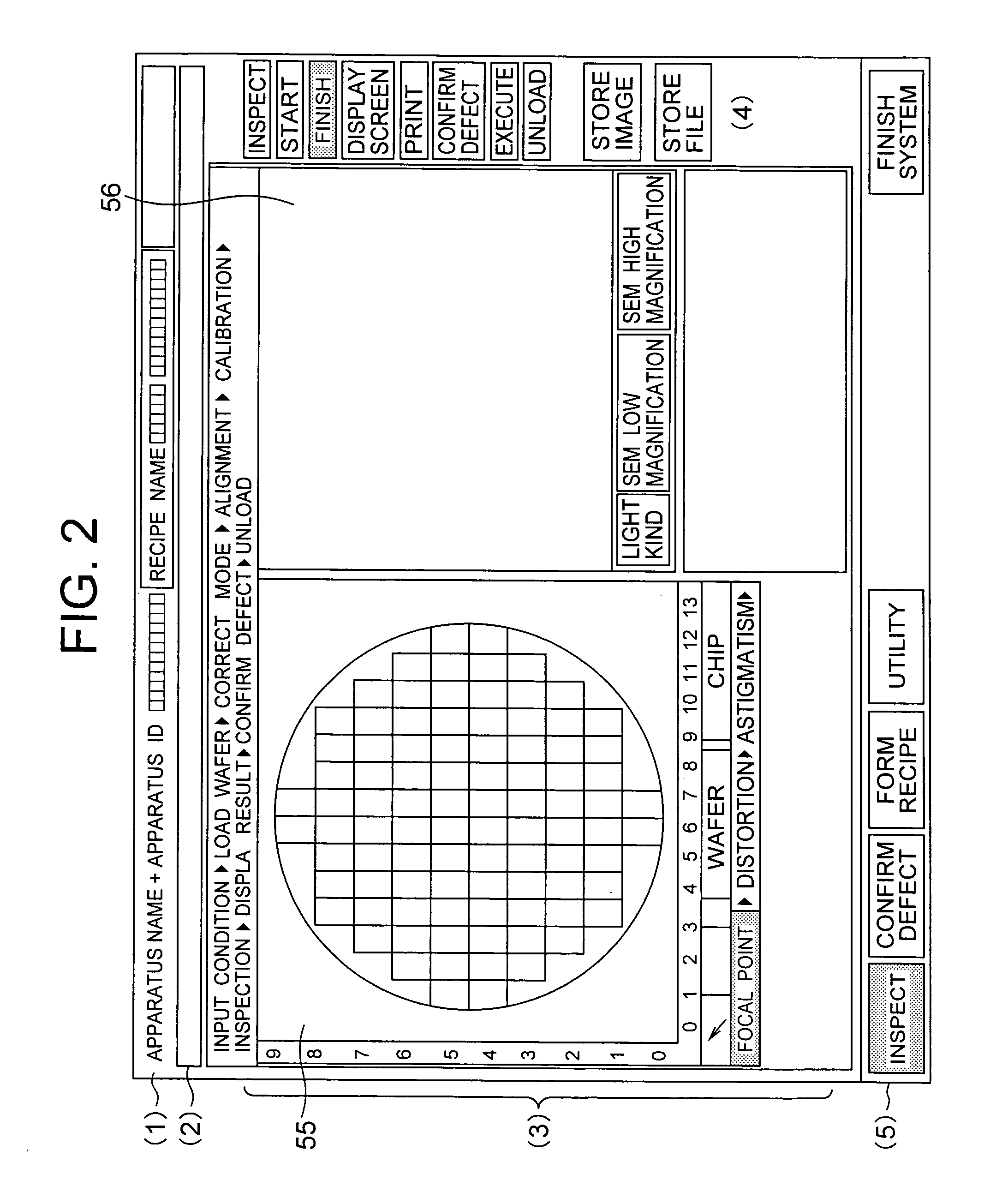
[0176] The inspection threshold value will now be described with respect to the memory cell area as an example with reference to FIG. 24. As shown in FIG. 24, the same pattern is periodically repeated in the memory cell areas in the chip. The images are compared in accordance with such a repetitive period and the pattern in which the brightness, size, or the like of the image is equal to or larger than a specific value which is determined by the user designation or the like is determined to be a defect. Such a specific value as a comparing condition is called an inspection threshold value. There is a case where a plurality of memory cell areas of different cell pitches exist in the chip. In this case, since the degrees of the brightness of the memory cell areas differ, if the comparison inspection is executed by the inspection threshold value 1 in the memory cell area A and the comparison inspection is executed by the inspection threshold v...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com