Transgenic mice expressing human cd20
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
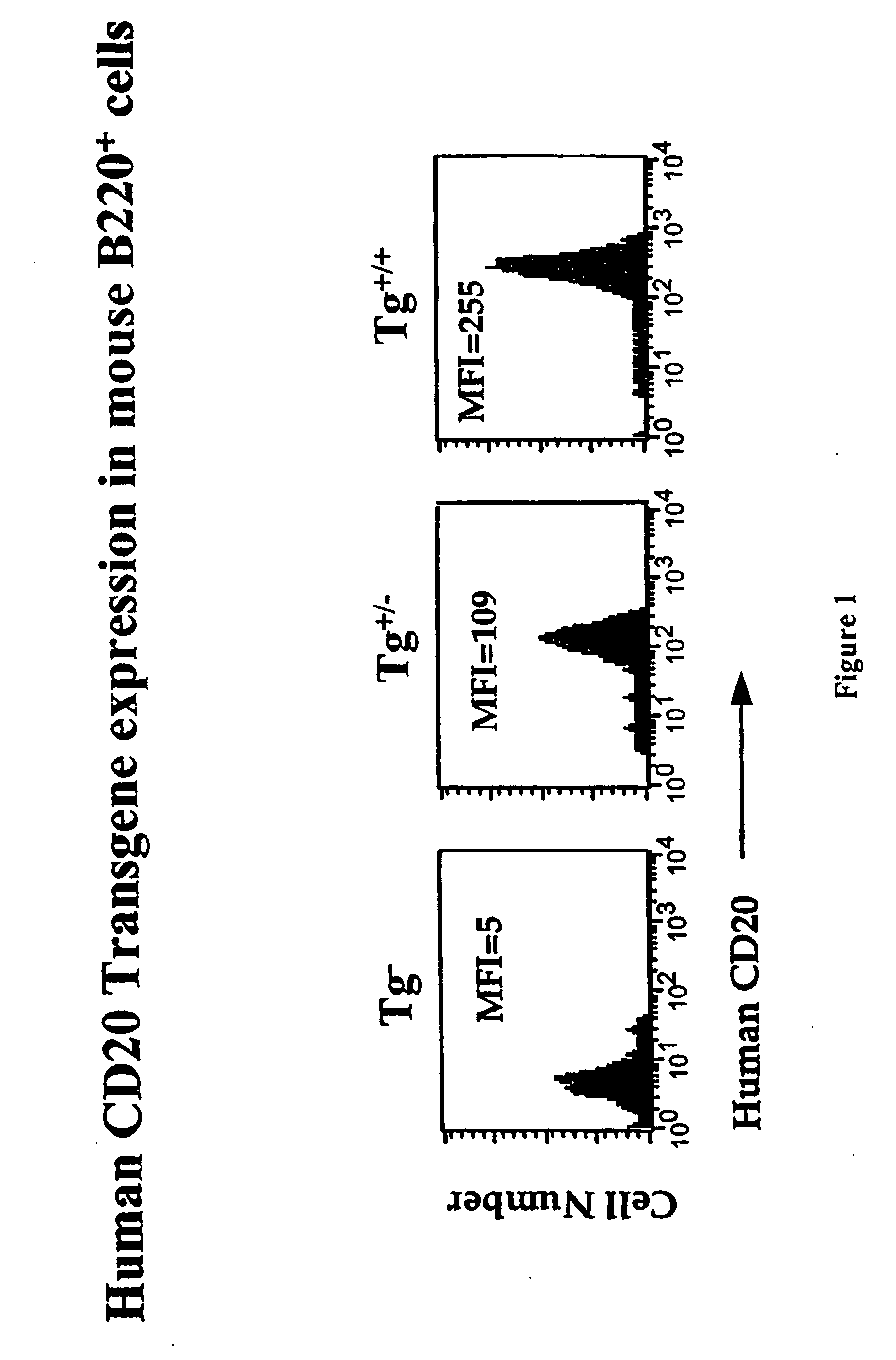
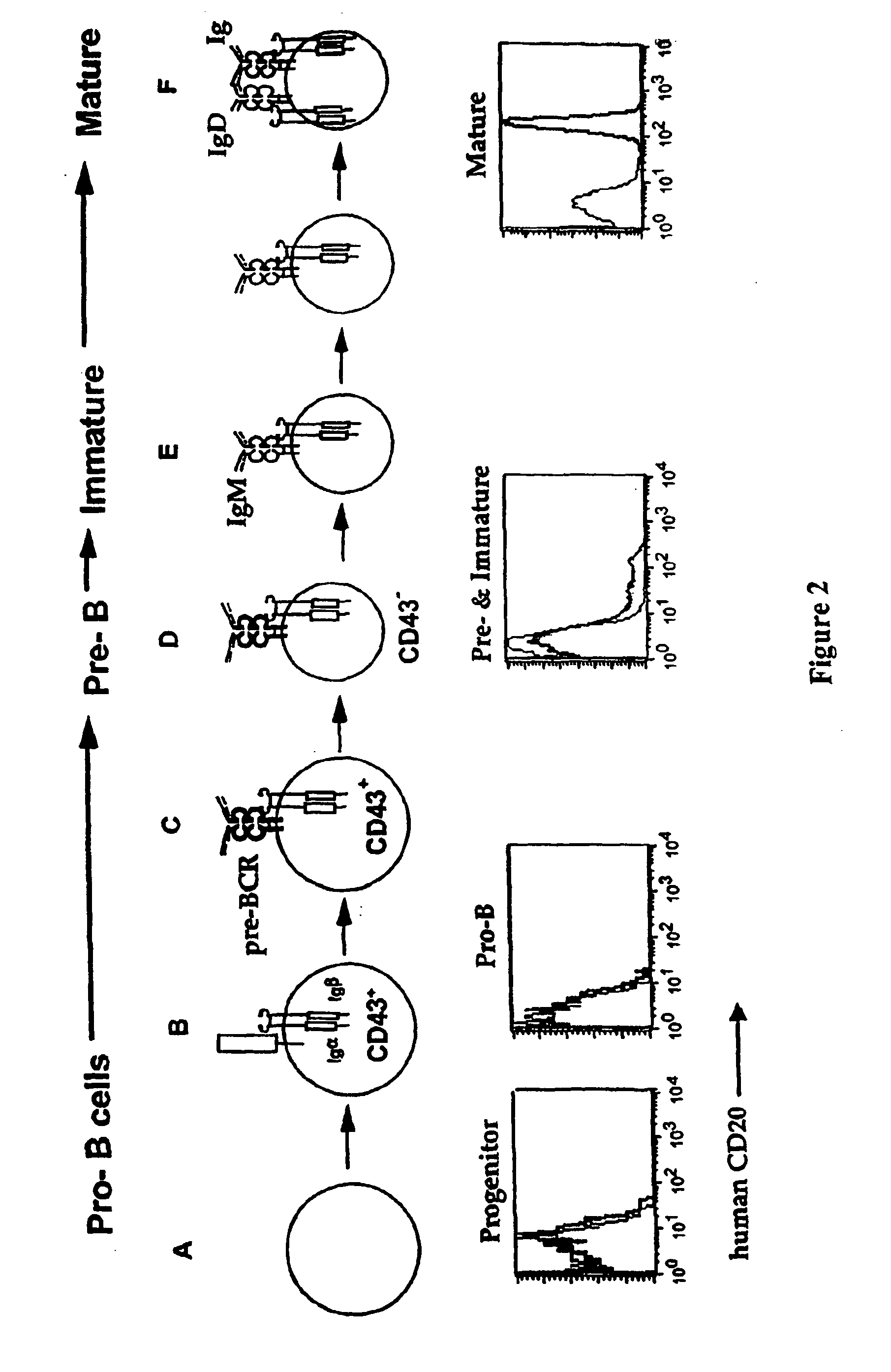
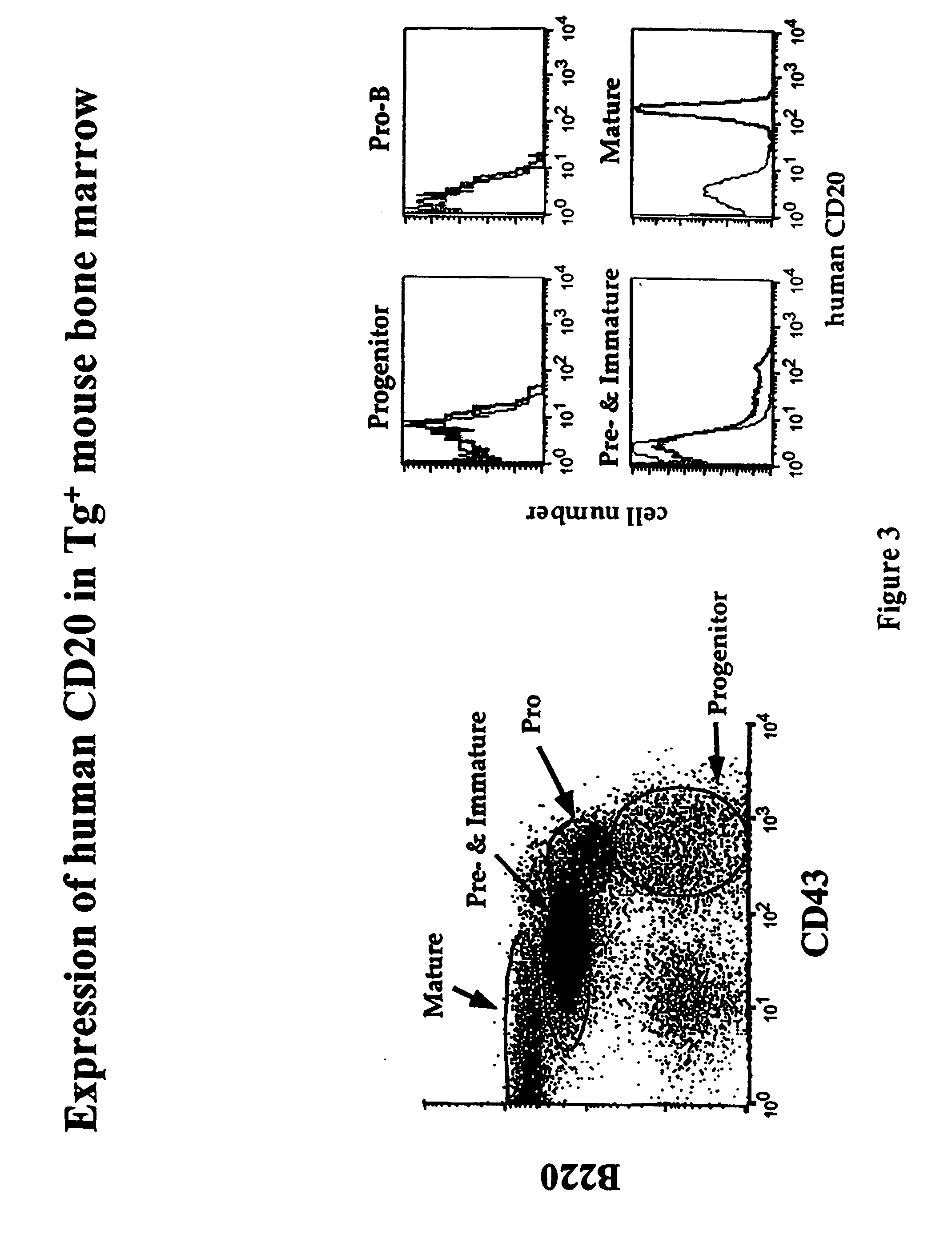
[0130] This example describes generation of human CD20 BAC transgenic (Tg+) mice and a study of the effects of anti-human CD20 antibody treatment in the hCD20+ mice.
[0131] Human CD20 transgenic mice were generated using CITB Human BAC-D-Clone No. 117H19 from Invitrogen. (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, Calif.) DNA encoding human CD20 was isolated from human lymphocytes and was sent to Invitrogen. Invitrogen tested the DNA against the filters with the clones from the human BAC library and identified clone 117H19. Previous attempts to generate transgenic mice expressing human CD20 were not successful, possibly due in part to the failure to include sufficient transcriptional control regions in the transgene construct. Transgenic mice were generated by micro injecting a human CD20 BAC construct prepared with clone 117H19 into a fertilized egg of FVB inbred strain of mice. The fertilized eggs were incubated for 1-7 days and then were implanted into surrogate mice. Mice were screened based on the ...
example 2
[0143] This example demonstrates the synergy between anti-CD20 mAb and BR3 antagonist treatments for B cell modulation / depletion. BR3-Fc is an immunoadhesin having the extracellular domain of human BR3 fused to constant domain of an immunoglobulin sequence in this case, human IgG1.
[0144] Human CD20 transgenic mice expressing (designated as hCD20+ mice) were treated with intraperitoneal injections of anti-CD20 mAb (single injection of 100 micrograms on day 9), BR3-Fc (100 micrograms every other day from days 1 through 12), or the combination of anti-CD20 mAb and BR3-Fc. Each group consisted of 4 mice. Two days following the last injection, the mice were sacrificed and analyzed for hCD20+ B cells. FACS analysis of spleen, blood, lymph node and Peyer's Patches were analyzed for B cell markers (CD21+CD23+).
[0145] The results indicate that anti-CD20 mAb therapy depleted >99% of the mature circulating B cells in the blood and lymph nodes and BR3-Fc treatment decreased mature circulating...
example 3
[0148] In this experiment, it was demonstrated that natural killer cells play a role in anti-CD20 mAb mediated B cell depletion.
[0149] Hybridoma clone, which produces PK-136 mAb (specific against mouse NK1.1), was obtained from ATCC. Four groups of human CD20 transgenic mice were injected ip with control mAb, PK-136, anti-CD20 mAb and the combination of PK-136 / anti-CD20, respectively. Doses of ip were as follows:
[0150] control mAb: 200 ug / ip, 3 ip / week, for 1 week
[0151] PK-136: 200 ug / ip, 3 ip / week, for 1 week
[0152] anti-CD20 mAb: 10 ug / ip, single dose
[0153] Lymphocytes from peripheral blood, lymph nodes and spleen were analyzed 3 days after anti-CD20 mAb ip. Data is expressed as mean+ / −standard error, with n=8.
[0154] The results indicated that treatment with PK-136 resulted in an approximately 80% to 90% reduction in NK cell population among the tissues examined (liver, spleen and blood) (FIG. 19). In the absence of majority of NK cells, 2H7 mediated B cell depletion is less ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com