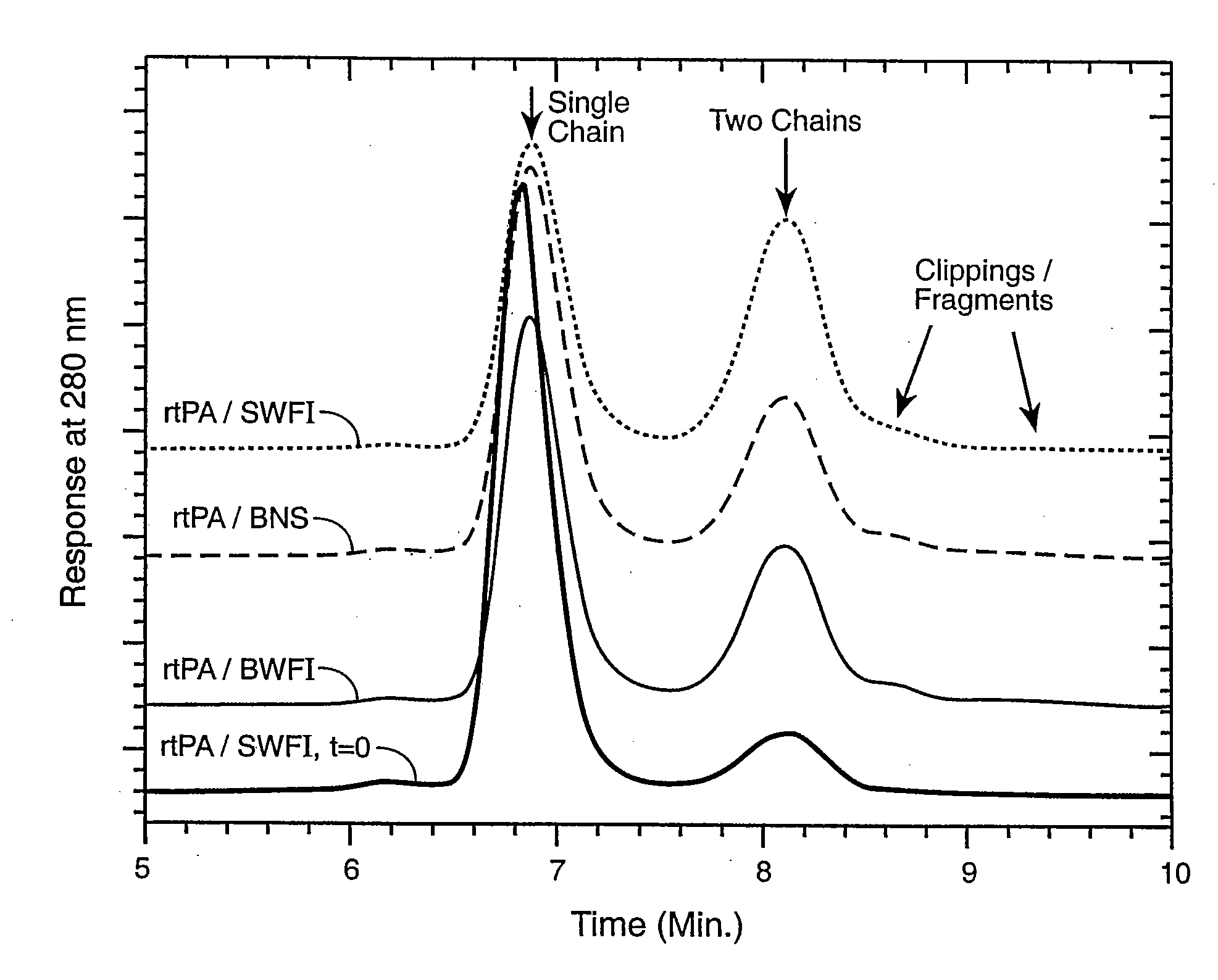
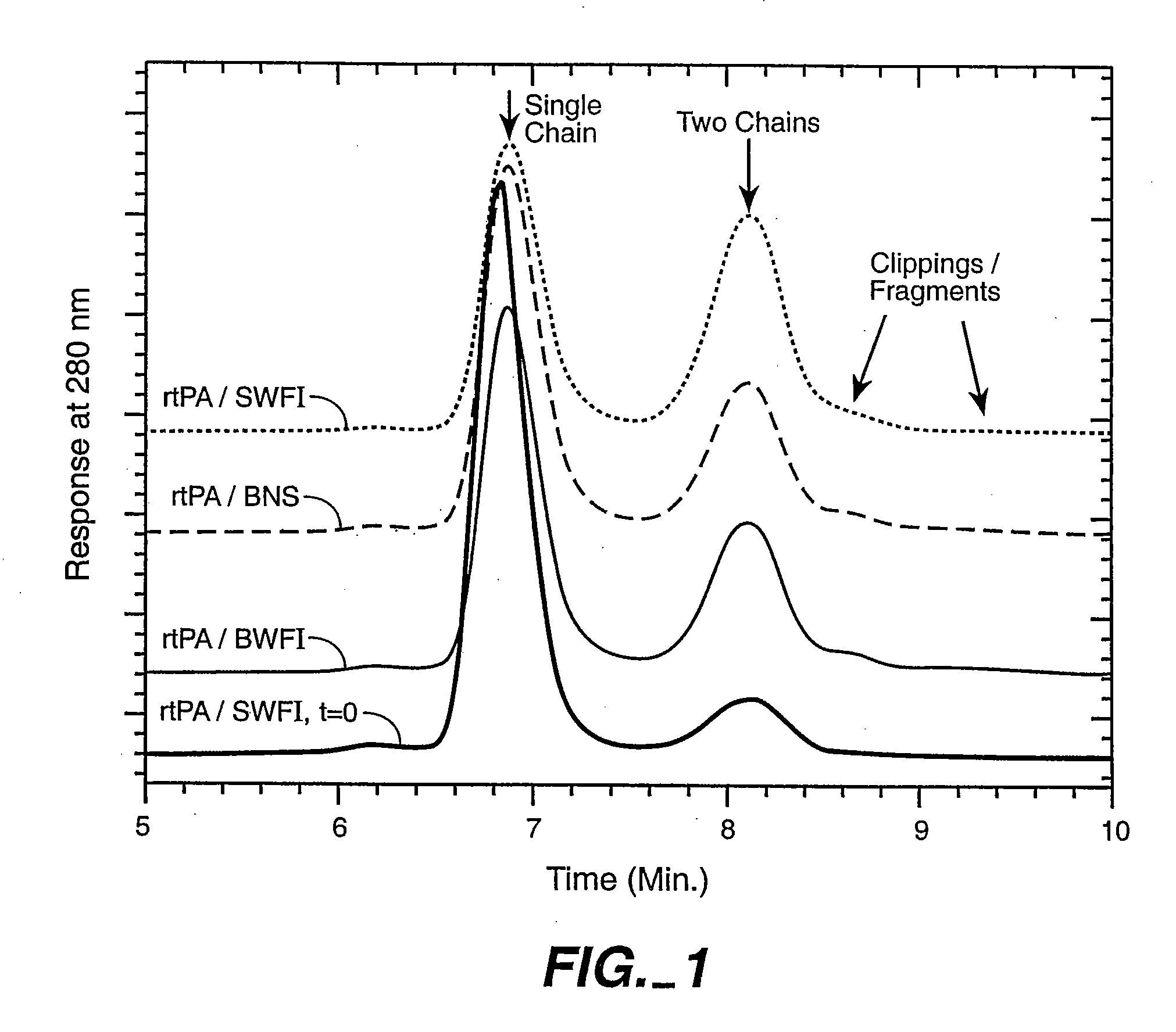
Catheter Composition and Uses Thereof
a catheter and composition technology, applied in the field of catheters, can solve the problems of serious peritonitis, serious infection of the urogenital tract, and none of the clinically proven problems to be completely satisfactory
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 2
Summary
[0101] Testing was performed as disclosed above for anti-microbial effectiveness to evaluate the efficacy of 0.8% benzyl alcohol as a preservative in 2 mg / mL of ACTIVASE® t-PA against the USP requirements. This sample met the requirements of the USP anti-microbial effectiveness test.
Materials, Equipment, and Procedures
[0102] The sample was ACTIVASE®) t-PA (2 mg / mL) in a vial with 0.8% benzyl alcohol. Specifically, the diluent was sterile water plus the appropriate amount of benzyl alcohol for a final concentration of 0.8%.
[0103] The challenge organisms were those described in Example 1.
[0104] Media, supplies, and major equipment were the same as noted in Example 1.
[0105] The procedure used was the same as that described in Example 1 and the incubation conditions were as in Table 1. The acceptance criteria and interpretation were the same as in Example 1.
Results
[0106] The results were the same as in Table 4 and Table 5 for calculated initial concentration of challen...
example 3
Summary
[0110] Testing was performed as disclosed above for anti-microbial effectiveness to evaluate the efficacy of 0.9% benzyl alcohol as a preservative in 2 mg / mL of ACTIVASE® t-PA against the USP requirements. This sample met the requirements of the USP anti-microbial effectiveness test.
Materials, Equipment, and Procedures
[0111] The sample was ACTIVASE® t-PA (2 mg / mL) in a vial with 0.9% benzyl alcohol. Specifically, the diluent was sterile water plus the appropriate amount of benzyl alcohol for a final concentration of 0.9%.
[0112] The challenge organisms were those described in Example 1.
[0113] Media, supplies, and major equipment were the same as noted in Example 1.
[0114] The procedure used was the same as that described in Example 1 and the incubation conditions were as in Table 1. The acceptance criteria and interpretation were the same as in Example 1.
Results
[0115] The results were the same as in Table 4 and Table 5 for calculated initial concentration of challeng...
example 4
Summary
[0120] Testing was performed as disclosed above for anti-microbial effectiveness to evaluate the efficacy of 1.0% benzyl alcohol as a preservative in 2 mg / mL of ACTIVASE® t-PA against the USP requirements. This sample met the requirements of the USP anti-microbial effectiveness test.
Materials, Equipment, and Procedures
[0121] The sample was ACTIVASE® t-PA (2 mg / mL) in a vial with 1.0% benzyl alcohol. Specifically, the diluent was sterile water plus the appropriate amount of benzyl alcohol for a final concentration of 1.0%.
[0122] The challenge organisms were those described in Example 1.
[0123] Media, supplies, and major equipment were the same as noted in Example 1.
[0124] The procedure used was the same as that described in Example 1 and the incubation conditions were as in Table 1. The acceptance criteria and interpretation were the same as in Example 1.
Results
[0125] The results were the same as in Table 4 and Table 5 for calculated initial concentration of challeng...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| internal volumes | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| organic | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com