Polyvalent cation-sensing receptor in atlantic salmon
a technology of atlantic salmon and cations, which is applied in the direction of animal/human proteins, peptides/protein ingredients, peptides, etc., can solve the problems of inability to determine from these experiments, and achieve the effects of reducing mortality, increasing growth, and efficient growth of atlantic salmon
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Molecular Cloning of Shark Kidney Calcium RECEPTOR RELATED PROTEIN (SKCaR)
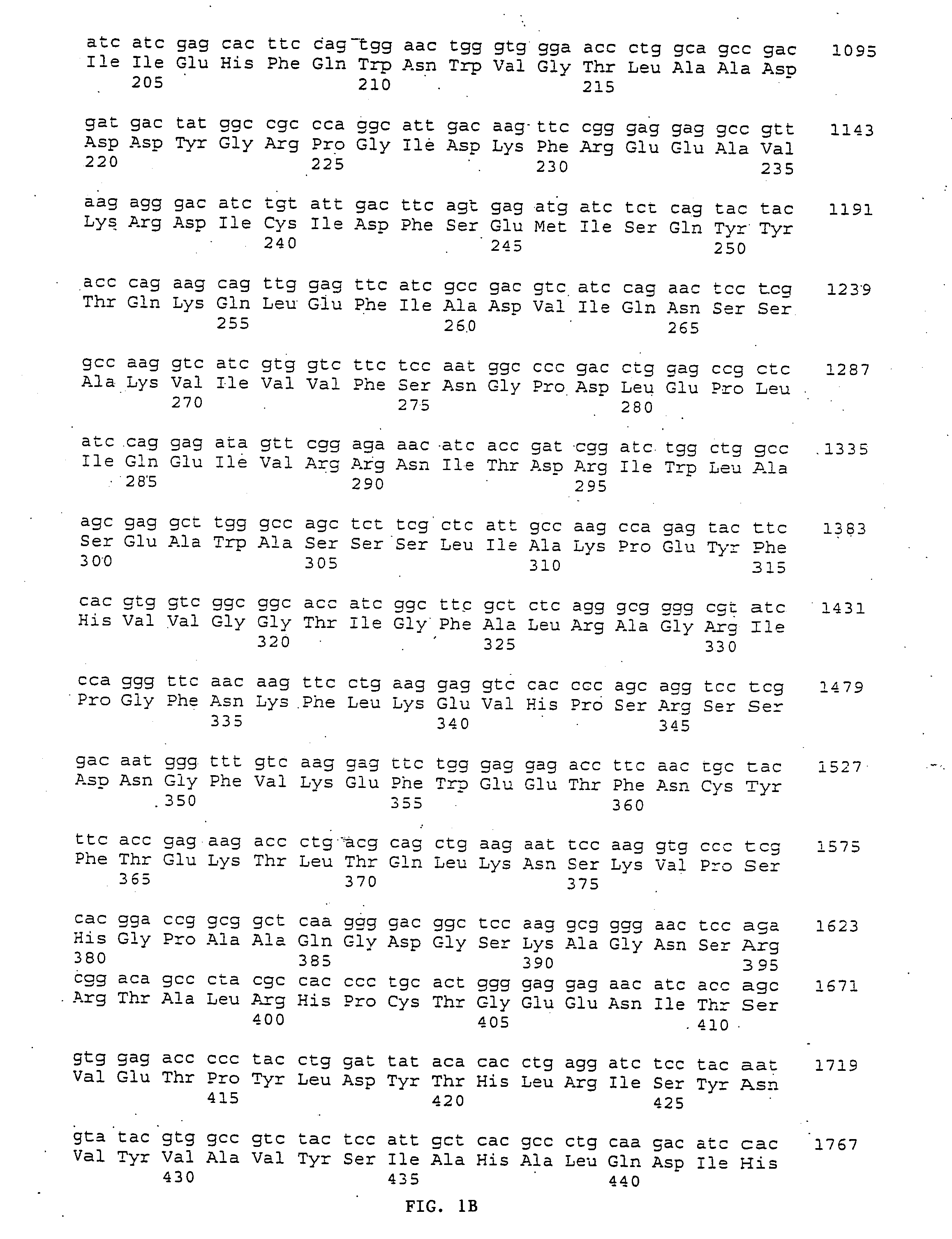
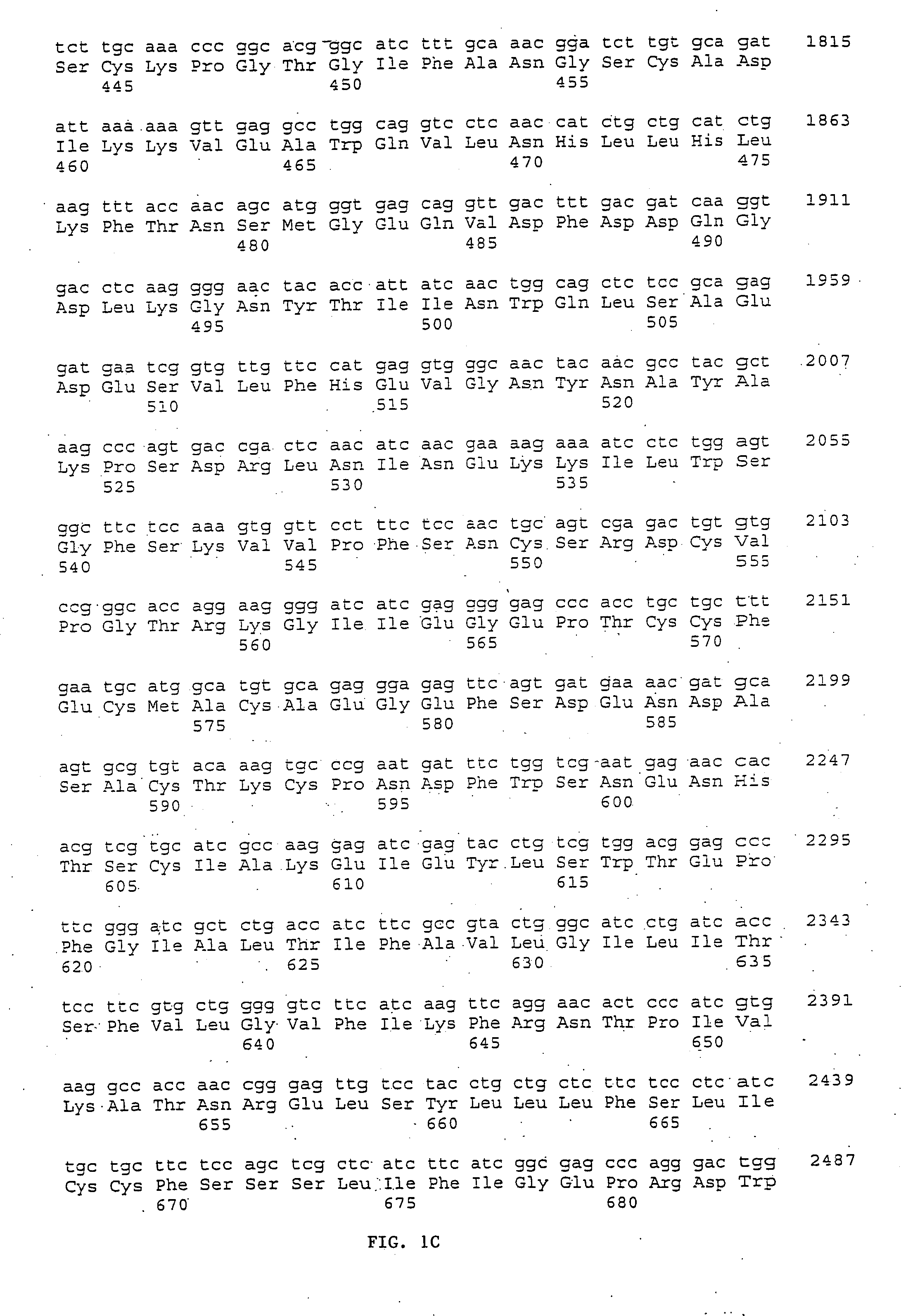
[0171] A shark λZAP cDNA library was manufactured using standard commercially available reagents with cDNA synthesized from poly A+ RNA isolated from shark kidney tissue as described and published in Siner et al. Am. J. Physiol. 270:C372-C381, 1996. The shark cDNA library was plated and resulting phage plaques screened using a 32P-labeled full length rat kidney CaR (RaKCaR) cDNA probe under intermediate stringency conditions (0.5×SSC, 0.1% SDS, 50° C.). Individual positive plaques were identified by autoradiography, isolated and rescued using phagemid infections to transfer cDNA to KS Bluescript vector. The complete nucleotide sequence, FIG. 1, (SEQ ID NO: 1) of the 4.1 kb shark kidney PVCR related protein (SKCaR) clone was obtained using commercially available automated sequencing service that performs nucleotide sequencing using the dideoxy chain termination technique. The deduced amino acid sequence (SEQ I...
example 2
Expression / Activation Studies of SKCaR in Human Embryonic Kidney (HEK) Cells
[0172] PVCRs serve as salinity sensors in fish. These receptors are localized to the apical membranes of various cells within the fish's body (e.g., in the gills, intestine, kidney) that are known to be responsible for osmoregulation. A full-length cation receptor (CaR, also referred to as “PVCR”) from the dogfish shark has been expressed in human HEK cells. This receptor was shown to respond to alterations in ionic compositions of NaCl, Ca2+ and Mg2+ in extracellular fluid bathing the HEK cells. The ionic concentrations encompassed the range which includes the transition from freshwater to seawater. Expression of PVCR mRNA is also increased in fish after their transfer from freshwater to seawater, and is modulated by PVCR agonists. Partial genomic clones of PVCRs have also been isolated from other fish species, including winter and summer flounder and lumpfish, by using nucleic acid amplification with dege...
example 3
Defining Salinity Limits as an Assay to Identify Fish With Enhanced Salinity Responsive and Altered PVCR Function
[0184] Both anadromous fish (Atlantic salmon, trout and Arctic char) and euryhaline fish (flounders, alewives, eels) traverse from freshwater to seawater environments and back again as part of their lifecycles in the natural environment. To successful accomplish this result; both types of fish have to undergo similar physiological changes including alterations in their urine output, altering water intake and water absorption. In some cases, naturally occurring mutations to PVCR would provide for altered salinity adaptation capabilities that would have significant value for both commercial and environmental restoration uses. For example, identification of selective traits associated with PVCR mediated salinity responses might allow identification of new strains of fish for commercial aquaculture. Similarly, identification of selected environmental parameters from a host o...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| periods of time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| periods of time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com