Acid-base mixture and ion conductor comprising the same
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Mixture of 2-ethyl-4-methylimidazole / 4-methylimidazole and sulfuric acid (2E4MZ / 4MI.H2SO4; molar ratio=1:1:2)
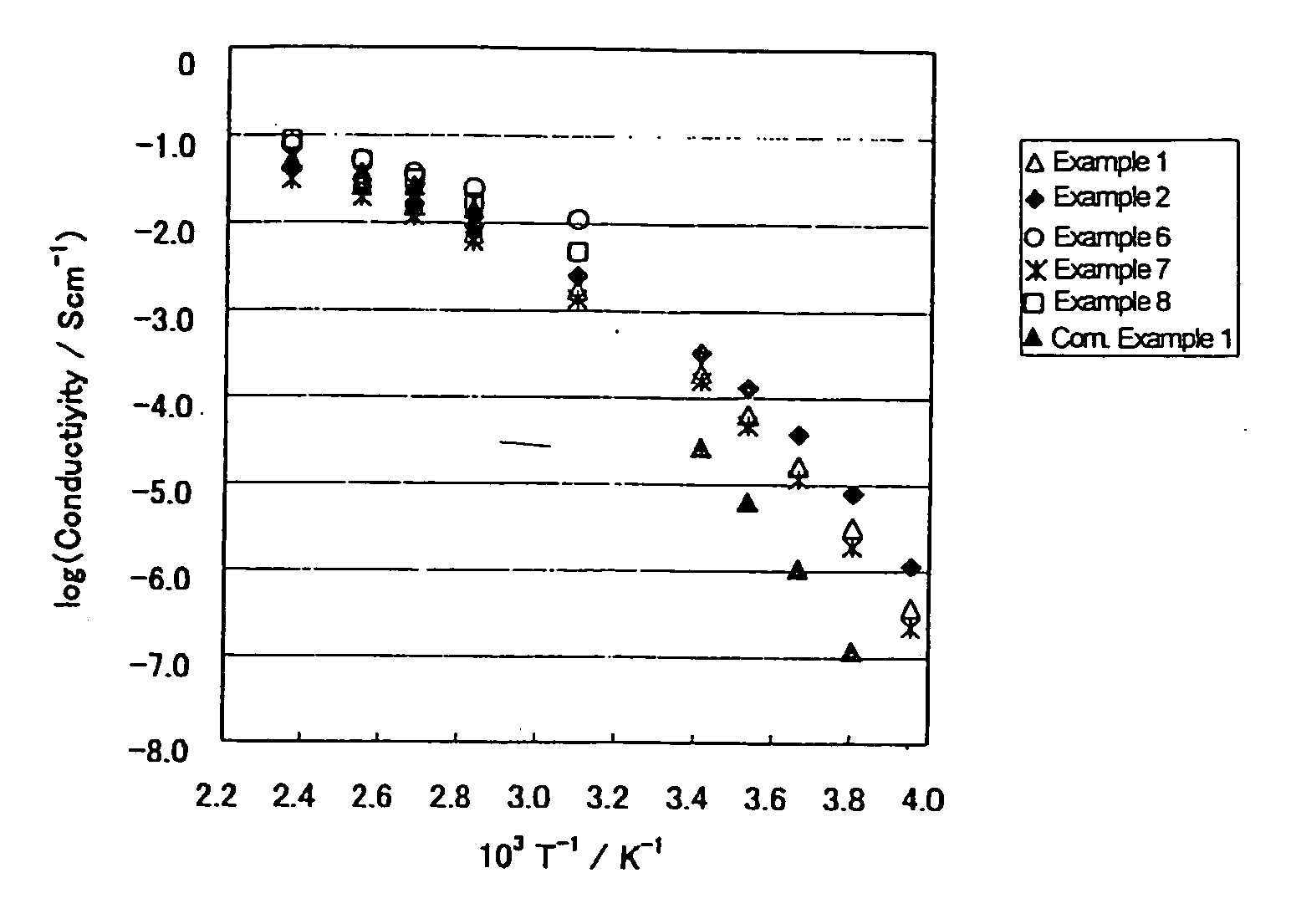
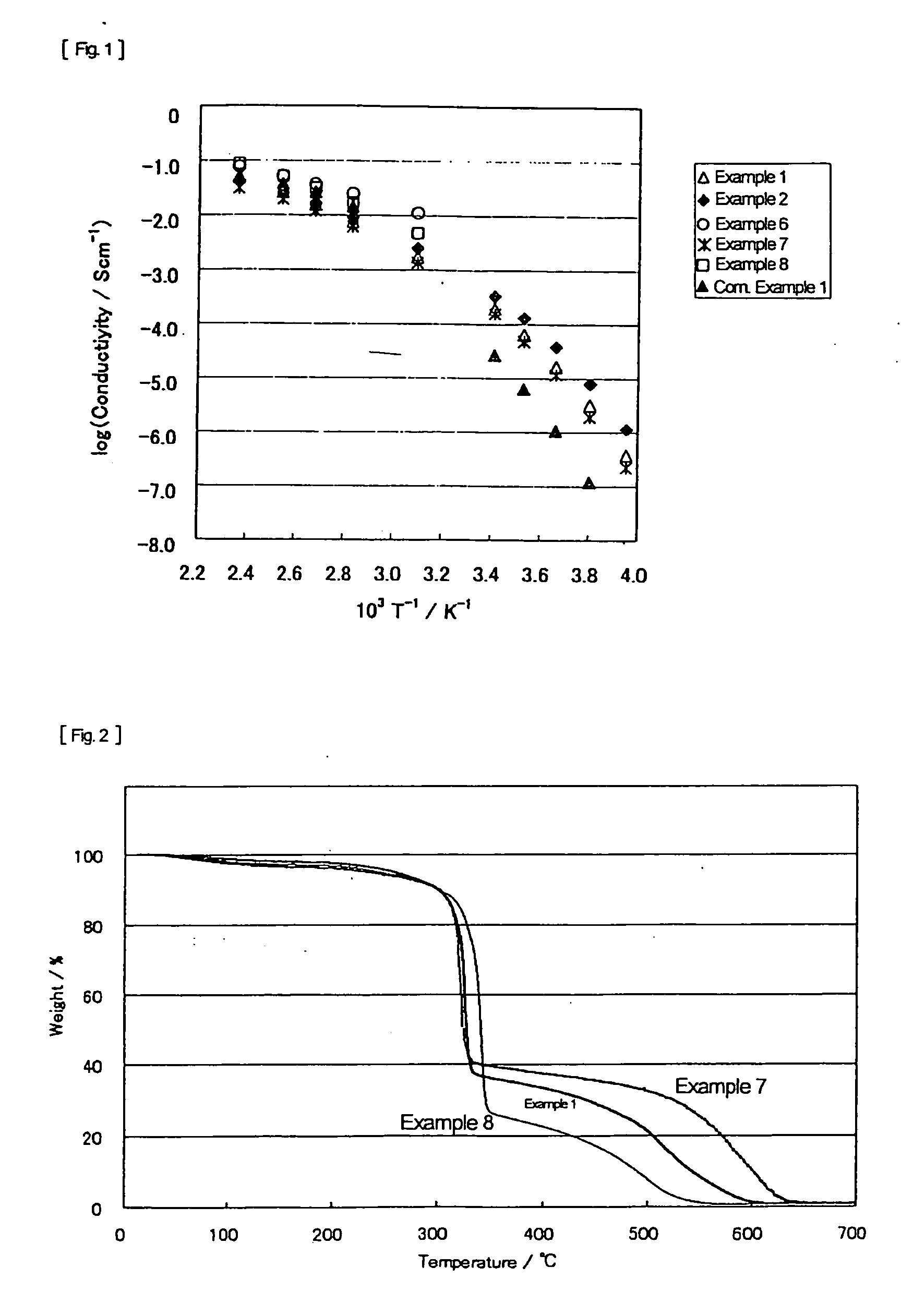
[0066] In 12.7 g of 2E4MZ (from Shikoku Chemicals Corp.) was added dropwise 6 ml of 98% sulfuric acid in a nitrogen atmosphere while stirring. After 2 hour stirring, 20.5 g of 4MI.H2SO4 prepared in Example 8 given later was added thereto, followed by stirring overnight at room temperature. The mixture was dried under reduced pressure at 110° C. for 6 hours to remove water to give 2E4MZ / 4MI.H2SO4 (molar ratio=1:1:2). The acid-base mixture maintained the liquid state for more than 4 months. The results of DSC showed no melting point and a Tg of −54° C. The temperature dependence of the ion conductivity of the acid-base mixture is shown in FIG. 1.
example 2
Mixture of 2-ethyl-4-methylimidazole / 2-ethylimidazole and sulfuric acid (2E4MZ / 2EI.H2SO4; molar ratio=1:1:2)
[0067] In a flask were put 15.7 g of 2E4MZ and 13.7 g of 2EI (from Aldrich), and the 2EI was melted at 100° C. to make a uniform mixture. Into the mixture was added dropwise 15 ml of 98% sulfuric acid in a nitrogen atmosphere while stirring. The mixture was stirred at room temperature overnight, followed by drying under reduced pressure at 110° C. for 6 hours to remove water thereby to give 2E4MZ / 2EI.H2SO4 (molar ratio=1:1:2). The resulting acid-base mixture maintained the liquid state for more than 5 months. The DSC results revealed no melting point and a Tg of −61° C. The temperature dependence of the ion conductivity of the acid-base mixture is shown in FIG. 1. Owing to the mixed base system, the acid-base mixture of Example 2 exhibited improvement in ion conductivity in a low temperature region over the acid-base mixture of Comparative Example 1 hereinafter given.
example 3
Mixture of 2-ethyl-4-methylimidazole / imidazole and sulfuric acid (2E4MZ / Im.H2SO4; molar ratio=1:1:2)
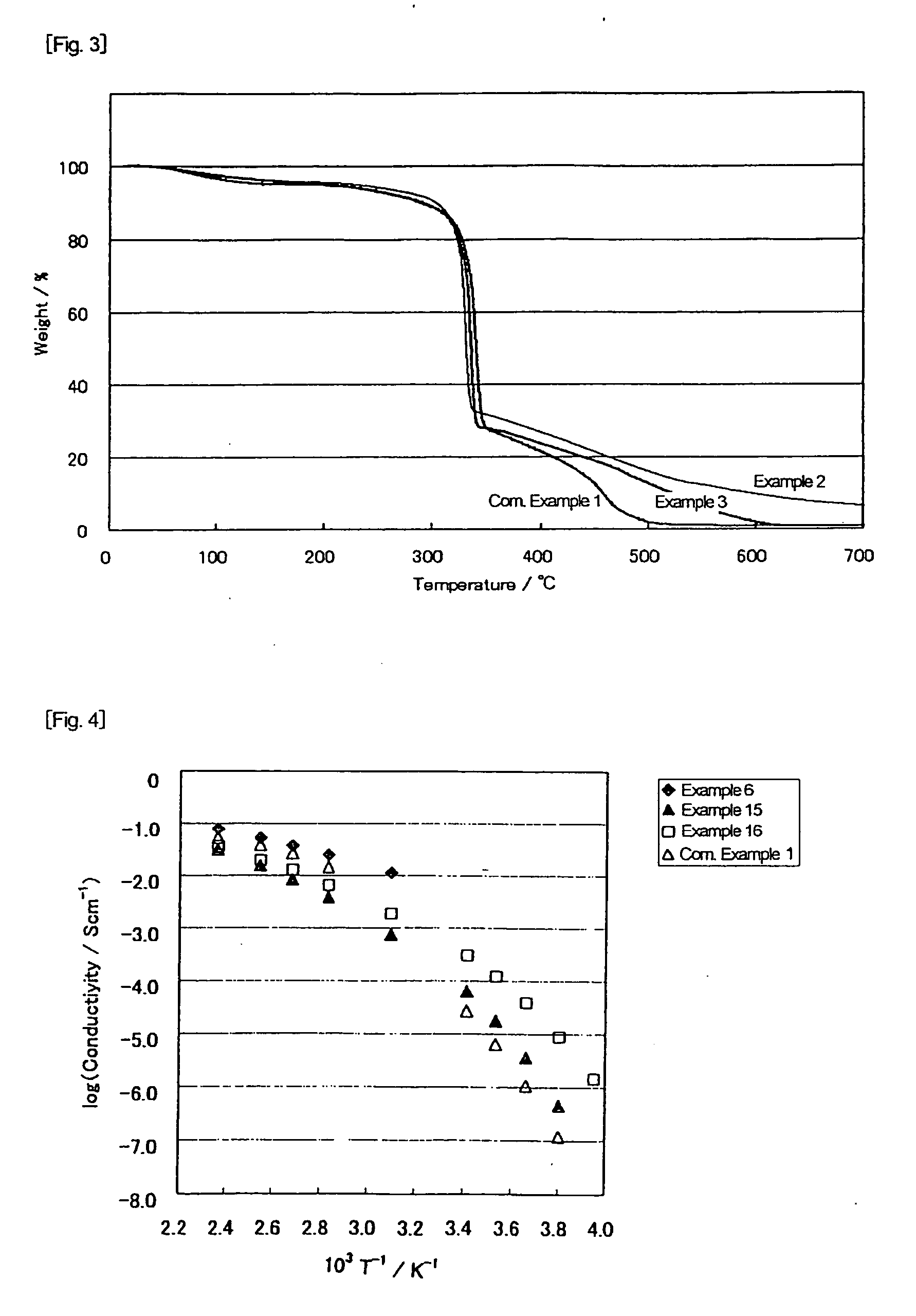
[0068] In 30 ml of ethanol were dissolved 5.17 g of 2E4MZ and 3.20 g of imidazole (from Sigma). The solution was cooled in an ice bath, and 5 ml of 98% sulfuric acid was added thereto dropwise in a nitrogen atmosphere while stirring. The stirring was continued at room temperature overnight, followed by drying under reduced pressure at 60° C. for 1 hour and then at 110° C. for 6 hours to remove ethanol and water to give 2E4MZ / Im.H2SO4 at a molar ratio of 1:1:2. The resulting acid-base mixture was solid at room temperature. In DSC, a sample was maintained at 100° C. to once melt, cooled to −150° C., and again heated from −150° C. up to 100° C. The sample showed only a Tg with no peak of crystallization or melting in both the cooling and the heating thermograms. The Tg was −56° C.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com