Hydrophobic catalyst layer for polymer electrolyte fuel cell and method of producing the same, and polymer electrolyte fuel cell and method of producing the same
a technology of electrolyte fuel cell and hydrophobic catalyst, which is applied in the manufacture of cell components, final product manufacturing, electrochemical generators, etc., can solve the problems of reduced utilization factor, reduced effective surface area, and reduced so as to increase the utilization factor of catalyst, the effect of low cost and additional stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
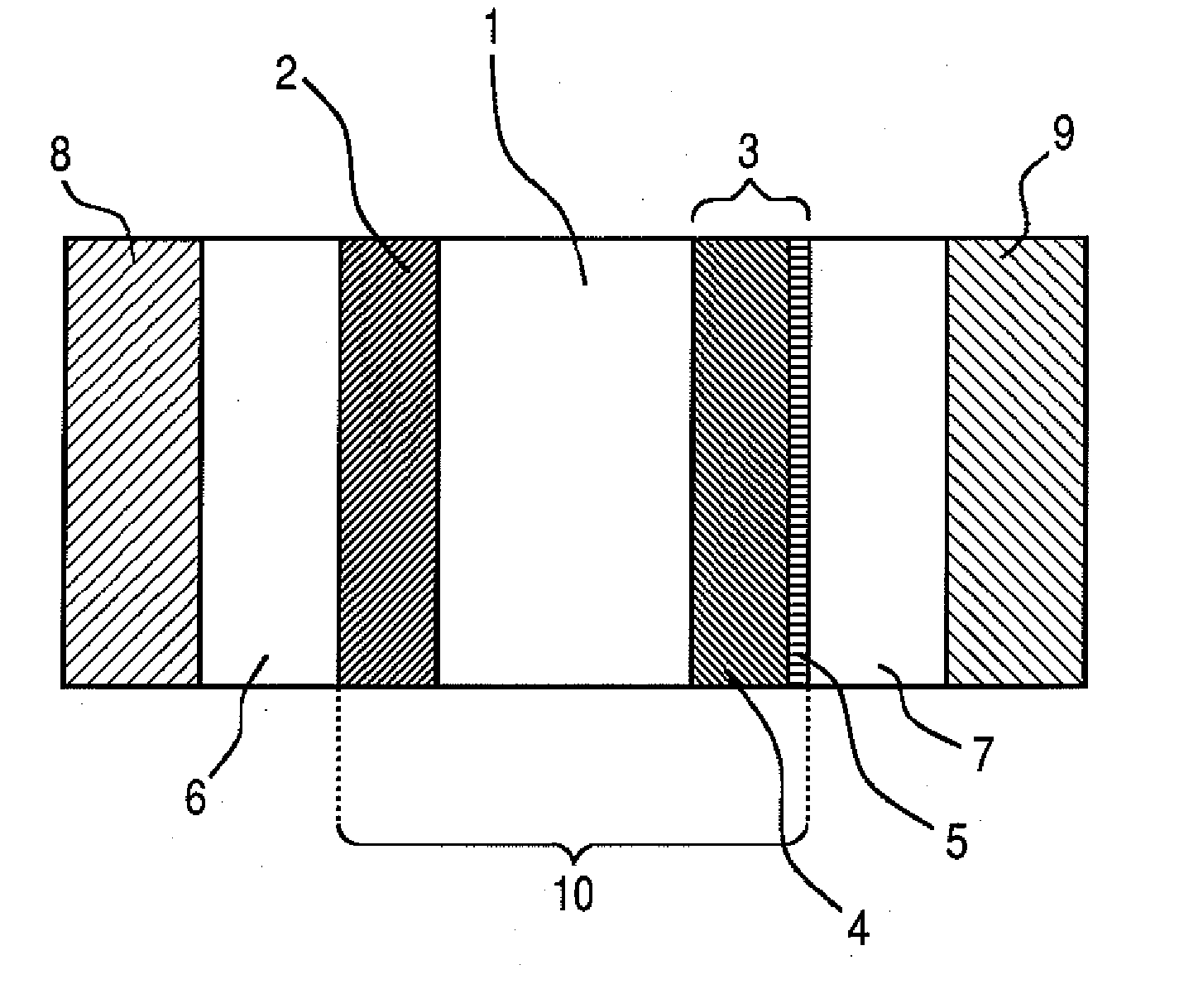
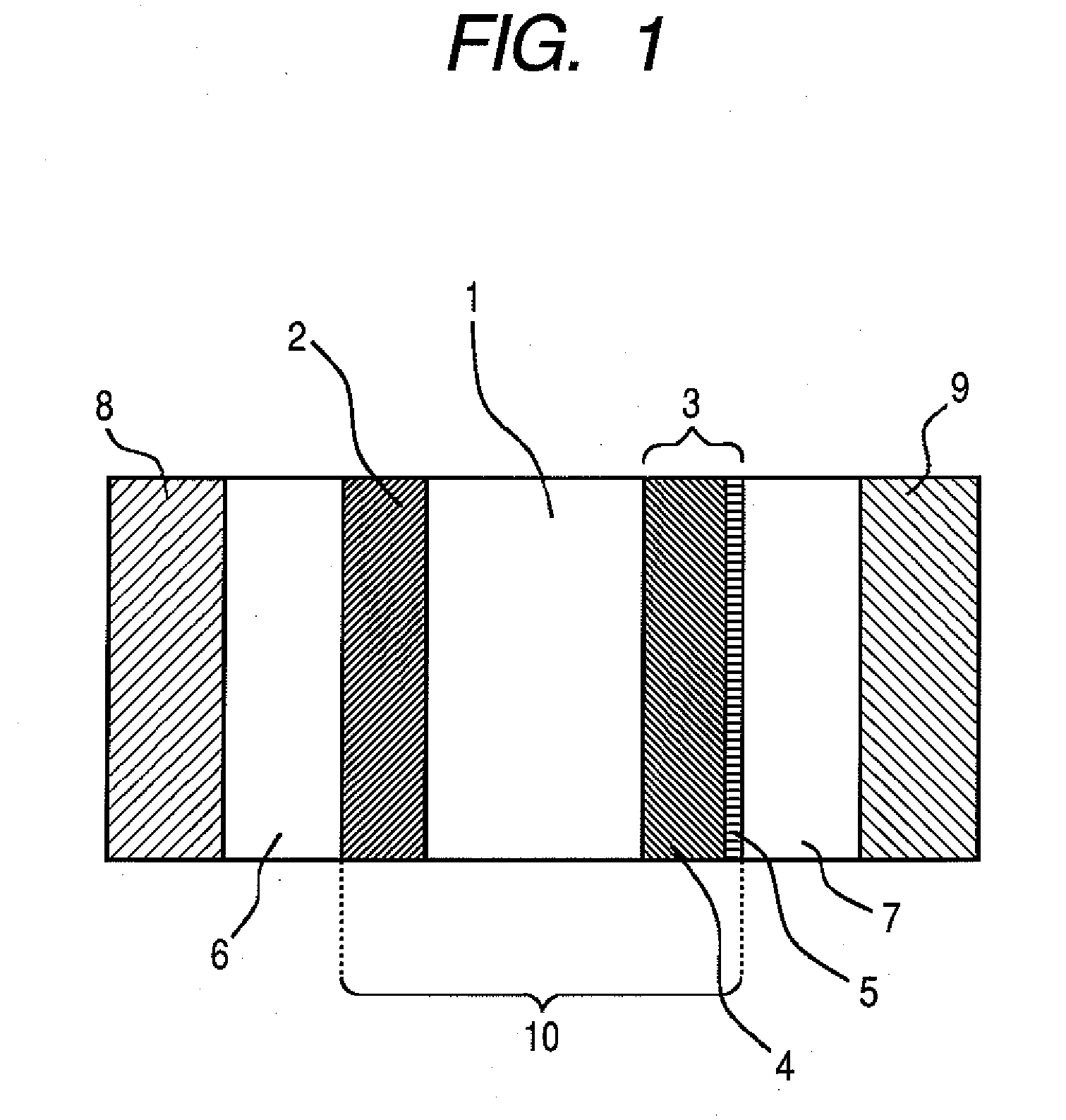
[0106] In this example, a polymer electrolyte fuel cell having the constitution shown in FIG. 1 as the embodiment of the present invention was produced.
[0107] Hereinafter, the production steps of the polymer electrolyte fuel cell according to this example will be described in detail.
[0108] (Step 1)
[0109] A gold thin film having a thickness of 50 nm was formed by means of an electron beam vacuum evaporation method on a PTFE sheet (NITFLON manufactured by NITTO DENKO CORPORATION) as a layer to be transferred onto a polymeric electrolyte membrane. A porous platinum oxide layer having a thickness of 2 μm was formed thereon by means of a reactive sputtering method. The reactive sputtering was performed under the conditions of: a total pressure of 5 Pa; an oxygen flow rate ratio (QO2 / (QAr+QO2) ) of 70%; a substrate temperature of 25° C.; and an RF input power of 5.4 W / cm2.
[0110] (Step 2)
[0111] Subsequently, the porous platinum oxide layer was brought into contact with the steam of 2,...
example 3
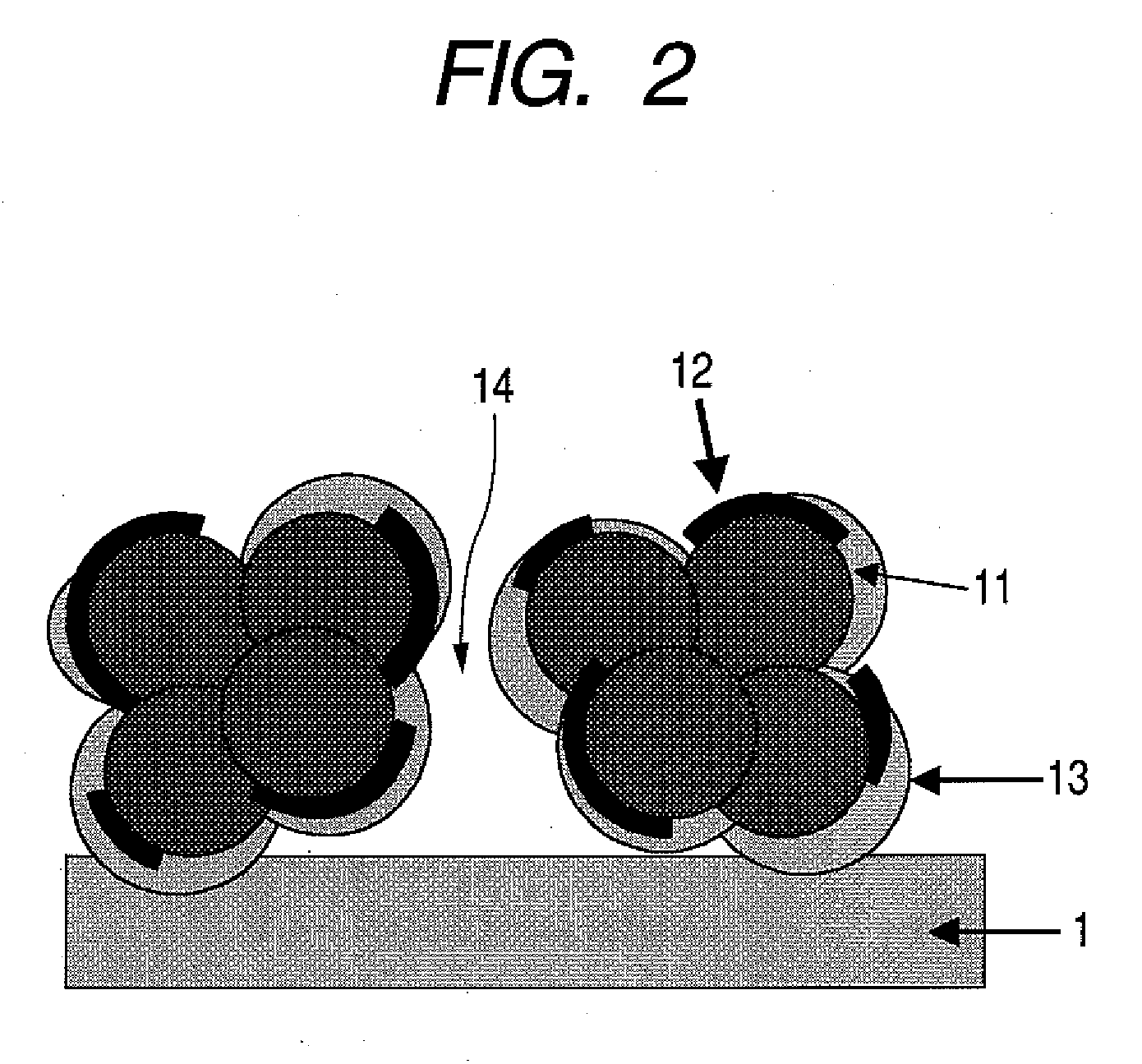
[0152] (Step 1)
[0153] A porous platinum oxide layer having a thickness of 2 μm was formed by means of a reactive sputtering method on a surface composed of carbon fine particles of carbon cloth (LT-1400W manufactured by E-TEK) as a substrate for a catalyst layer serving also as a gas-diffusion layer. The reactive sputtering was performed under the conditions of: a total pressure of 5 Pa; an oxygen flow rate ratio (QO2 / (QAr+QO2)) of 70%; a substrate temperature of 25° C.; and an RF input power of 5.4 W / cm2.
[0154] (Step 2)
[0155] Subsequently, the composite of the porous platinum oxide layer and the gas-diffusion layer was brought into contact with the steam of TMCTS (having a partial pressure of 0.05 Pa) at 25° C. for 5 minutes, whereby a methylsiloxane polymer was formed on the surface of a platinum oxide. In Example 3, a heat treatment like Example 1 was not performed as a subsequent step.
[0156] (Step 3)
[0157] Subsequently, the obtained catalyst layer was subjected to a reducti...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com