Nonvolatile semiconductor memory device having excellent charge retention and manufacturing process of the same
a semiconductor memory and charge retention technology, applied in the direction of semiconductor devices, electrical appliances, nanotechnology, etc., can solve the problems of high device integration difficulty, data erasure operation speed improvement difficulty, etc., and achieve excellent adhesiveness and excellent productivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
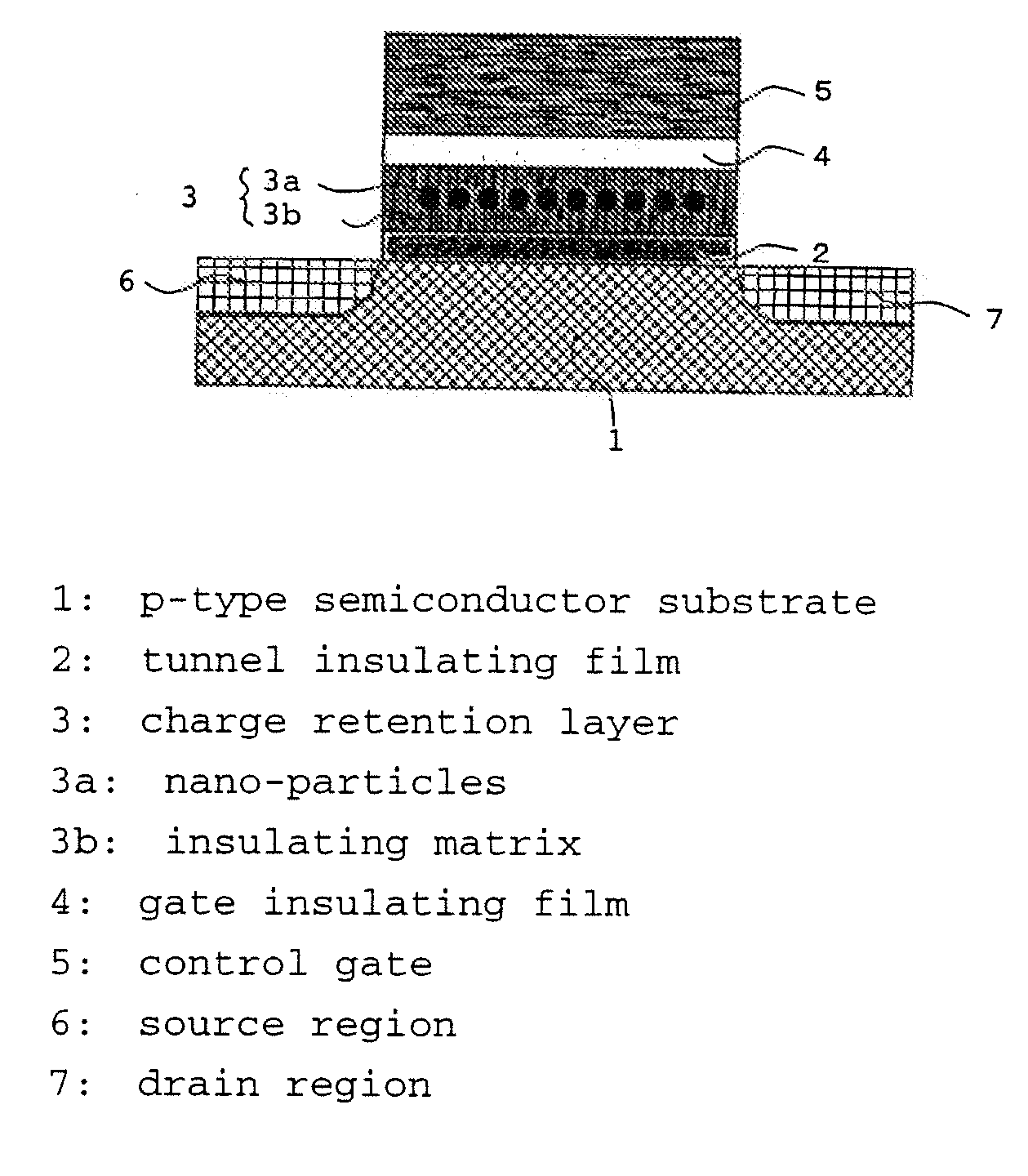
[0097] The nonvolatile semiconductor memory device of this Example will be explained, referring to FIG. 2. A tunnel insulating film 2 was formed on a p-type semiconductor substrate 1. The tunnel insulating film 2 was formed on the surface of the semiconductor substrate 1 by subjecting the semiconductor substrate to thermal oxidation at 800° C. and had a thickness of 5 nm.
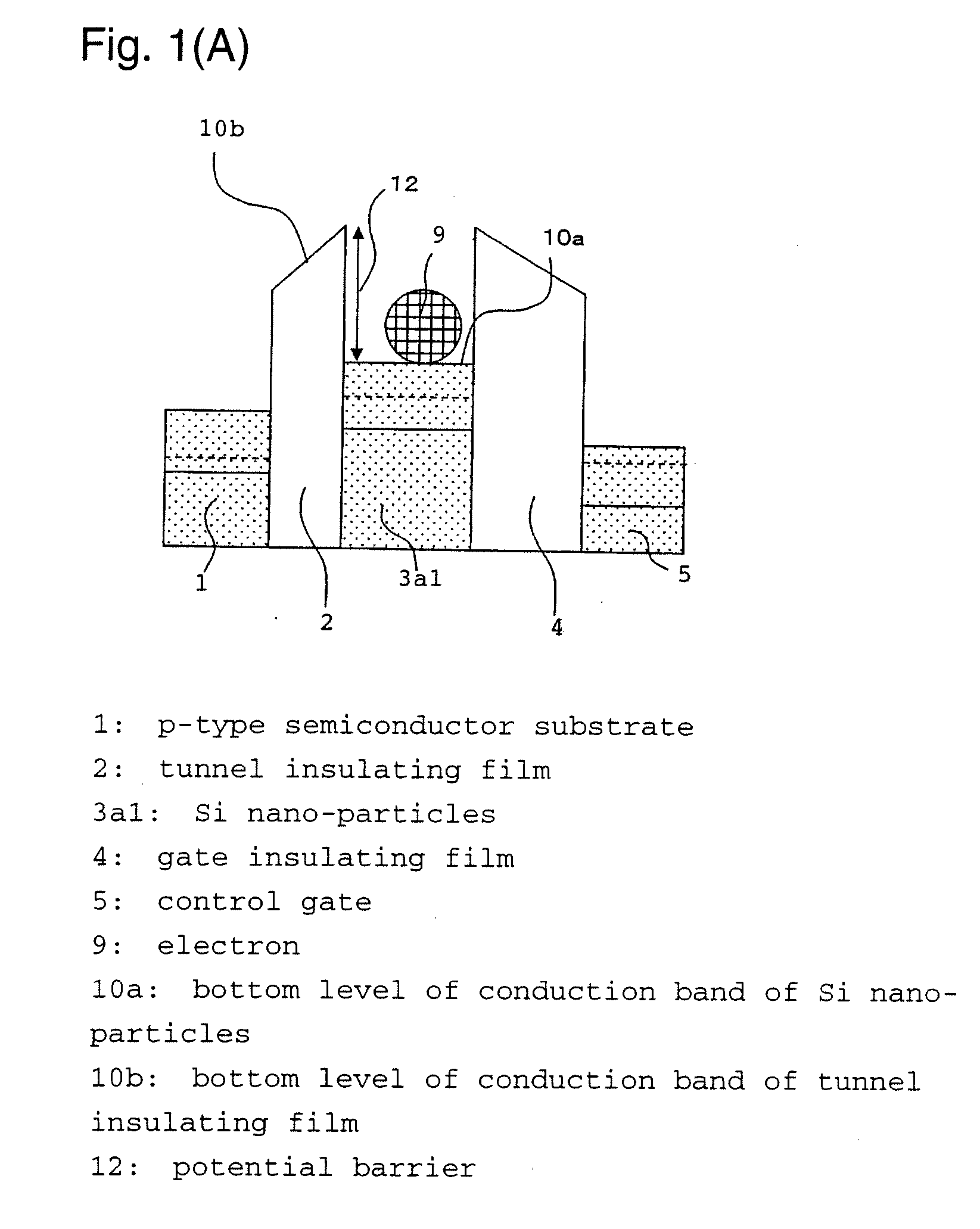
[0098] Then a charge retention layer 3 constituted by an insulating matrix 3b containing nano-particles 3a, was formed so as to have a thickness of 5 nm by a capacitively coupled magnetron sputtering method as described below. Metal Co having a work function of 5.0 eV was selected for the nano-particles and amorphous SiO2 having an electron affinity of 1.0 eV for the insulating matrix. In the sputtering step, a target composed of a SiO2 target having a diameter of 3 inches (7.62 cm) and Co chips of 5 mm square placed thereon, was employed. The amount of the Co chips was adjusted so that the chips occupy 20% of the ...
example 2
[0102] The nonvolatile semiconductor memory device of this example is explained, referring to FIG. 3. An SOI (Silicon On Insulator) substrate having a p-type SOI layer 1a, was employed for a p-type semiconductor substrate 1. An isolation was performed by a mesa process and boron was implanted to adjust the threshold voltage. The work function of the p-type SOI layer 1a was estimated to be 4.95 eV at this time. Then, a tunnel insulating film 2 was formed on the surface of the p-type SOI layer 1a. The tunnel insulating film 2 was formed by subjecting the semiconductor substrate to thermal oxidation at 800° C. and has a thickness of 3 nm.
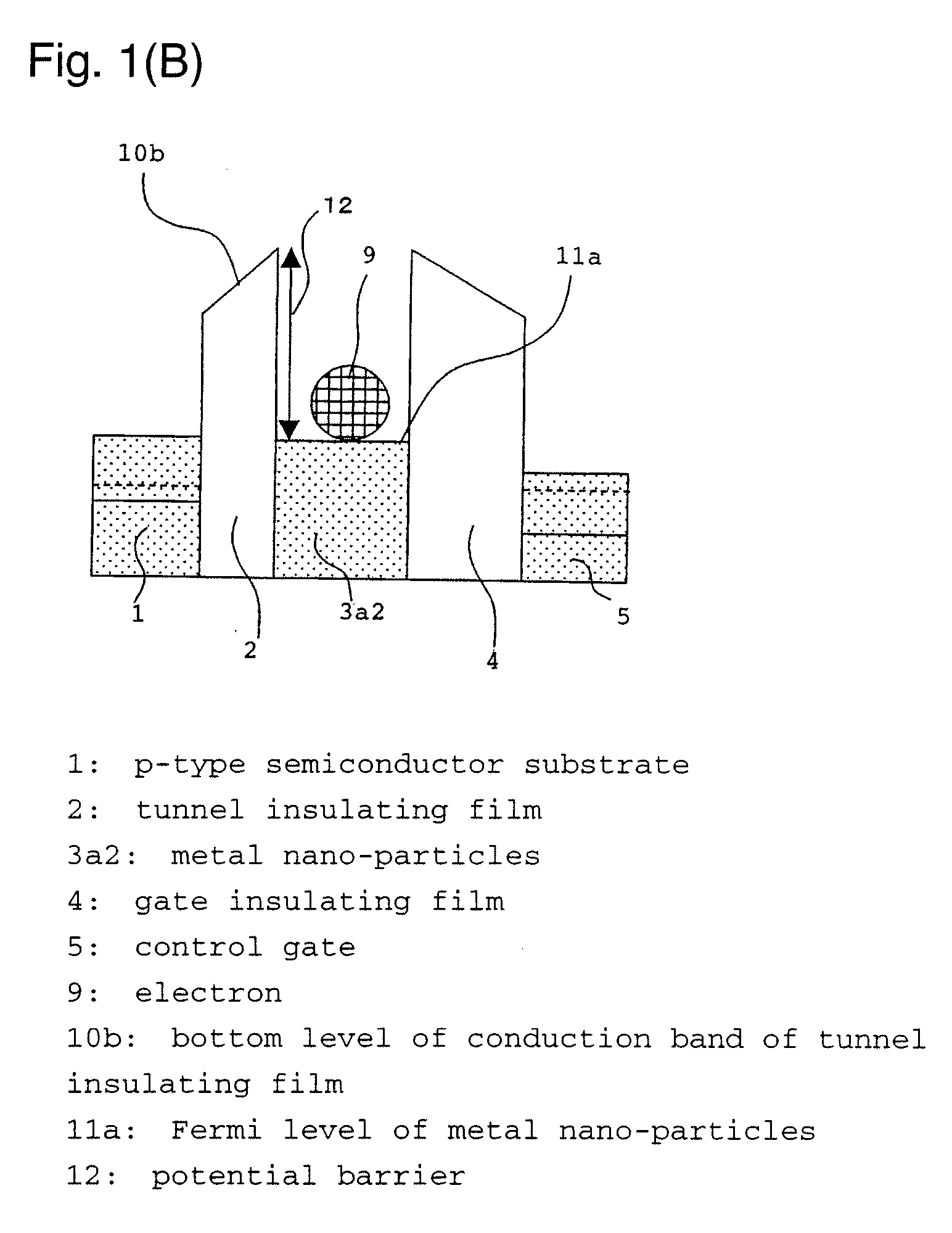
[0103] Then, a charge retention layer 3 composed of an insulating matrix 3b containing nano-particles 3a was formed to have a thickness of 5 nm by a capacitively coupled magnetron sputtering method as follows. Metal Ru having a work function of 4.7 eV was selected for the material of the nano-particles, and AlN having a negative electron affinity was ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com