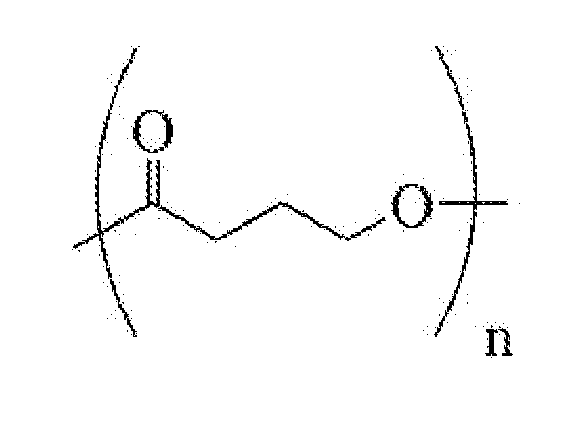
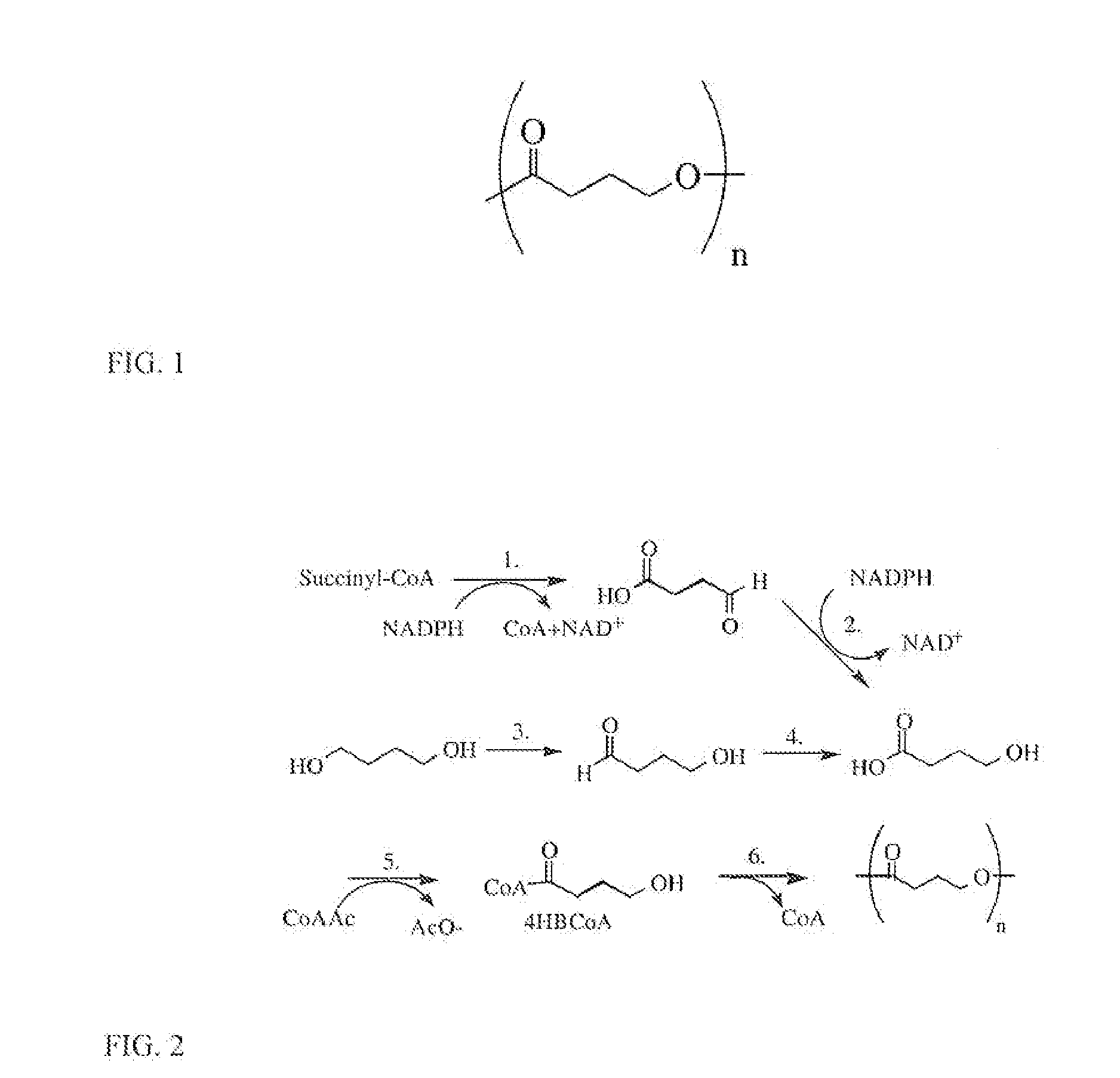
Toughened Polylactic Acid Polymers and Copolymers
a polylactic acid polymer and copolymer technology, applied in the field of polymer compositions, can solve the problems of poor mechanical properties of blends, brittle glassy objects of plla at room temperature, and general stiffness of objects, and achieves the effects of reducing the number of elongation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Preparation of a Blend of PLA Polymer and P4HB Polymer
[0041]PLLA polymer (Resomer L 214 lot #1012474, Boehringer Ingelheim, Germany) with a viscosity of 5.9 dl / g (IV) was compounded with P4HB (poly-4-hydroxybutyrate, Mw 178,000, 2.3 dl / g (IV) (Tepha, Inc., Cambridge, Mass.) using a Leistritz 18 mm twin screw extruder (24:1 L / D). Compounding was undertaken at a temperature of 110° C. at the feed, and 230° C. at the die. The polymers were mixed i the molten state, extruded into large diameter filament, quenched into a water bath set at 5-20° C., and cut into 2-5 mm length pellets. The PLLA and P4HB were compounded in the following three different ratios by weight: PLLA (90%):P4HB (10%); PLLA (77.5%):P4HB (22.5%); and PLLA (10%):P4HB (90%).
example 2
Preparation of a Blend of PLA Polymer and P4HB Polymer
[0042]PLLA polymer (Resomer L 214 lot #1002260, Boehringer Ingelheim, Germany) with a high intrinsic viscosity of 7.0 dl / g (IV) was dry mixed with P4HB (poly-4-hydroxybutyrate, Mw 170,000, 2.1 dl / g (IV) Tepha, Inc., Cambridge, Mass.) by tumble mixing at room temperature. The PLLA and P4HB were compounded in the following three different ratios by weight: PLLA (90%):P4HB (10%); PLLA (77.5%):P4HB (22.5%); and PLLA (10%):P4HB (90%).
example 3
Fiber Extrusion of PLA / P4HB Blends
[0043]The blends prepared in Example 1 were extruded into monofilament fiber using the following method. The blends were dried under vacuum overnight to less than 0.01% (w / w) water. Dried pellets of the blended polymers were fed into an extruder barrel of an AJA (Alex James Associates, Greer, S.C.) ¾″ single screw extruder (24:1 L:D, 3:1 compression) equipped with a Zenith type metering pump (0.16 cc / rev) and a die with a single hole spinneret (0.026″, 2:1 L:D) under a blanket of nitrogen. The 4 heating zones of the extruder were set at 140°, 190°, 200° and 205° C. The block, metering pump and the die were maintained at a constant temperature, preferably 180-250° C. Pump discharge pressure was kept below 1500 psi by controlling the temperatures and the speed of the metering pump. The fiber spinning system was set up with a drop zone, air quench zone, a guide roll, three winders and a pickup. The fiber was oriented in-line with extrusion by drawing i...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| elongation to break | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Tm | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Tg | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com