Peptides with antioxidant and antimicrobial properties
a technology of antioxidant and antimicrobial properties, applied in the direction of peptide/protein ingredients, peptide sources, metabolic disorders, etc., can solve the problems of airspace collapse, reduced lung compliance, impaired gas exchange, etc., to prevent lipid oxidation and/or microbial proliferation, reduce lung injury, and prevent spoilage of products
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples
Methods
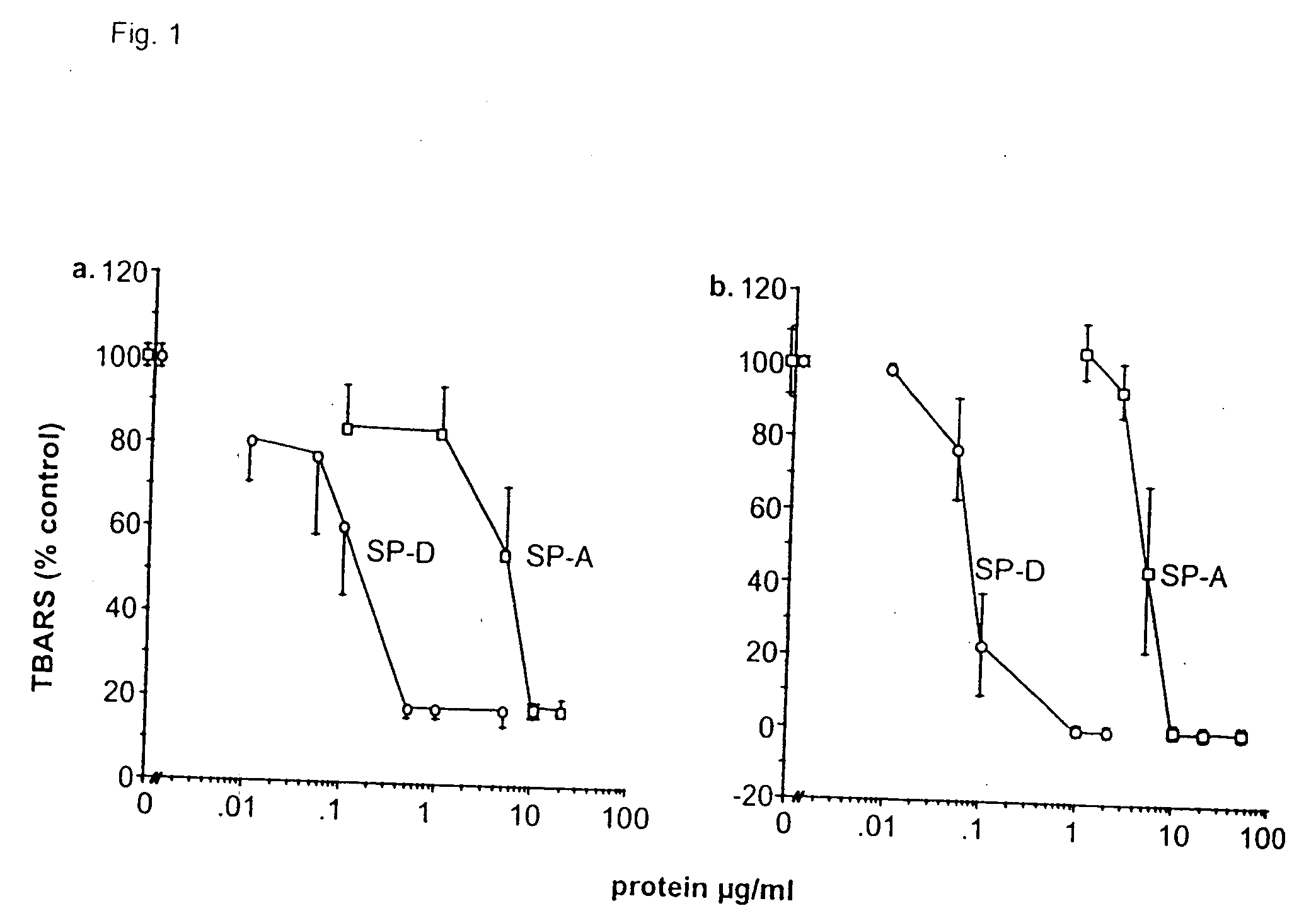
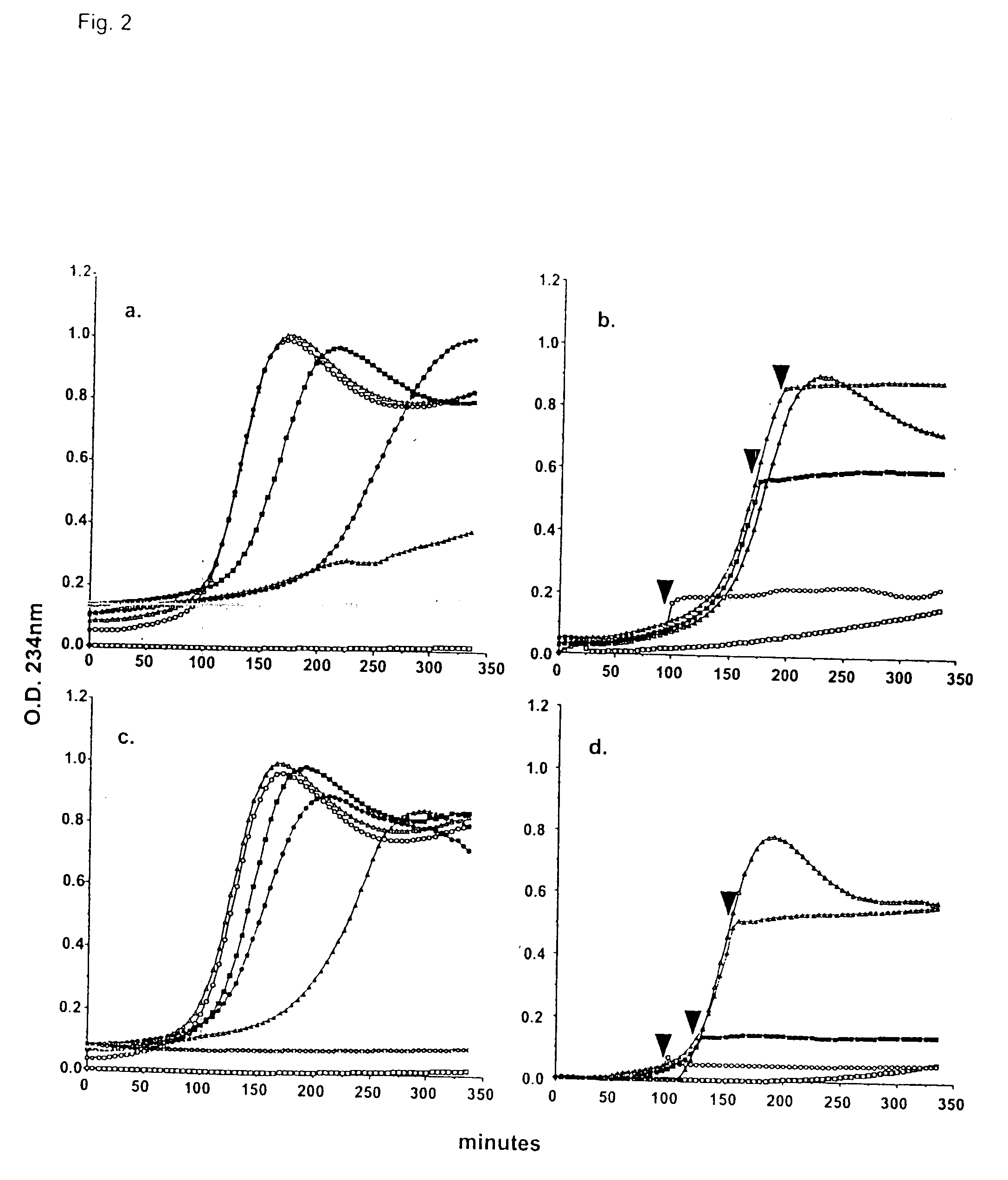
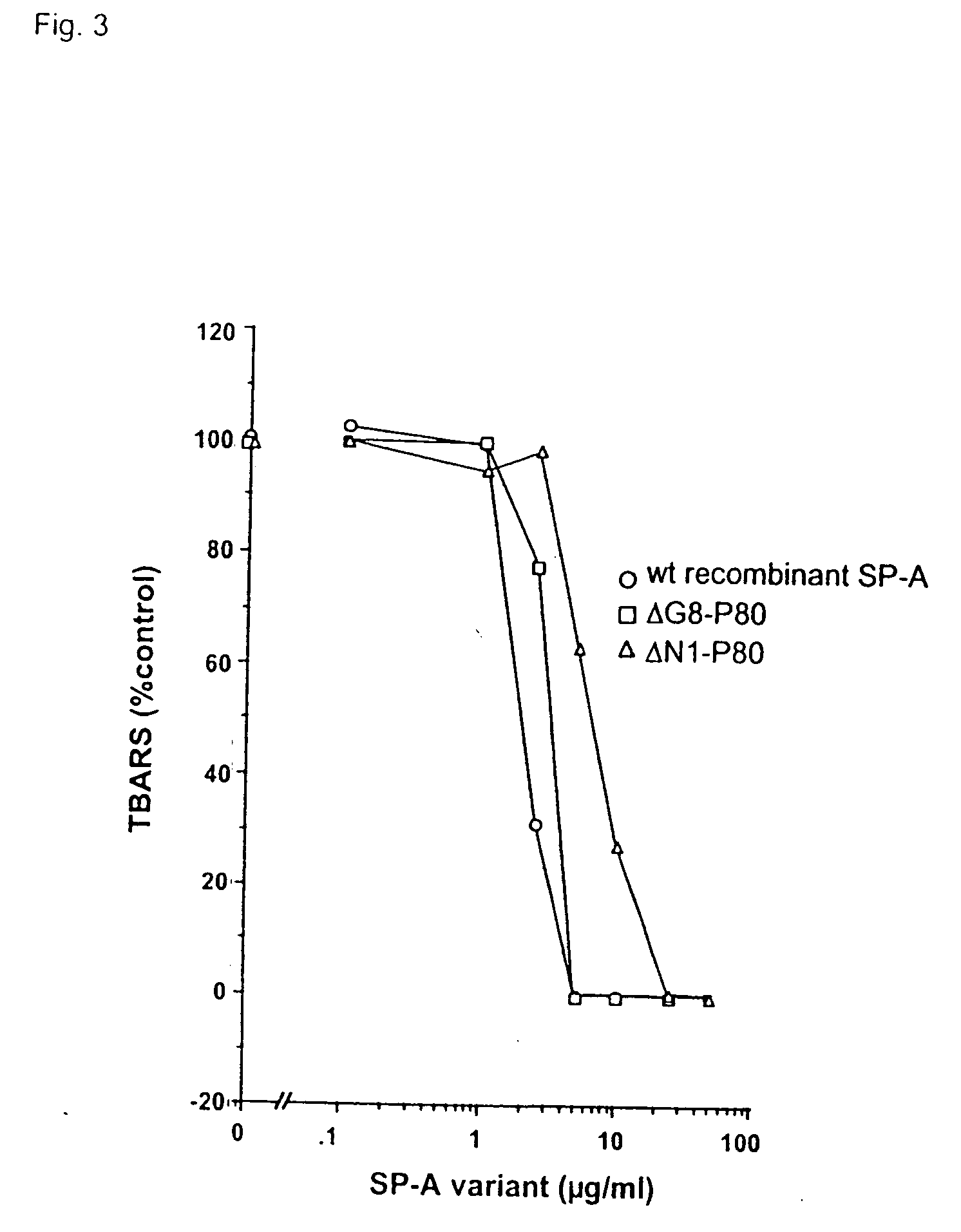
Purification and Modification of Surfactant Proteins—Antioxidant Properties
[0168] Native SP-A and SP-D were isolated from the alveolar wash of rats which had been pretreated with intratracheal silica to enhance the collectin yield, in accordance with the method of Dethloff et al., Biochem. J. 233:111-118 (1986). After centrifugation, rat SP-D was purified by maltose-Sepharose affinity chromatography of the supernatant and rat SP-A was purified from the pellet by NaBr flotation, butanol extraction and mannose-Sepharose affinity chromatography, in accordance with the method of McCormack et al., J. Biol. Chem. 272:27971-27979 (1997). Mouse SP-D was used interchangeably with rat SP-D. All proteins were extensively dialyzed to remove residual EDTA. For some experiments, rat SP-A and rat SP-D were alkylated by incubation with 0.5 M iodoacetamide at 37° C. in the dark for 1 hr and then extensively dialyzed. The wild type and mutant recombinant SP-A, SP-D and MBP used in this stu...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| weight percent | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| weight percent | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| weight percent | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com