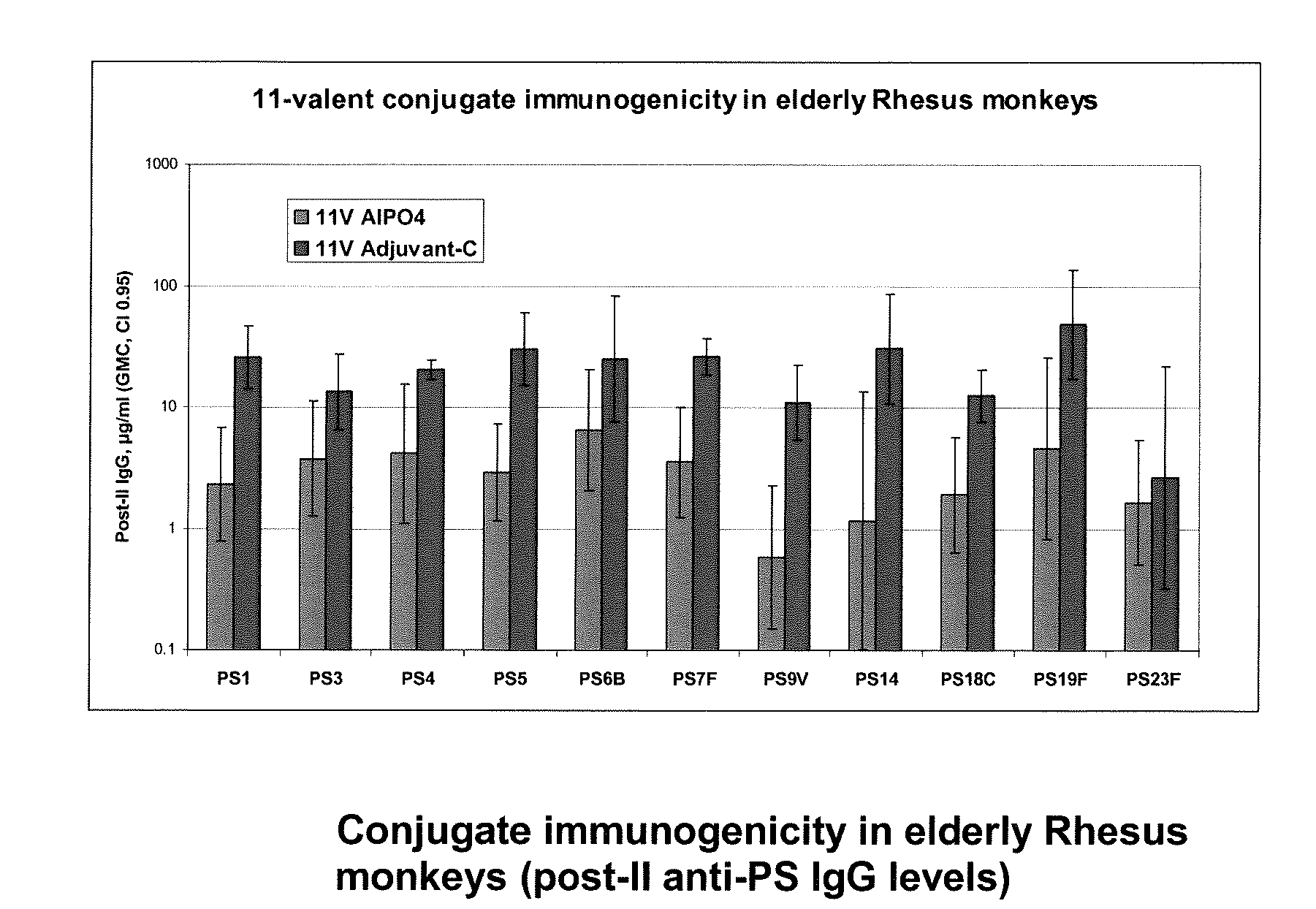
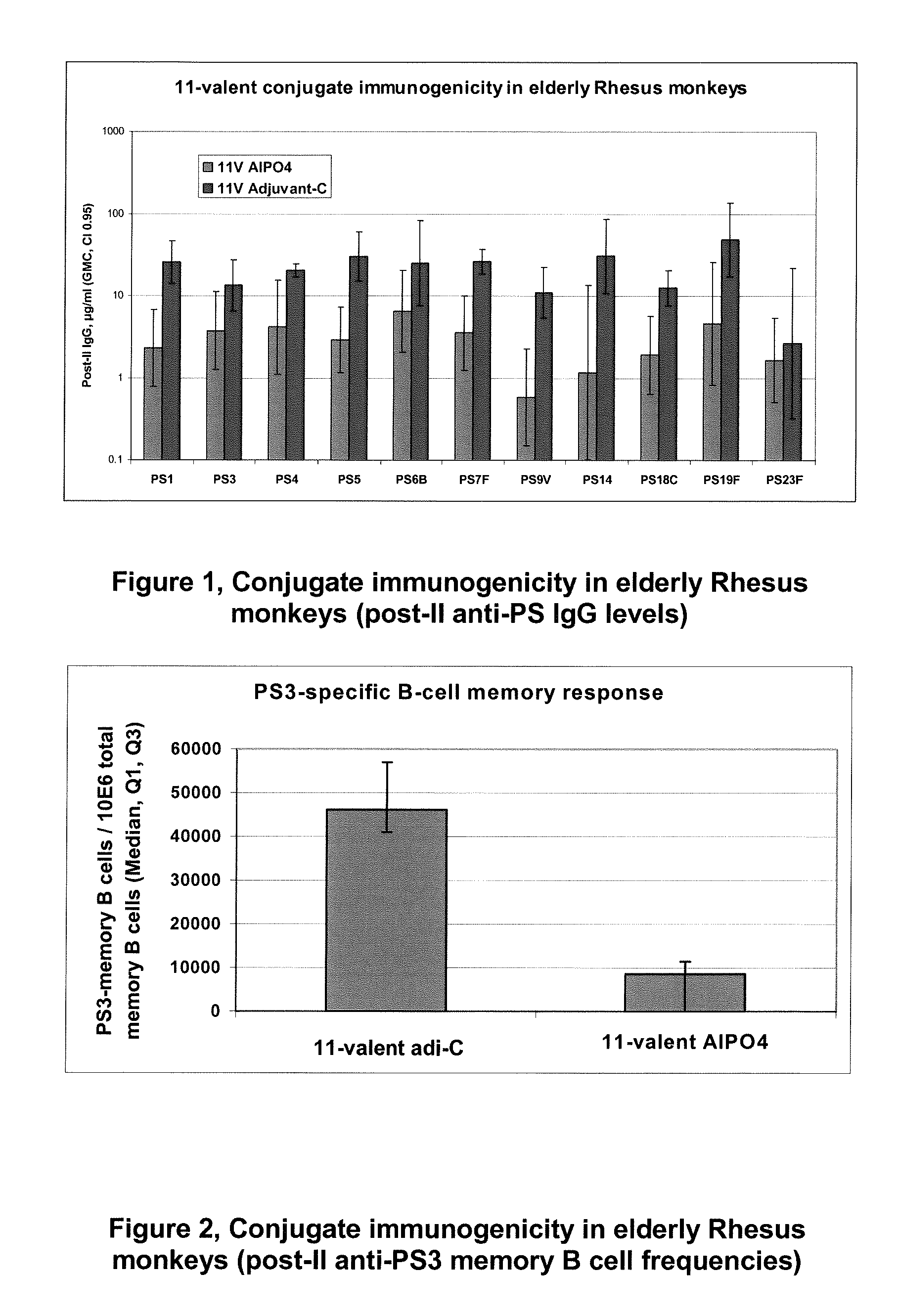
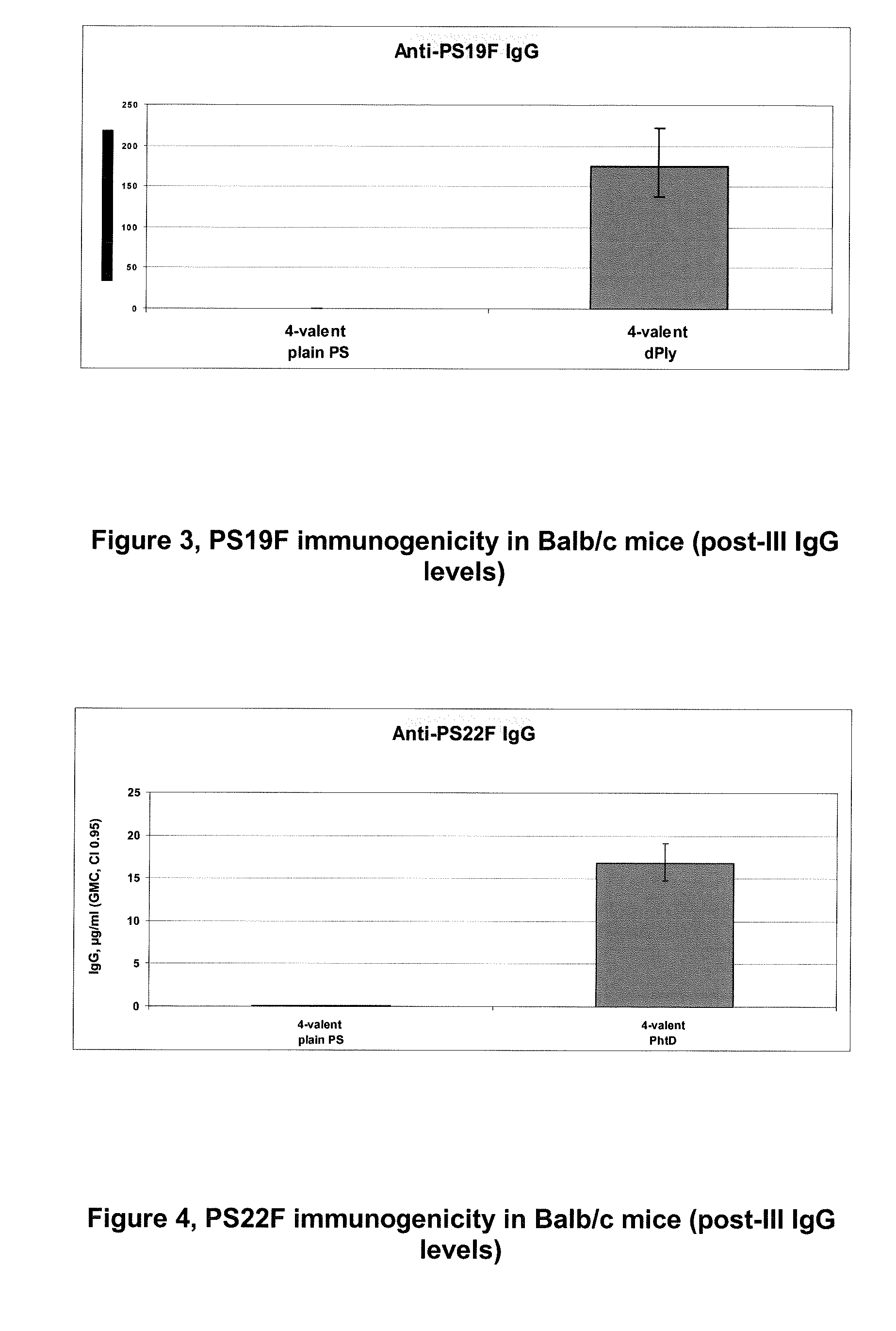
Pneumococcal Polysaccharide Conjugate Vaccine
a polysaccharide and conjugate technology, applied in the field of improved streptococcus pneumoniae vaccine, can solve the problems of reducing the immune response, immunological effects, and th-cells available to provide the necessary help
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Expression of Protein D
Haemophilus Influenzae Protein D
Genetic Construction for Protein D Expression
[0152]Starting Materials
The Protein D encoding DNA
[0153]Protein D is highly conserved among H. influenzae of all serotypes and non-typeable strains. The vector pHIC348 containing the DNA sequence encoding the entire protein D gene has been obtained from Dr. A. Forsgren, Department of Medical Microbiology, University of Lund, Malmo General Hospital, Malmö, Sweden. The DNA sequence of protein D has been published by Janson et al. (1991) Infect. Immun. 59: 119-125.
The Expression Vector pMG1
[0154]The expression vector pMG1 is a derivative of pBR322 (Gross et al., 1985) in which bacteriophage λ derived control elements for transcription and translation of foreign inserted genes were introduced (Shatzman et al., 1983). In addition, the Ampicillin resistance gene was exchanged with the Kanamycin resistance gene.
The E. Coli Strain AR58
[0155]The E. coli strain AR58 was generated by transductio...
example 1b
Expression of PhtD
[0173]The PhtD protein is a member of the pneumococcal histidine-triad (Pht) protein family characterized by the presence of histidine-triads (HXXHXH motif). PhtD is a 838 aa-molecule and carries 5 histidine triads (see MedImmune WO00 / 37105 SEQ ID NO: 4 for amino acid sequence and SEQ ID NO: 5 for DNA sequence). PhtD also contains a proline-rich region in the middle (amino acid position 348-380). PhtD has a 20 aa-N-terminal signal sequence with a LXXC motif.
Genetic Construct
[0174]The gene sequence of the mature Medimmune PhtD protein (from aa 21 to aa 838) was transferred recombinantly to E. coli using the in-house pTCMP14 vector carrying the pλ promoter. The E. coli host strain is AR58, which carries the cI857 thermosensitive repressor, allowing heat-induction of the promotor.
[0175]Polymerase chain reaction was realized to amplify the phtD gene from a MedImmune plasmid (carrying the phtD gene from Streptococcus pneumoniae strain Norway 4 (serotype 4)-SEQ ID NO: 5 ...
example 1c
Expression of Pneumolysin
[0184]Pneumococcal pneumolysin was prepared and detoxified as described in WO2004 / 08 1515 and WO2006 / 032499.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Electric charge | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com