Methods of PCR-Based Detection of "Ultra Short" Nucleic Acid Sequences
a nucleic acid sequence and ultra-short technology, applied in the field of pcr-based detection of ultra-short nucleic acid sequences, can solve the problems of necrosis considered to be catastrophic metabolic failure, short specific nucleic acid biomarkers, and inflammation of surrounding cells, so as to reduce the degradation of nucleic acids, inhibit nuclease activity, and reduce the effect of nucleic acid degradation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0190]Example 1 shows the design of primers with internally located fluorophores for detection of ultra short DNA targets by PCR using fret-dependent fluorescence.
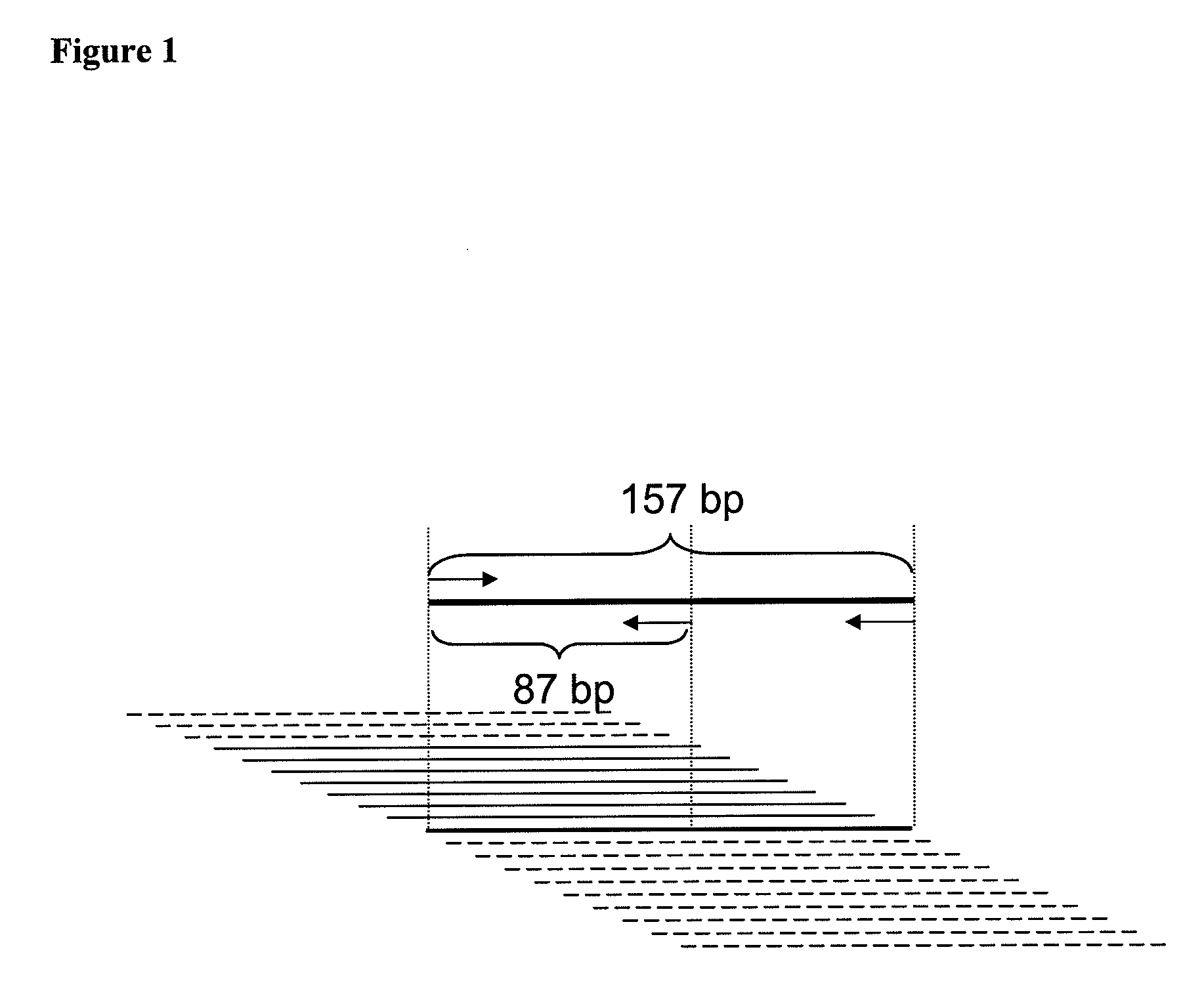
[0191]The specificity of a typical labeled-primer qPCR assay is determined solely by the specificity of the two primers, and therefore such an assay is not capable of distinguishing between templates having identical primer binding sites but different intervening sequences. To detect very short target fragments and overcome this limitation, novel labeled-primer assays were developed specific for targets in which the primer binding sites are either immediately adjacent to each other or even slightly overlapping, thus lacking any intervening sequences. Such amplicons are characterized by the pair of primer-derived sequences positioned in close proximity to each other in the double-stranded PCR product. In the assay, the mutual proximity of fluorescently labeled oligonucleotides was detected by Förster resonance energy transf...
example 2
[0200]Example 2 shows the design of primers with fluorophores located on 5′-end for detection of ultra short DNA targets by PCR using fret-dependent fluorescence
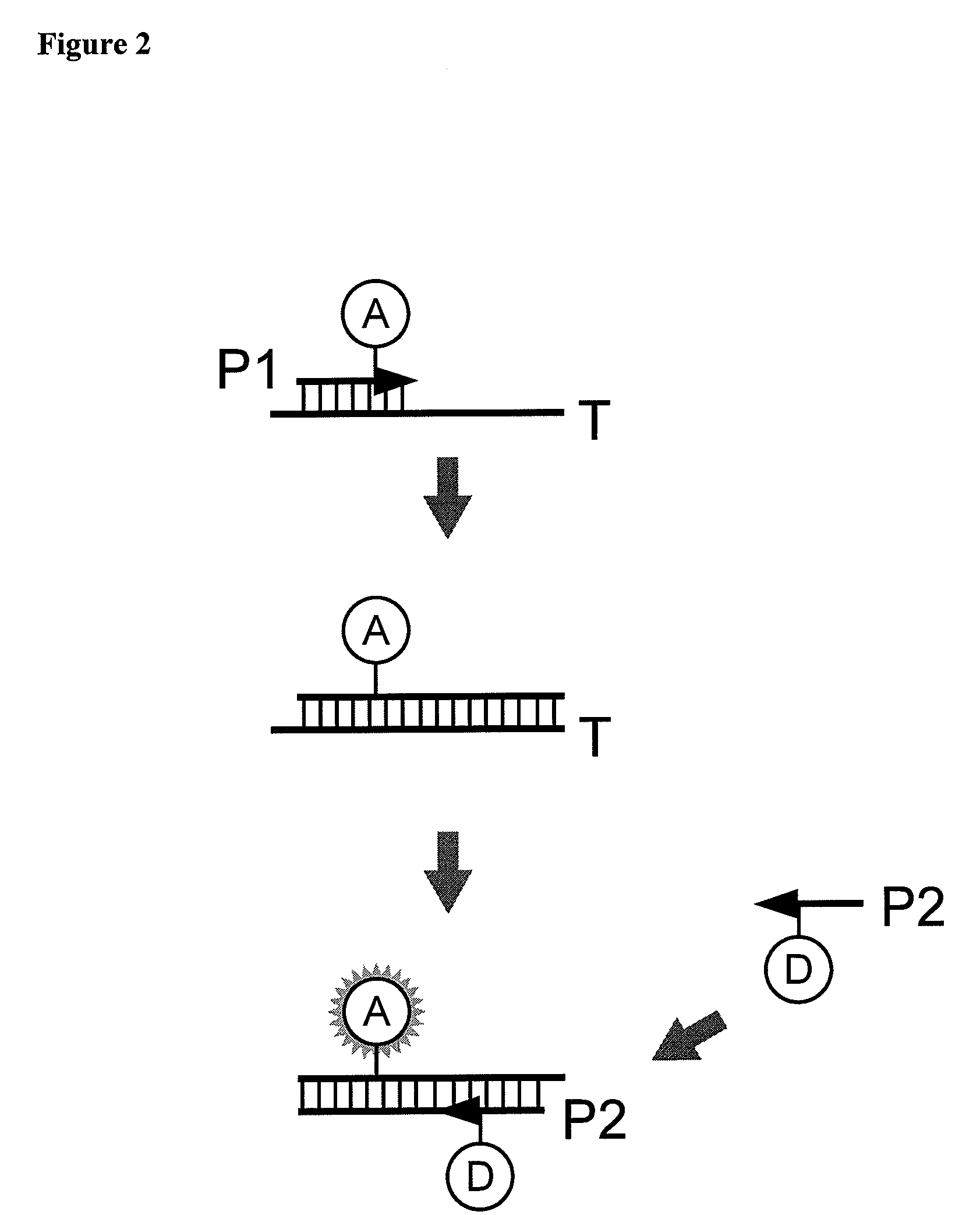
[0201]Compared to unlabeled primers, the use of primers labeled with fluorophores near their 3′ ends may lower the efficiency of the PCR, most likely due to reduction in polymerase processivity as it reads fluorophore-labeled bases of the primers incorporated into templates. To overcome this problem, another variant of the labeled-primer FRET qPCR scheme was developed. In this example, as shown in FIG. 7, the primers contain oligonucleotide tails at the 5′ ends of their target-binding sequences. In FIG. 7, T designates a template; P1 and P2 designate primers; D and A designate donor and acceptor fluorophores, respectively; black circles denote the positions of replication-blocking modifications. The tails are labeled at their 5′ ends with appropriate fluorophores, so that each double-stranded PCR product molecule carries a F...
example 3
[0203]Example 3 shows the design of single-tube PCR scheme for detection of ultra short DNA targets.
[0204]A novel qPCR scheme was developed that offers high target specificity by utilizing three sequence-specific components, including a TaqMan probe, yet allows for very short amplicons by means of a partial target recognition sequence overlap of the TaqMan probe with the sense (same-strand) target-specific primer. To accommodate the overlapping probe and primer, a novel 2-stage single-tube qPCR scheme was devised. The flow diagram provided in FIG. 8 shows the specific details and steps of the reaction. In FIG. 8, T designates a template; P1, P2, and P3 designate primers; IP1 and IP2 designate intermediate products; Pr designates TaqMan™ probe, dual-labeled with fluorophore F and quencher Q. In stage 1, the target DNA template T is amplified using primers P1 and P2, which map in very close proximity to each other on the target sequence, thus allowing for very short templates. Primer ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com