Imaging agents and methods of use thereof
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
In Vivo 13C PASADENA Imaging
[0046]Utilizing a PASADENA polarizer, the inventors injected hyperpolarized 13C-molecules in rats. Transmitting at the 13C-frequency, images were acquired using TrueFISP pulse sequences, 3D FIESTA (acronyms for transient versions of so-called steady state free procession image sequences) and fast CSI (chemical shift imaging) sequences. Examples of 13C images acquired utilizing PASADENA hyperpolarization (FIGS. 3-4) were produced using 13C-labeled hydroxyethyl acrylate which on hydrogenation forms hydroxyethyl propionate.
[0047]Sub-second carbon imaging is greatly simplified when the signal of interest exceeds the background signal from natural abundance resonances. This is possible when a 13C hyperpolarized agent is injected. Substantially enhanced images can be acquired during an interval several times the T1 of 13C polarization. Long T1 (in excess of ten seconds) is obtained for 13C in small molecules at sites where there is no directly attached proton. ...
example 2
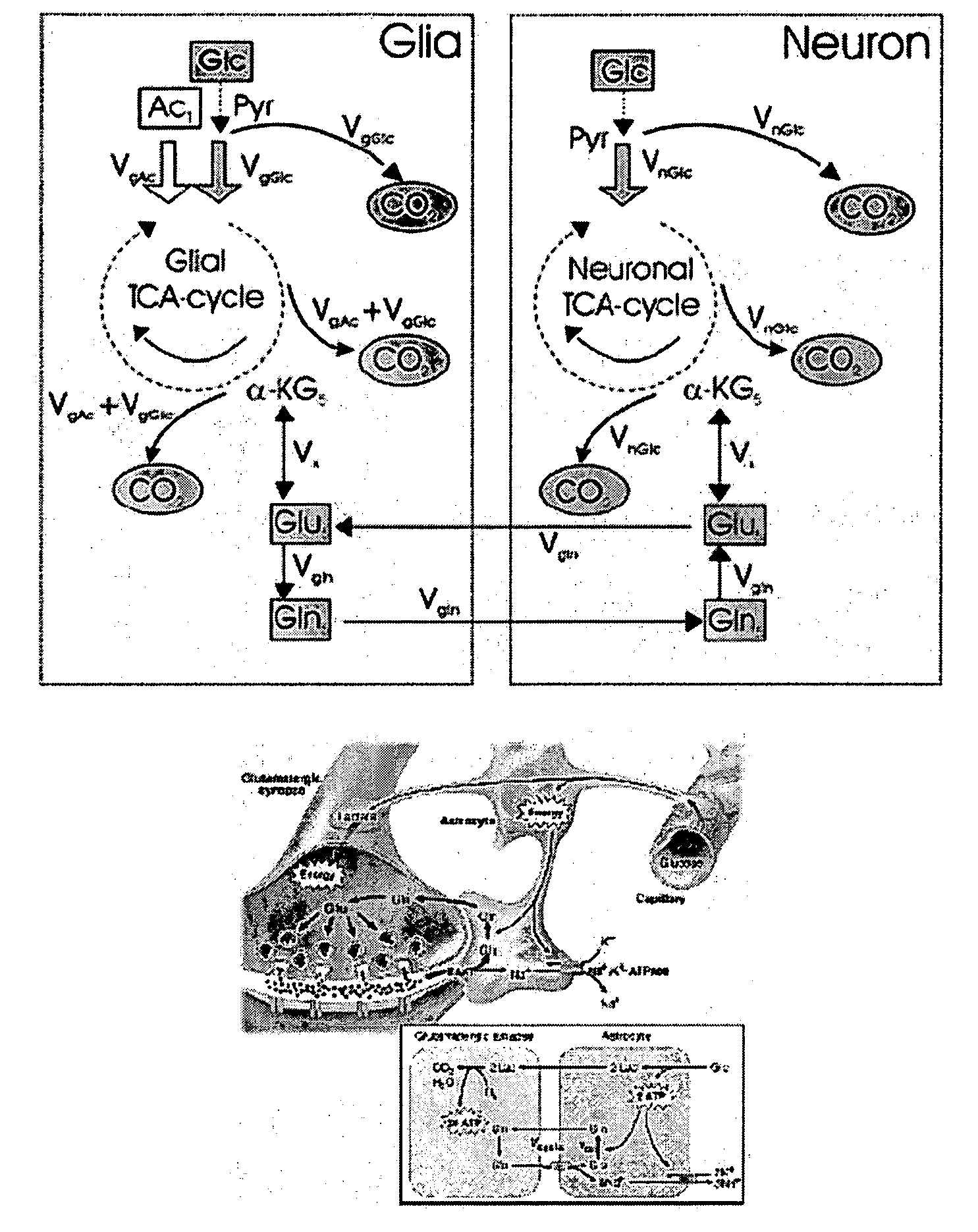
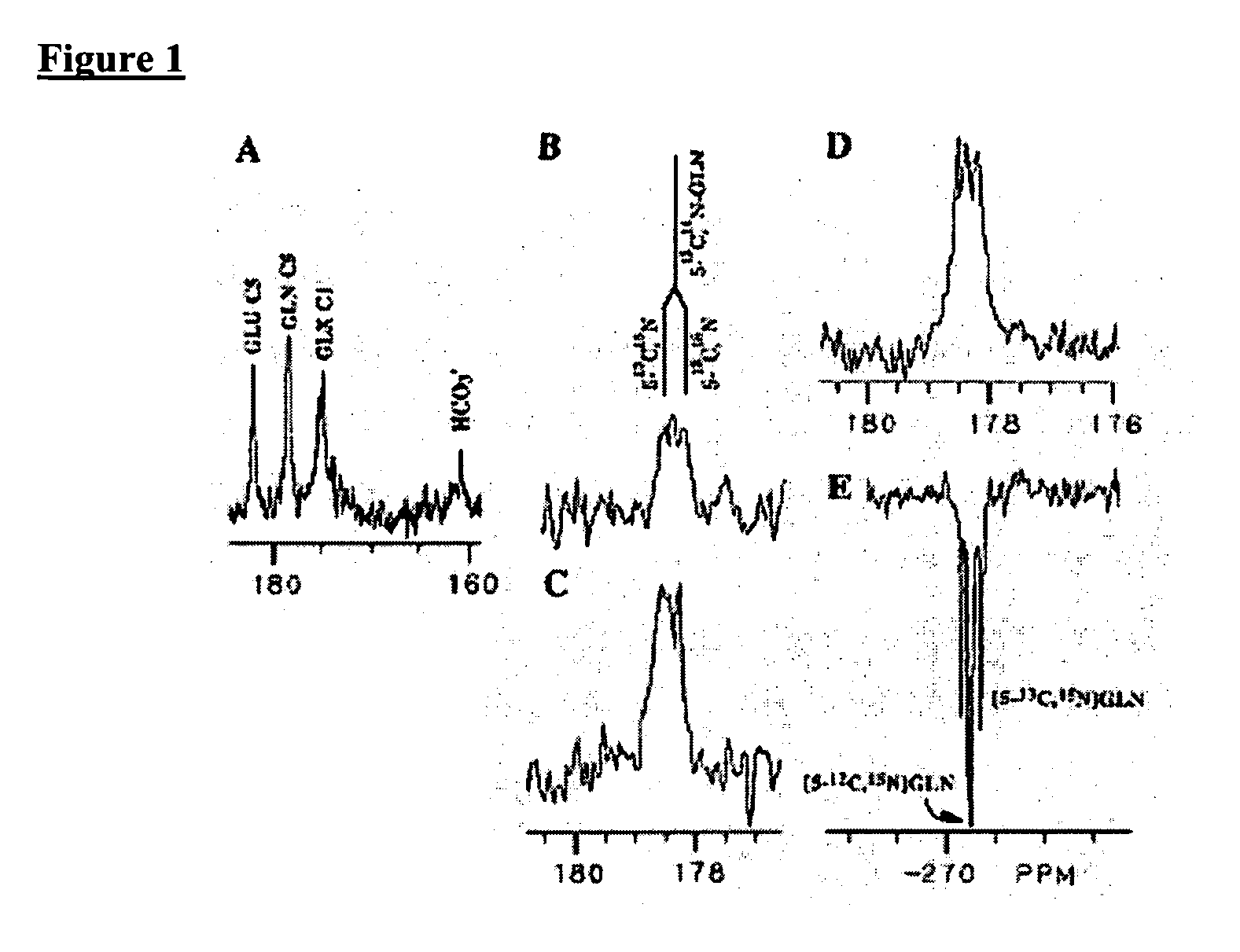
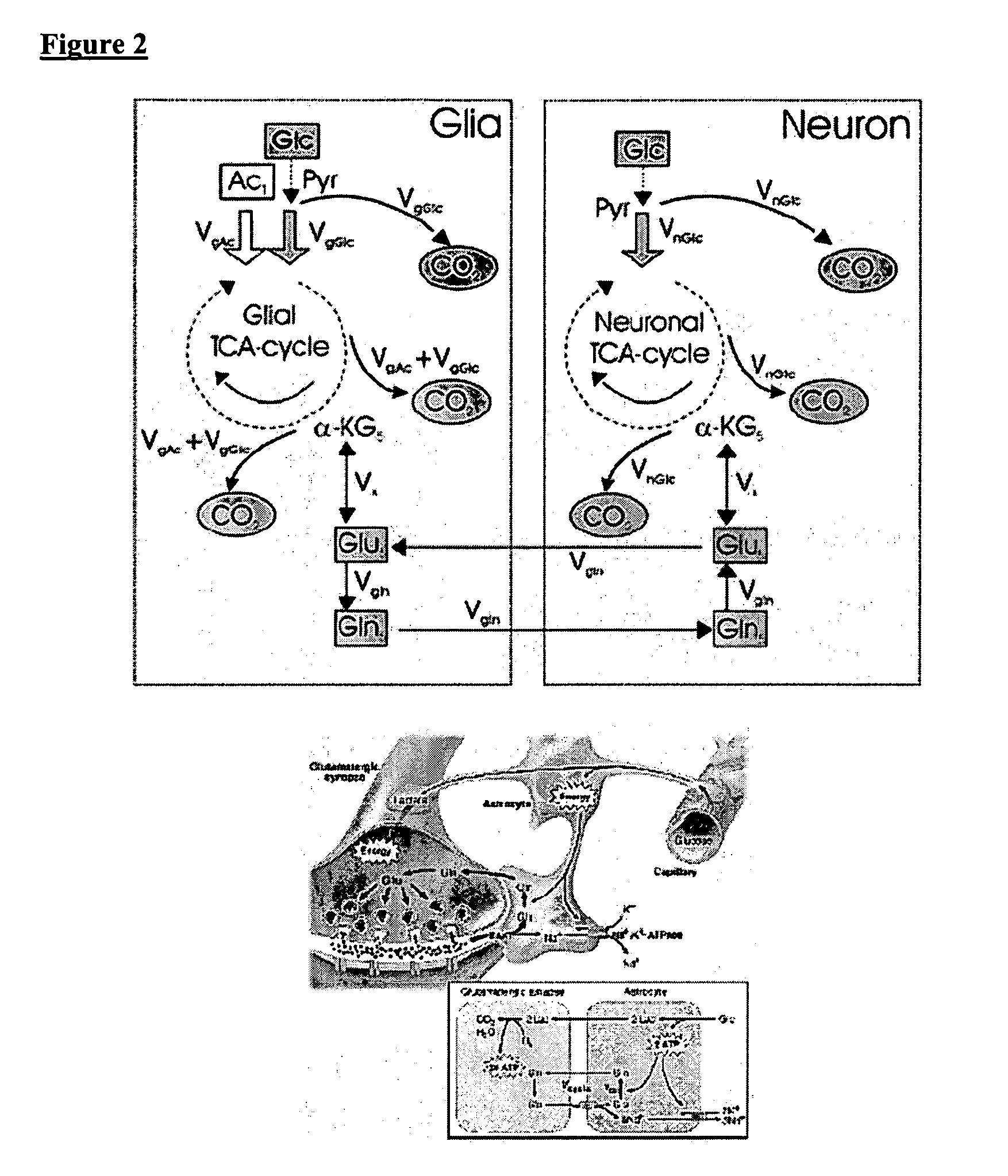
[0051]The inventors have used 13C labeled isotopes of intrinsic biological molecules, such as glucose, which are metabolized in the body via the TCA cycle that can be tracked with MR spectroscopy. This allows the elucidation of biochemical processes such as glutamate neurotransmission and metabolite synthesis rates in vivo. However, based on the Boltzmann distribution, 13C NMR suffers from inherently low SNR, requiring the use of lengthy pulse sequences which limits its use due to heat deposition and the instability of the subjects over literally hours of scan time. This is where hyperpolarization demonstrates strong potential. The low SNR issues are overcome by polarizations up to 26,000 times greater SNR as demonstrated above. One of the challenges of hyperpolarized imaging is the need for fast spectroscopy sequences due to the fast relaxation of the hyperpolarized signal. Therefore the inventors developed fast chemical shift imaging techniques that allow for t...
example 3
Identifying Hyperpolarization Precursors
[0053]PASADENA: Directed synthesis of PASADENA precursor molecules, suitably enriched with 13C, provides nontoxic tracking reagents with known desired biological properties, including in some cases intracellular transport and metabolism. New reagents may be necessary for the versatile implementation of PASADENA imaging and spectroscopy. Identifying molecules to introduce parahydrogen in biological systems is a feature of the invention.
[0054]The PASADENA precursors may have at least one of the following features: (1) an unsaturated bond suitable for hydrogenation by molecular addition; (2) a hydrogenation reaction with a time scale that is shorter than the low-field singlet state relaxation times (typically tens of seconds) of the nascent protons on intermediates and products; (3) an isotopically-enriched 13C site with scalar coupling to the added protons; (4) water solubility and low toxicity; (5) an ability to be introduced into a specific bi...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Magnetic field | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Composition | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Dynamic | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com