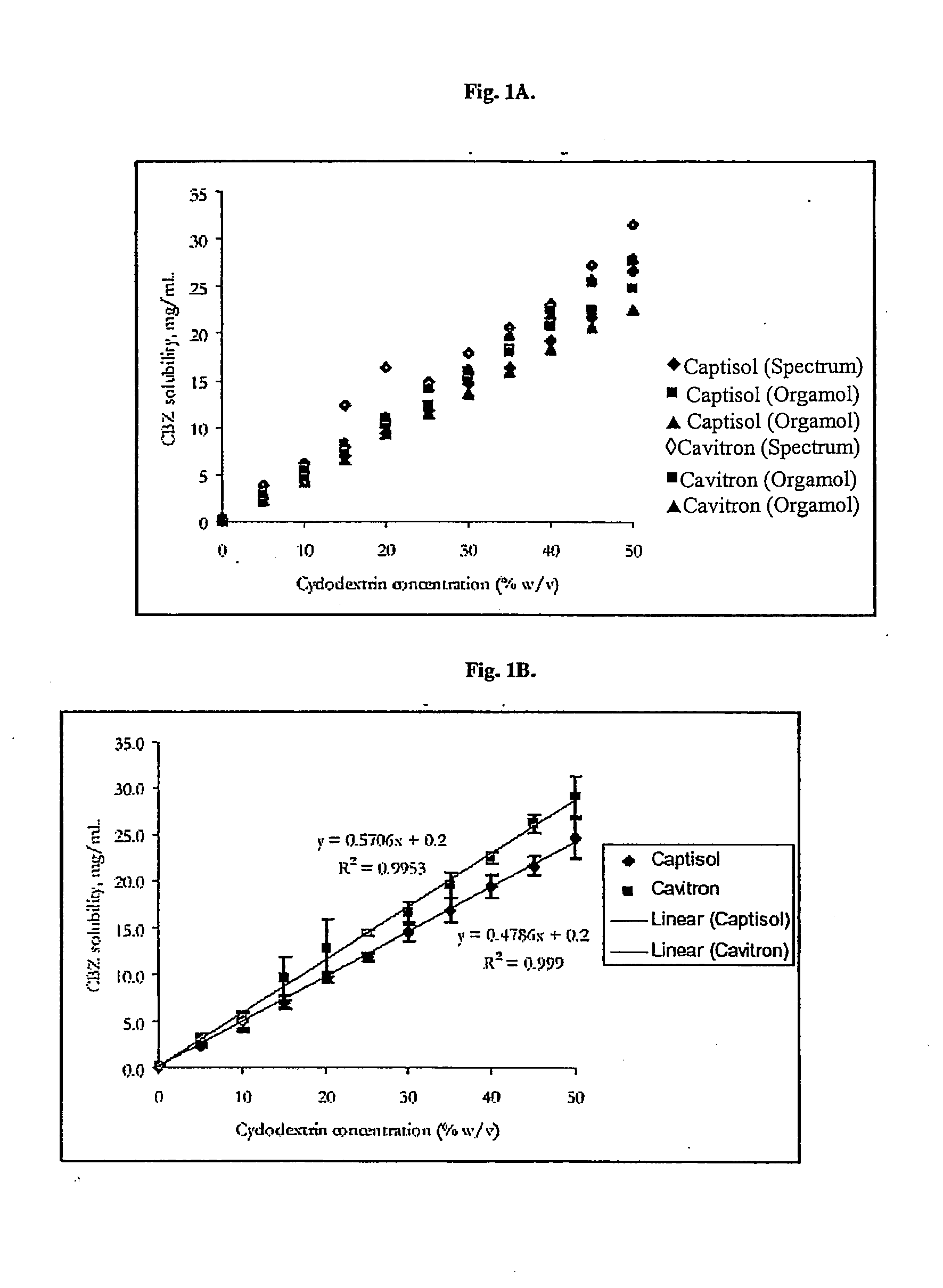
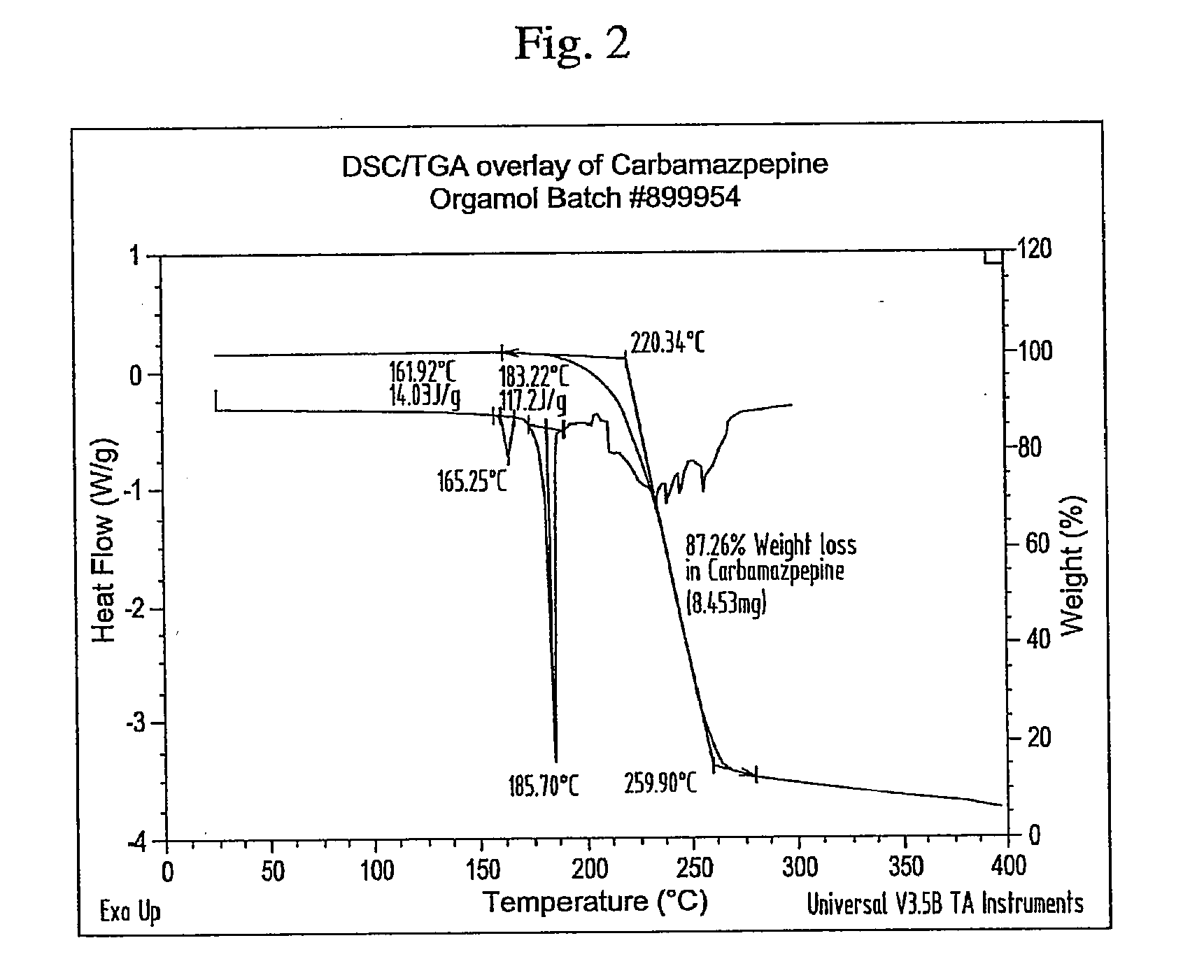
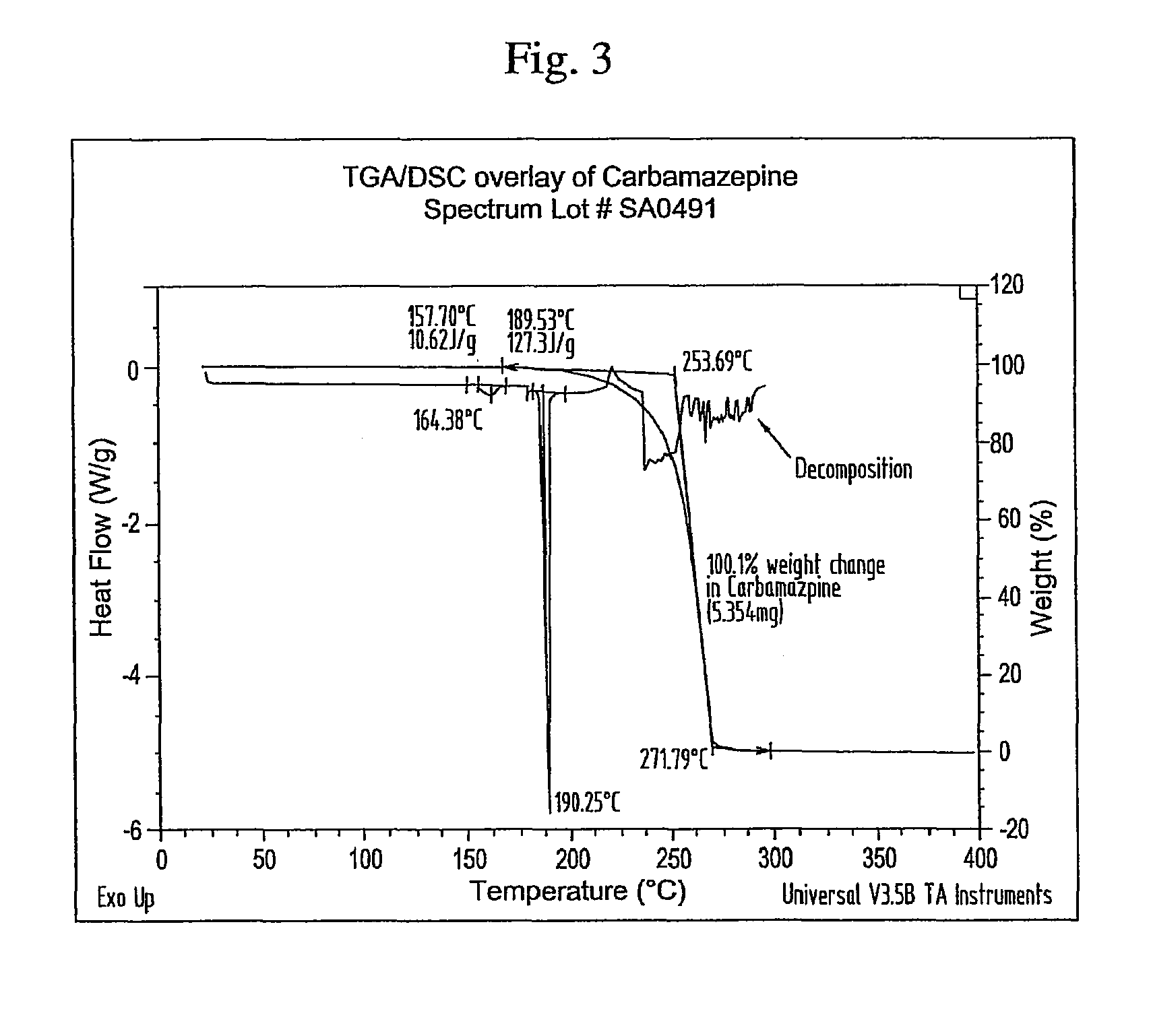
Novel parenteral carbamazepine formulation
a carbamazepine and formulation technology, applied in the field of antiepileptics, can solve the problems of complex use of carbamazepine, no method for providing emergent carbamazepine therapy to a patient in need, and the risk of intravenous formulation for patients treated with carbamazepine (sometimes referred to herein as cbz)
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Preparation of Carbamazepine-Cyclodextrin Inclusion Complex
[0043]450 Grams of hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin (HPBCD) was dissolved in 2.0 L of deionized water to generate a 22.50 w / v solution. 13C, 15N-labeled carbamazepine (CBZ) [purchased from Cambridge Isotope Laboratories (CIL), 50 Frontage Road, Andover, Mass. 01810], 20 grams, was added to this solution. The resulting admixture was stirred for 24 hours at room temperature (20-25° C.). After 24 hours, the solution was sterile filtered through a sterile 0.22 micron Durapore filter into a sterile receiver. Previously sterilized ampoules were then filled and sealed under a nitrogen flush. The filled ampoules were stored at 2-8° C. The resulting inclusion complex had a CBZ concentration of approximately 10 mg / ml.
example 2
Stability Testing
[0044]Ampoules containing 10.1 mg / ml carbamazepine-cyclodextrin inclusion complex were placed on room temperature stability studies and sampled every six months. CBZ was detected by HPLC using UV detection at 215 nm. Results are presented in Table 2.
TABLE 2Stability of Intravenous, Stable-labeled Carbamazepine SolutionInitialDegradationTestingConcentration%Product- CBZ:Datein VialRecoveryiminostilbineMay 31, 200510.1 mg / ml104.65%not detectedNov. 10, 200410.1 mg / ml97.07%not detectedMay 2, 200410.1 mg / ml96.67%not detected
example 3
Pharmacokinetics of Intravenous and Oral Carbamazepine in Patients on Maintenance Therapy
[0045]Indwelling catheters were placed into the arms of test subjects. A single 100 mg dose of stable-labeled (non-radioactive) CBZ (SL-CBZ) was then infused over 10 minutes. At the end of the infusion, the subject's usual morning dose of oral CBZ, less 100 mg, was administered. Blood pressure, heart rate and rhythm, and infusion site discomfort were monitored during and for an hour after the infusion. A single blood sample was collected prior to the infusion and 12 samples were collected over the ensuing 96 hours. Plasma was separated from blood and analyzed, using a LC-MS assay, for CBZ and CBZ-epoxide, an active metabolite, and glucuronidated metabolite that is inactive Unbound CBZ was measured following ultrafiltration. CBZ concentration-time data were analyzed using a non-compartmental approach with the pharmacokinetic software, WinNONLIN.
[0046]A validated LC-MS assay for SL-CBZ, CBZ and th...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com