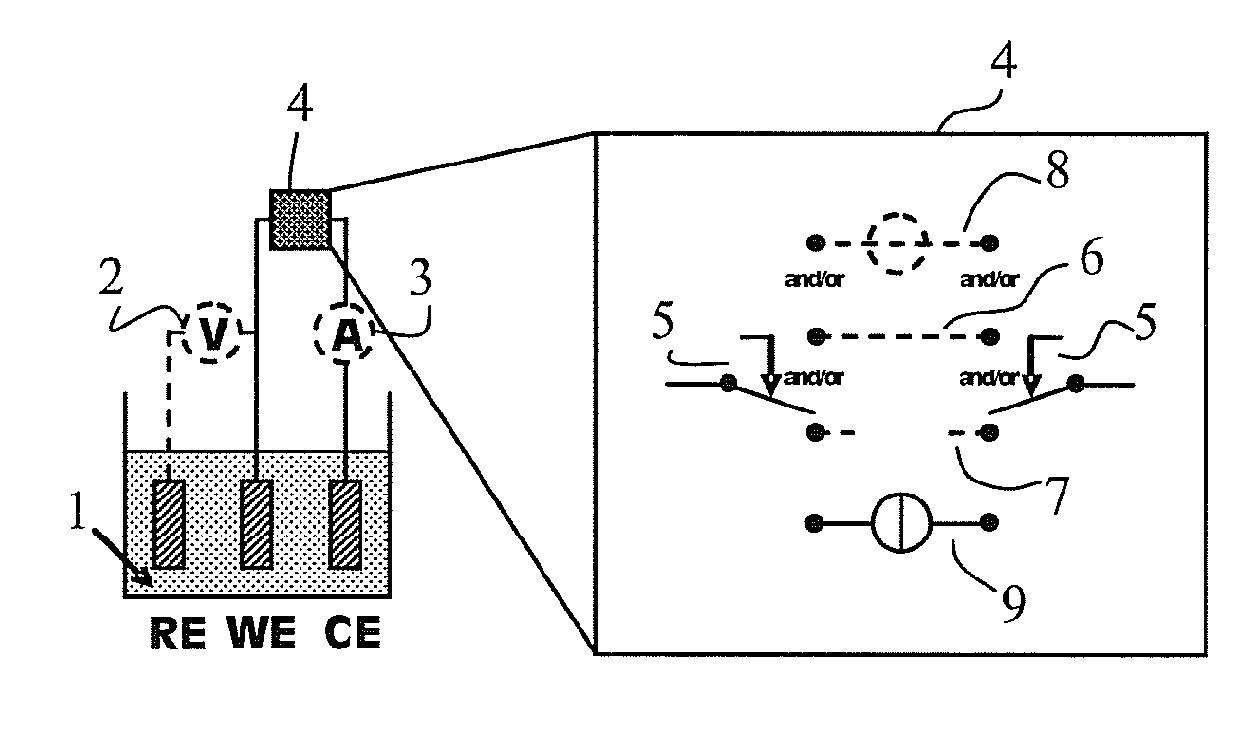
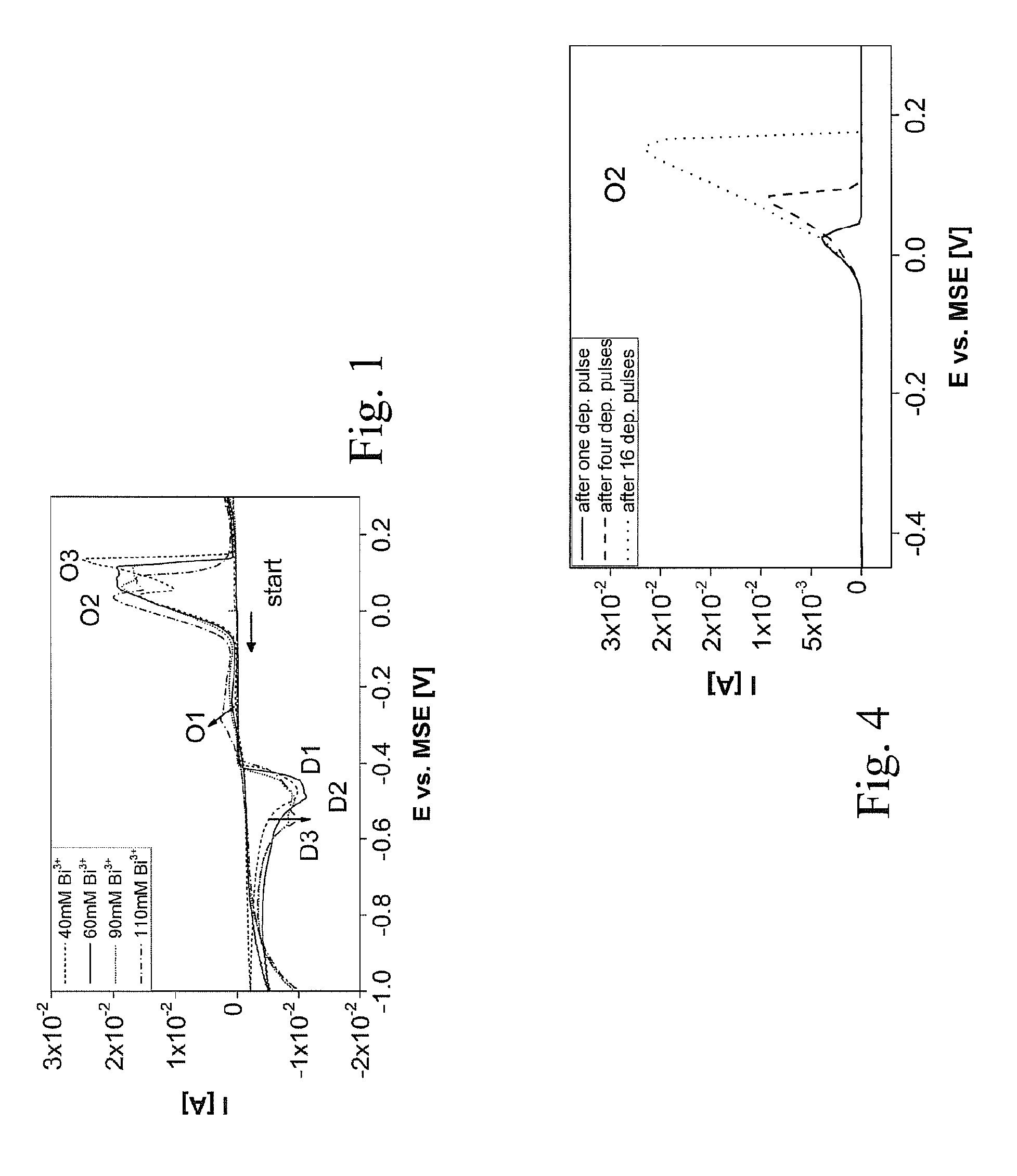
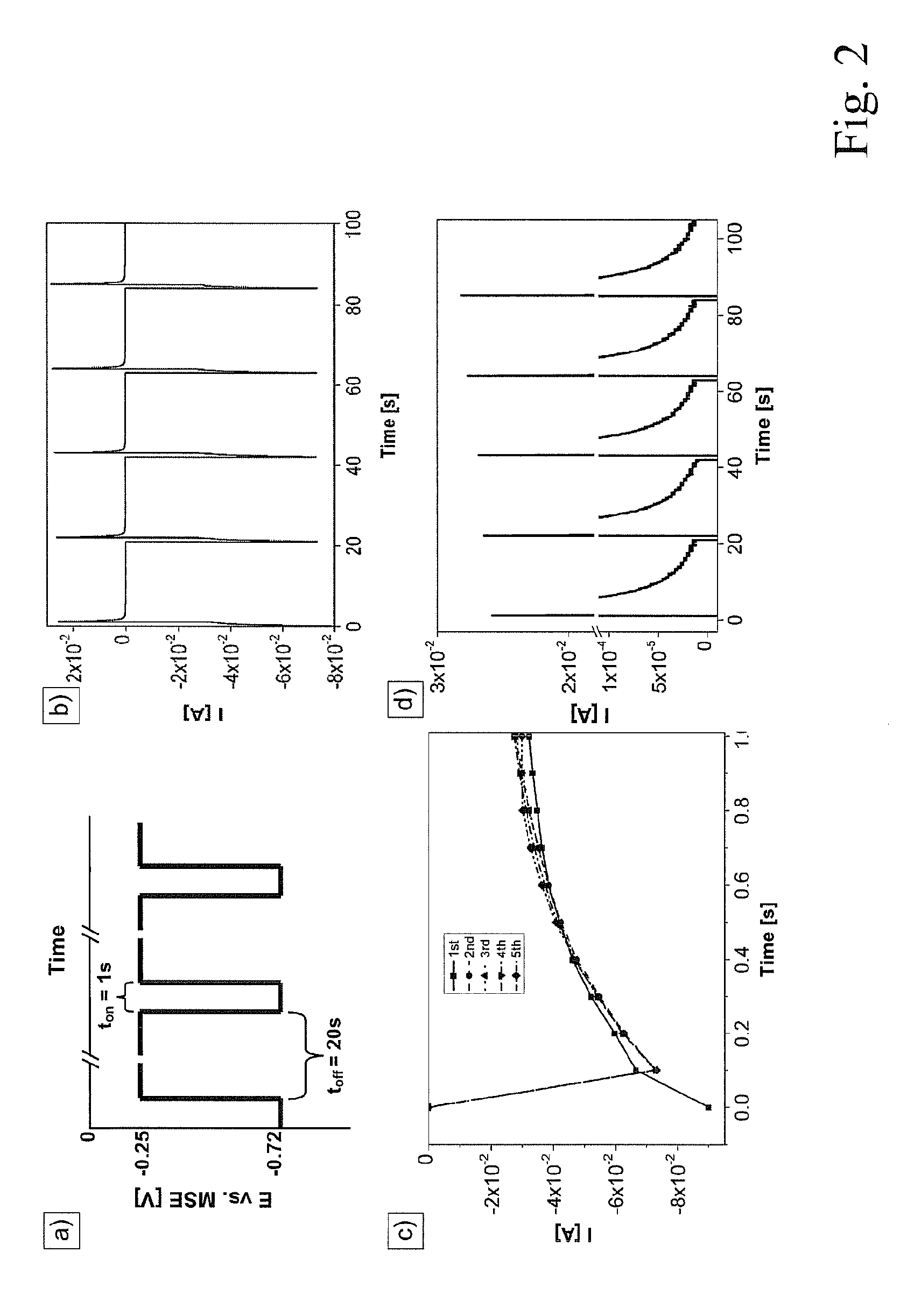
Device and method for the electrochemical deposition of chemical compounds and alloys with controlled composition and/or stoichiometry
a technology of chemical compounds and alloys, applied in the direction of manufacturing tools, electric circuits, electric circuits, etc., can solve the problems of insufficient adhesion, internal stress or undesired physical properties, insufficient stoichiometric control during the deposition, and insufficient layer properties and material properties, etc., to achieve simple and more accurate control
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0072]In the following reference is made to the drawings and figures. These and the following discussion are for the purpose of illustrating the present preferred embodiments of the invention and not for the purpose of limiting the same.
[0073]In this disclosure cyclic voltammetry, chronoamperometry and chronopotentiometry are reported to determine the electrochemical Bi2+xTe3−x formation on Pt electrodes from electrolyte solution with an HTeO3+ concentration 5 times higher then reported before. Based on these measurements, a new mixed method is introduced that allows full stoichiometric control throughout the entire deposition and that is appropriate to deposit very thick layers (up to 1 mm) at a high deposition rate that are free of stress. The influence of the deposition pulse duration, pulse height and electrolyte composition on the stoichiometry and morphology of the Bi2+xTe3−x is disclosed. The feasibility of the proposed method for fabrication of p- and n-type Bi2+xTe3−x is de...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| voltage | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| voltage | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| current density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com