Myostatin inhibitor enhancement of musculoskeletal repair
a myostatin inhibitor and musculoskeletal technology, applied in the field of muscle physiology and therapeutics, can solve the problems of insufficient novel strategies to utilize myostatin inhibitor enhancement, time-consuming treatment and care of these patients, etc., and achieve the effects of enhancing muscle regeneration, enhancing muscle regeneration, and improving fracture healing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Animals, Treatments, & Surgical Procedures
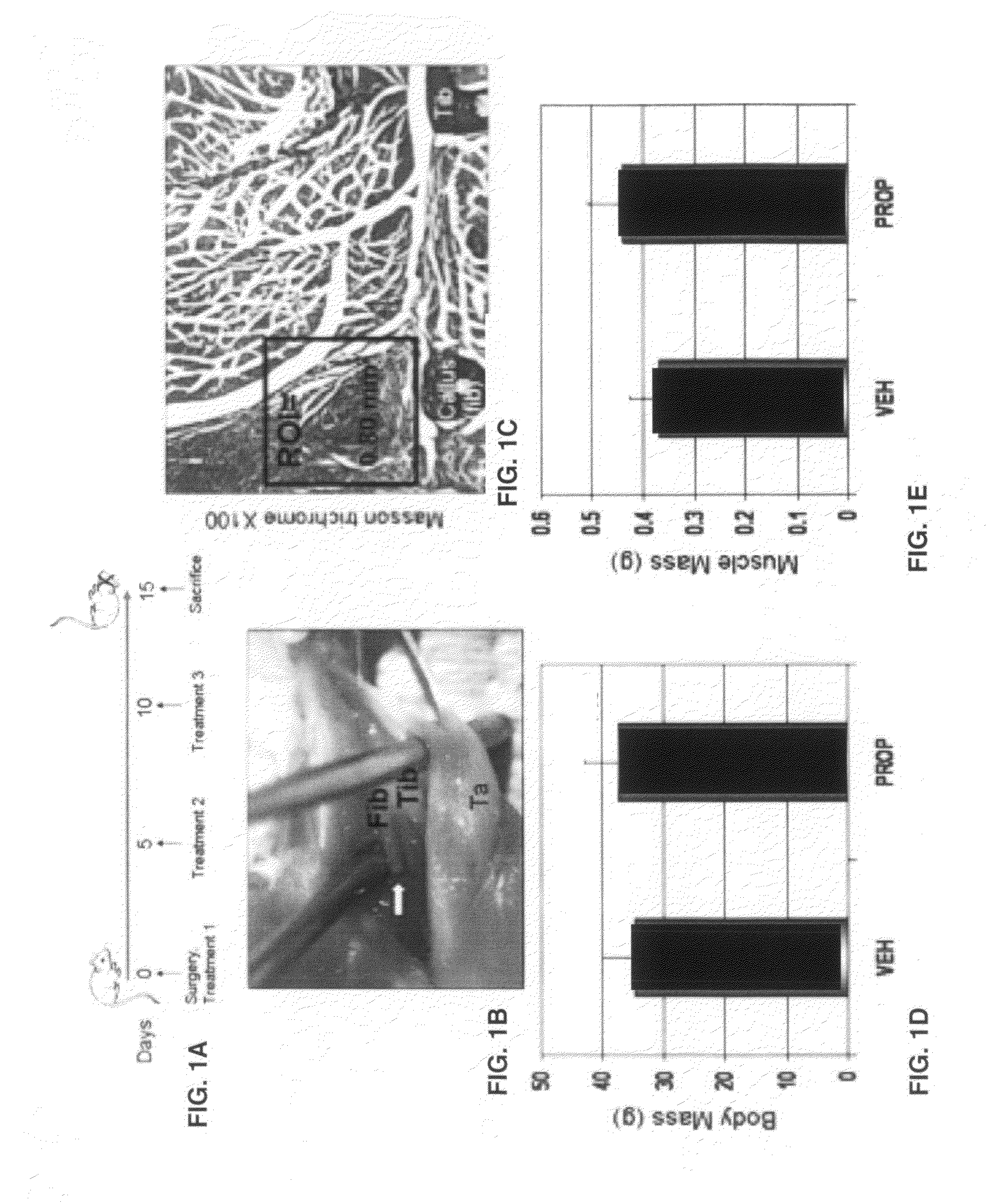
[0034]An initial dose-response study was performed to evaluate efficacy of the myostatin inhibitor in male CD-1 mice four months of age. Mice were treated with the propeptide at 0 mg / kg, 10 mg / kg, 20 mg / kg, or 50 mg / kg at day 0, day 5, and 10 and then sacrificed one week after the last treatment (FIG. 1A).
[0035]Results showed that three injections of the propeptide over a 15 day treatment period increased fore- and hindlimb muscle mass by 10% at the 10 mg / kg dose and increase muscle mass by more than 15% at the 20 mg / kg dose. The 50 mg / kg dose did not increase muscle mass beyond the increase observed in the 20 mg / kg group and so the 20 mg / kg dose was used. Adult CD-1 mice were separated into two groups: those receiving the propeptide (PRO) or saline (VEH). Each treatment group included 10-12 male and 10-12 female mice, for a total of 20-24 mice per treatment group. Fibula osteotomy was performed on the left leg under isoflurane anesthesia as...
example 2
MicroCT, Histology, & Histomorphometry
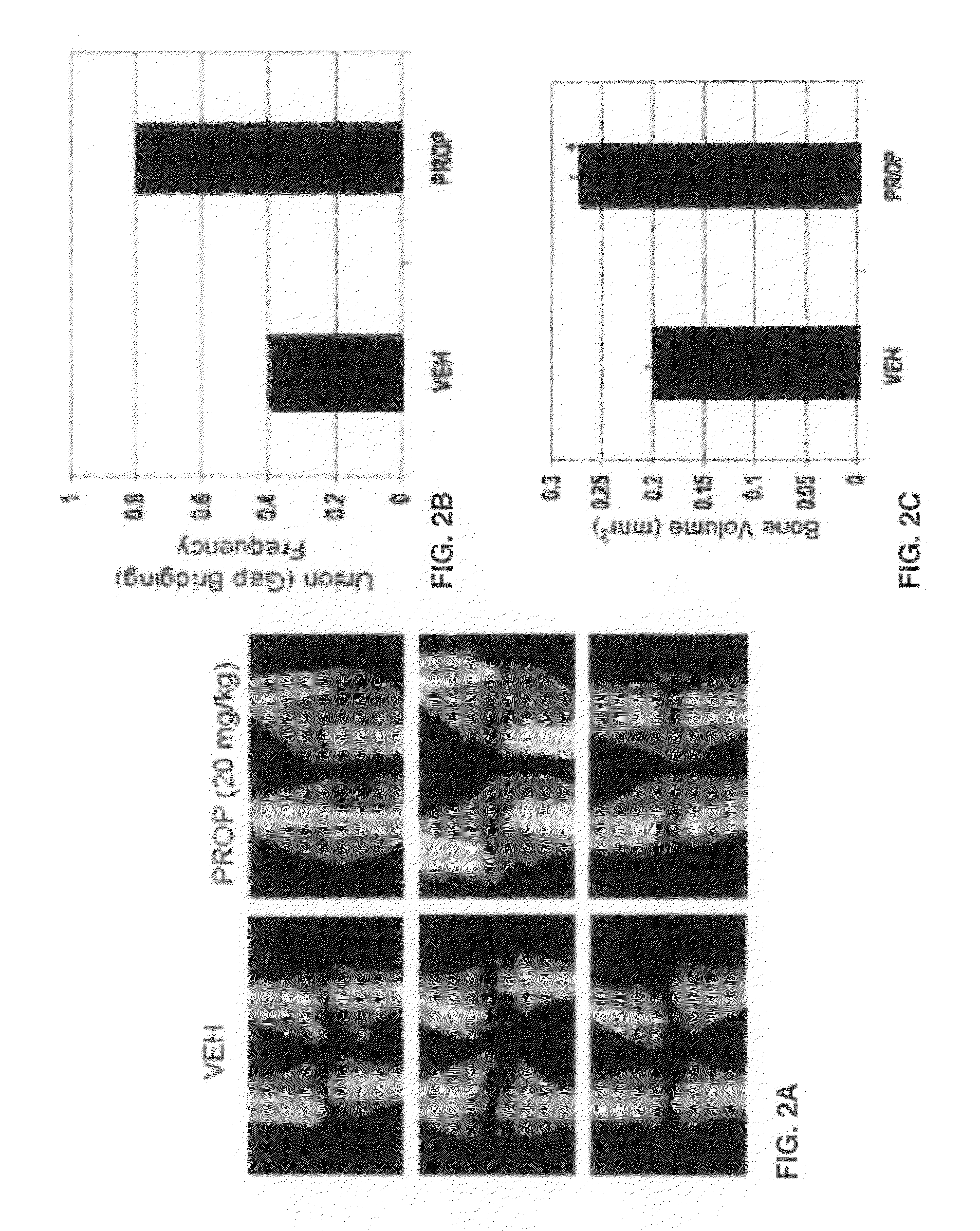
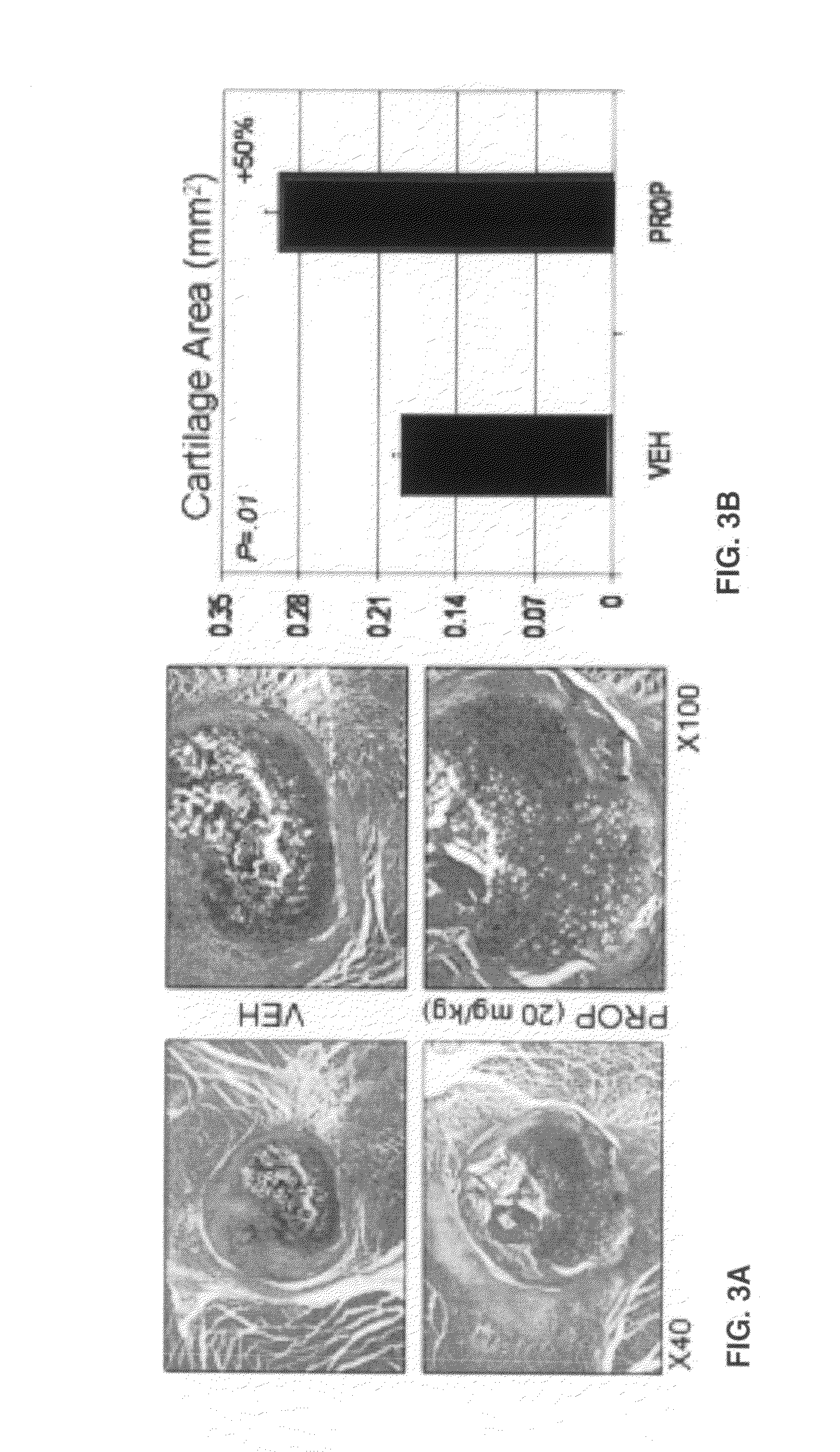
[0036]Intact legs with surrounding muscle were first imaged using a FAXITRON small-animal x-ray cabinet at 35 kVP, 2.5 mA for 45 seconds to verify that the fibula osteotomy was successful and that the tibia was not damaged. Specimens were sent to the Savannah River Site National Laboratory (Aiken, S.C.) for micro-computed tomography using a 160 kV micro-focus X-ray machine (Kevex Inc., Model 16010), a four-axis positioning system (New England Affiliated Technologies series 300), and an amorphous silicon imager (Varian Inc, Paxscan 4030) at 12 micron resolution. Measurements of total callus volume and callus bone mineral density were calculated 0.5 mm either side of the callus center. MicroCT images were then scored by a technician blind to the treatments as either having bone crossing the osteotomy site (‘bridged’) or showing no bone crossing the fracture gap ‘unbridged’). Specimens were then decalcified using EDTA, embedded in paraffin, and sec...
example 3
[0037]Experiments were performed in two blocks, with osteotomy performed in half the mice (n=20-24) for Block 1 and then a second group of 20-24 mice included for Block 2 approximately six weeks later. Single-factor ANOVA was used to detect significant effects of treatment and block on the outcome measures described above. Chi-square test was used to test for differences between treatment groups in the frequency of bridged or unbridged osteotomy sites.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com