Articles and devices for thermal energy storage and methods thereof
a technology of thermal energy storage and thermal energy, which is applied in the direction of indirect heat exchangers, lighting and heating apparatus, packaging goods types, etc., can solve the problems of more than 30% of the fuel energy supplied to an internal combustion engine (internal combustion engine) being lost to the environment via engine exhaust, and operating inefficiently, so as to achieve high heat storage density, high surface area, and high energy density
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples
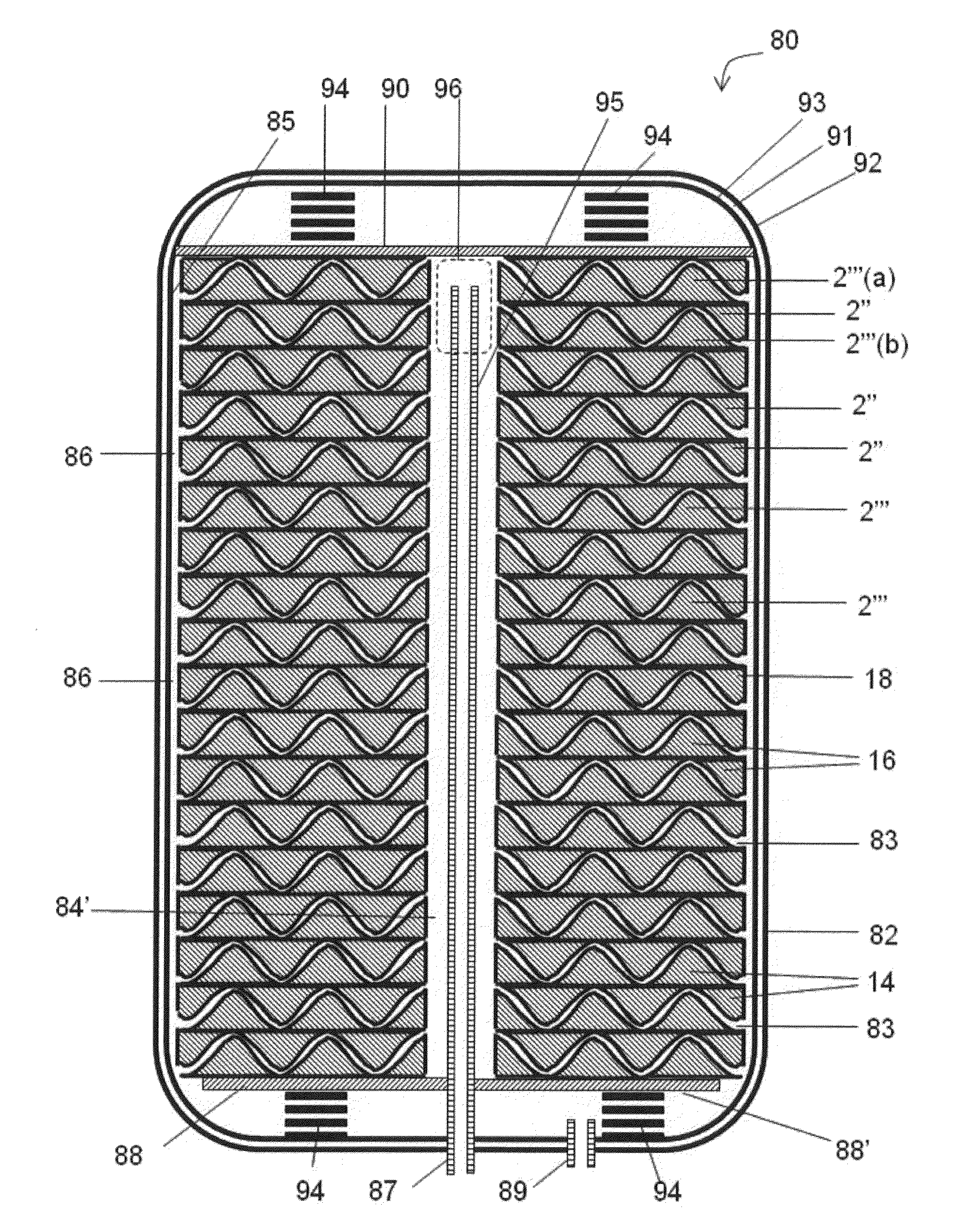
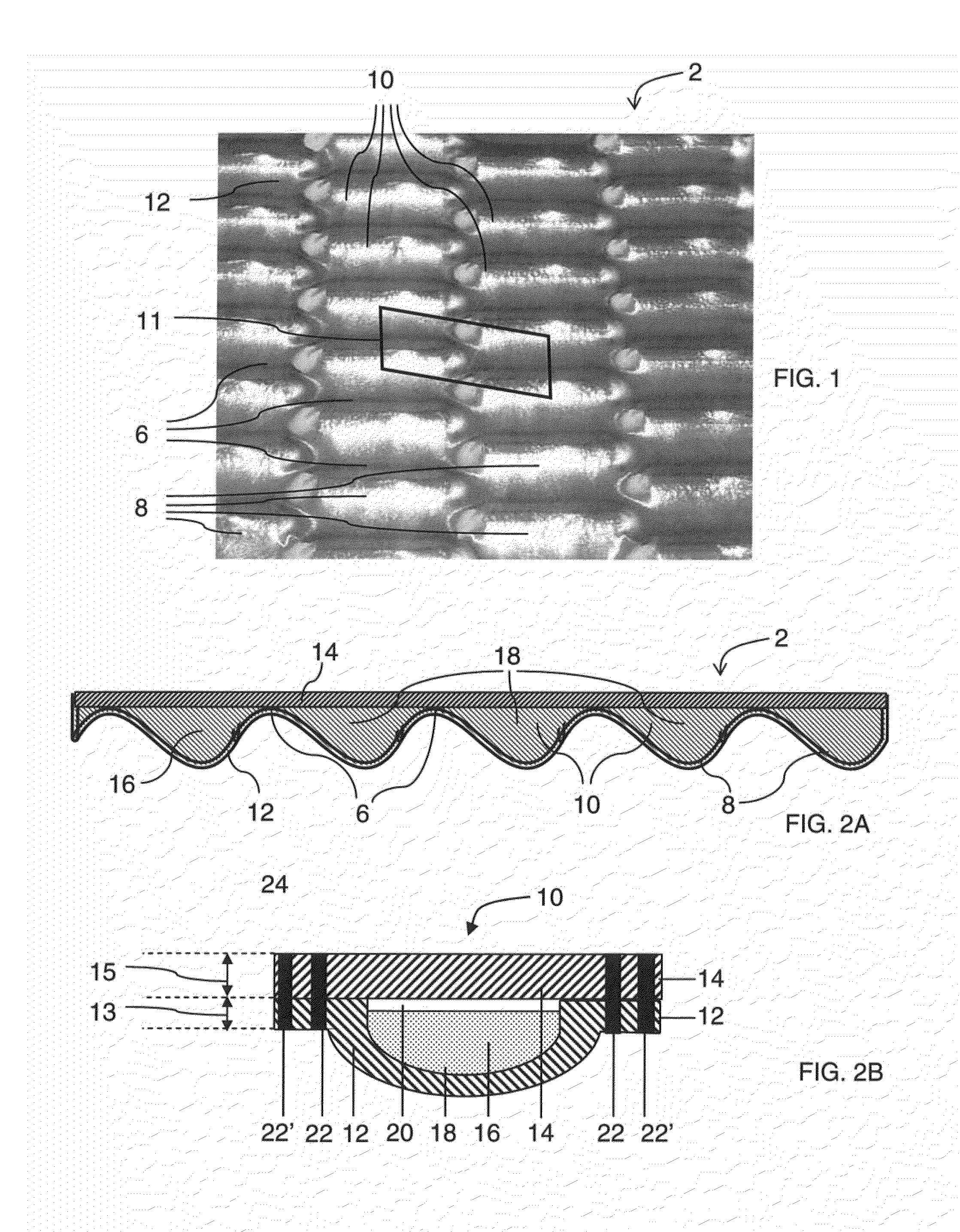
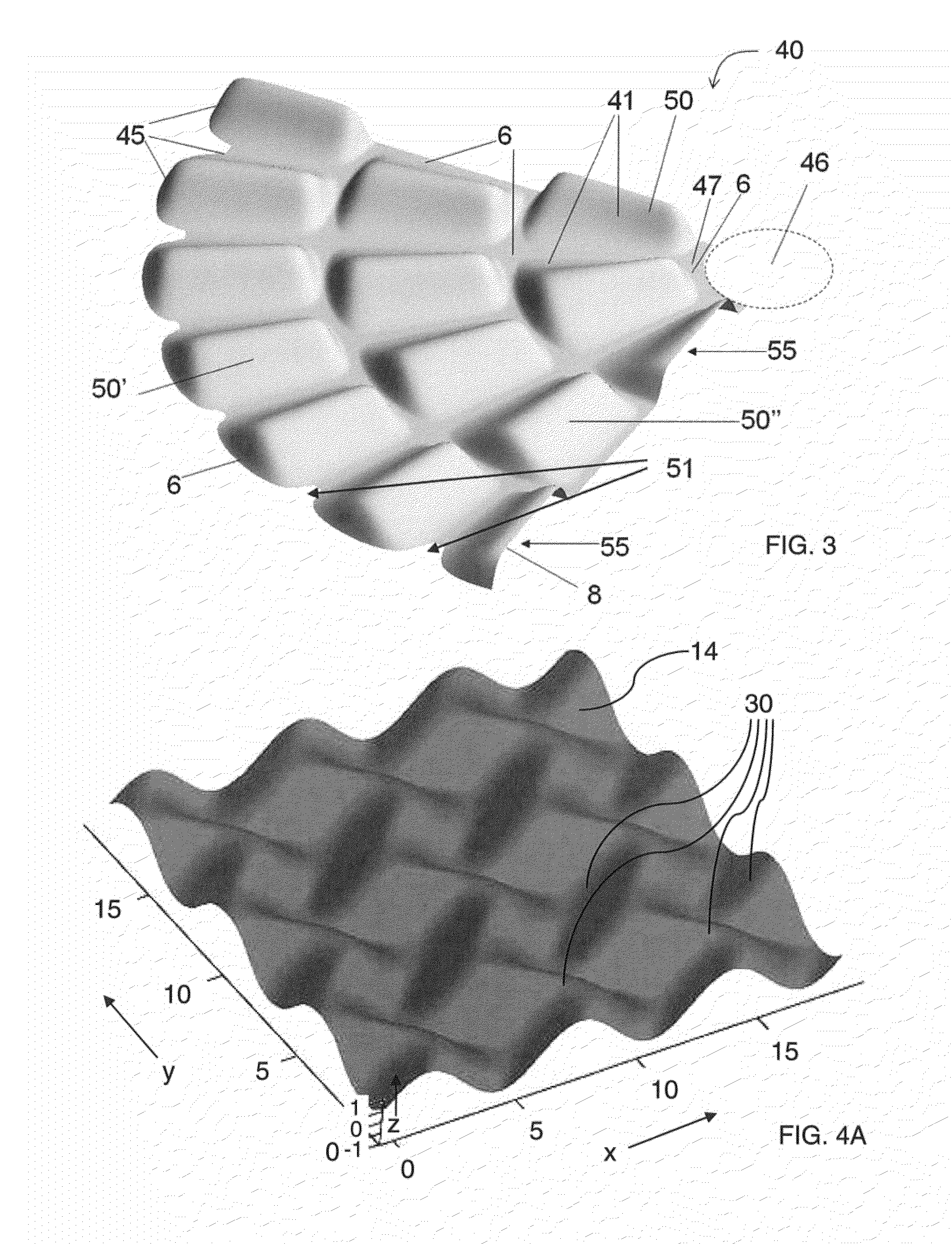
[0143]Example 1 is an article including 7 sealed spaces containing thermal energy storage material and suitable for heat storage. The packs are formed by filling a base sheet having 7 troughs with a thermal energy storage material. Each trough is capable of containing about 7 cm3 of a liquid. The base sheet is covered with a flat cover sheet. The base sheet and the cover sheet are made of stainless steel 304 and have a thickness of about 0.102 mm. The thermal energy storage material is a metal salt and has a liquidus temperature of about 195° C. The thermal energy storage material is anhydrous or has a moisture concentration of about 0.01 wt. % or less. The two sheets are joined while the thermal energy storage material is in a solid state (about 23° C.). A primary seal is provided by laser welding together the base sheet and the cover sheet about the periphery of each sealed space. When heated to a temperature of about 250° C., the sealed space has an internal pressure of about 69 ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pressure | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pressure | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com