Processes and systems for producing heat for rapid thermal processing of carbonaceous material
a technology of carbonaceous material and thermal processing process, which is applied in the direction of fluidised bed combustion apparatus, lighting and heating apparatus, combustion types, etc., can solve the problems of low yield of valuable liquids or gaseous products, liquefaction and conventional pyrolysis, and low energy fuel gaseous gaseous gaseous gaseous gaseous gaseous gaseous gaseous gaseous gaseous gaseous gaseous gaseous gaseous gas
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0018]The following Detailed Description is merely exemplary in nature and is not intended to limit the invention or the application and uses of the invention. Furthermore, there is no intention to be bound by any theory presented in the preceding Background of the Invention or the following Detailed Description.
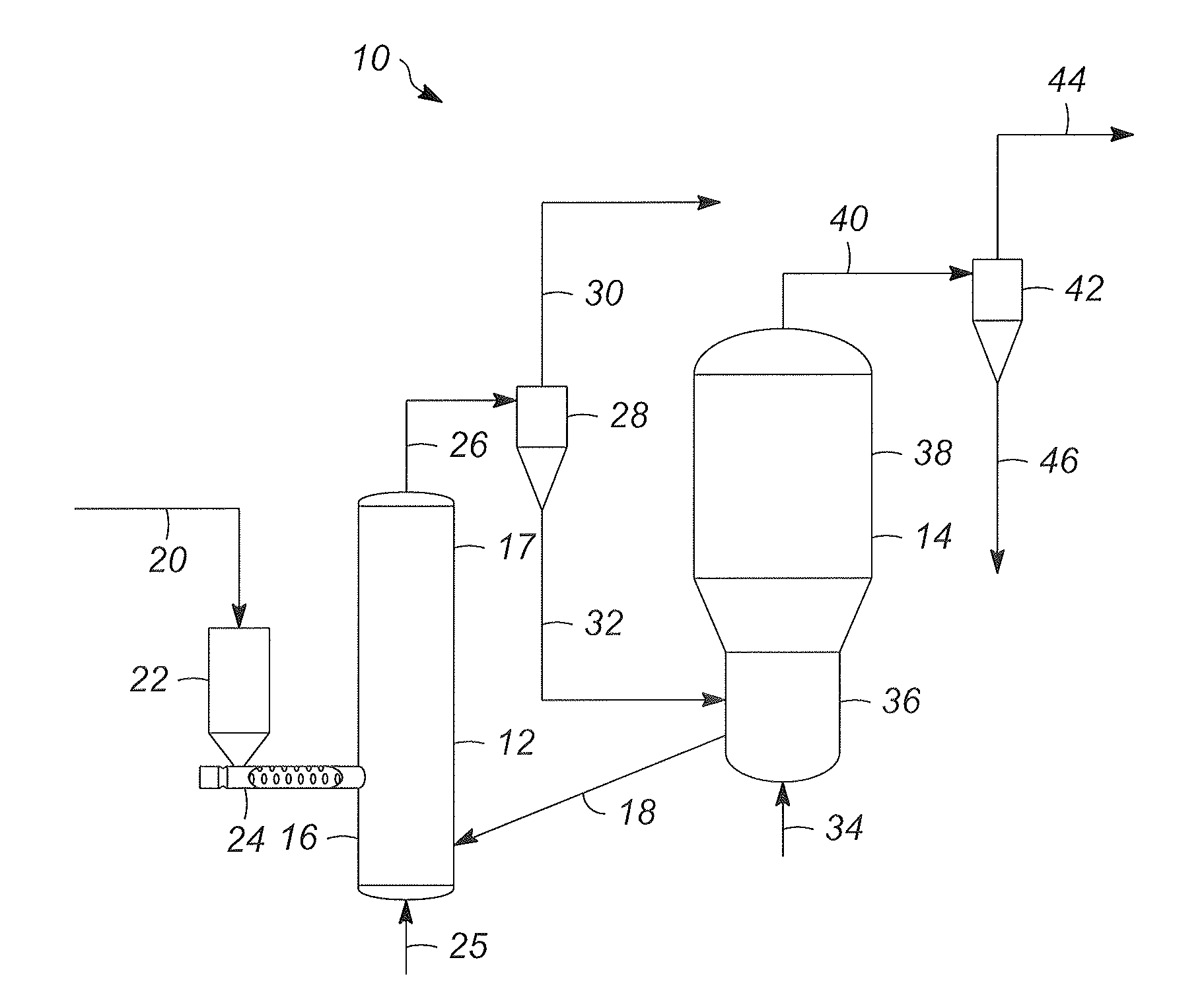
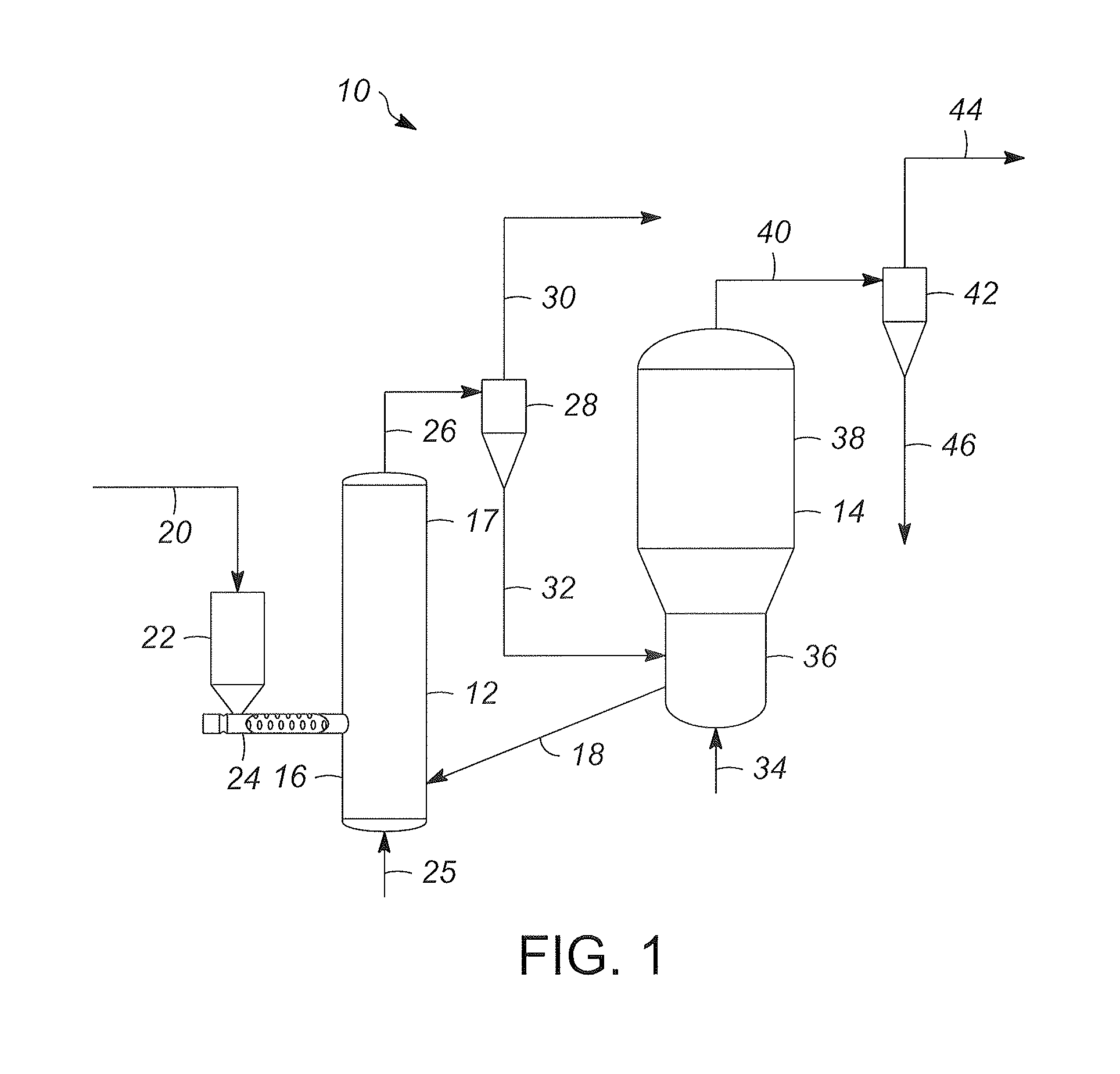
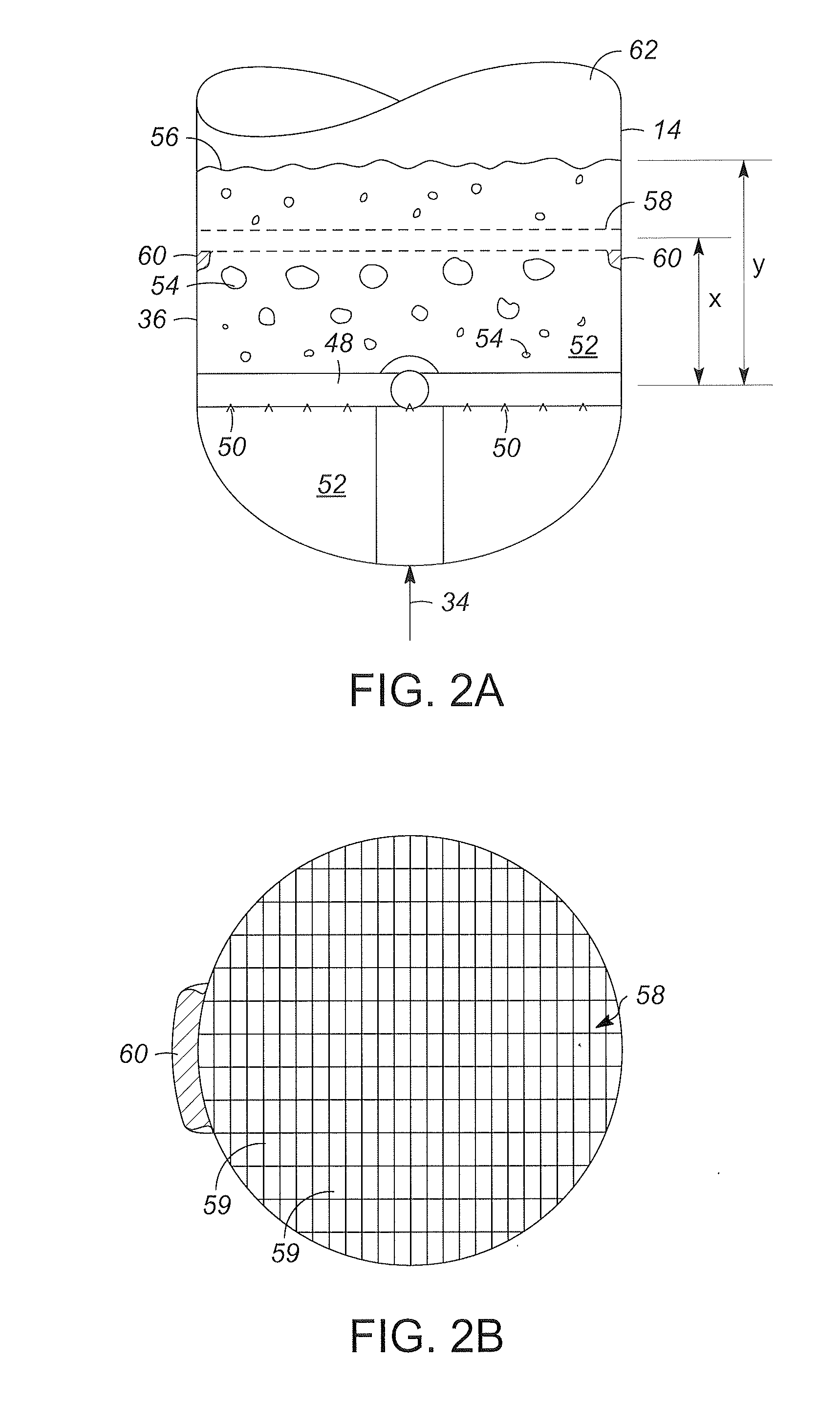
[0019]Various embodiments contemplated herein relate to processes and systems for producing heat for rapid thermal processing of carbonaceous material. In a reheater, bubbles of an oxygen containing gas advancing through a fluidized bubbling bed are contacted with a grating that is positioned within the fluidized bubbling bed. The fluidized bubbling bed comprises inorganic heat carrier particles and char. The reheater is operating at combustion conditions effective to burn the char into ash and heat the inorganic heat carrier particles to form heated inorganic particles. The inventor has found that by contacting the gas bubbles with one or more gratings at a predetermined le...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| distance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com