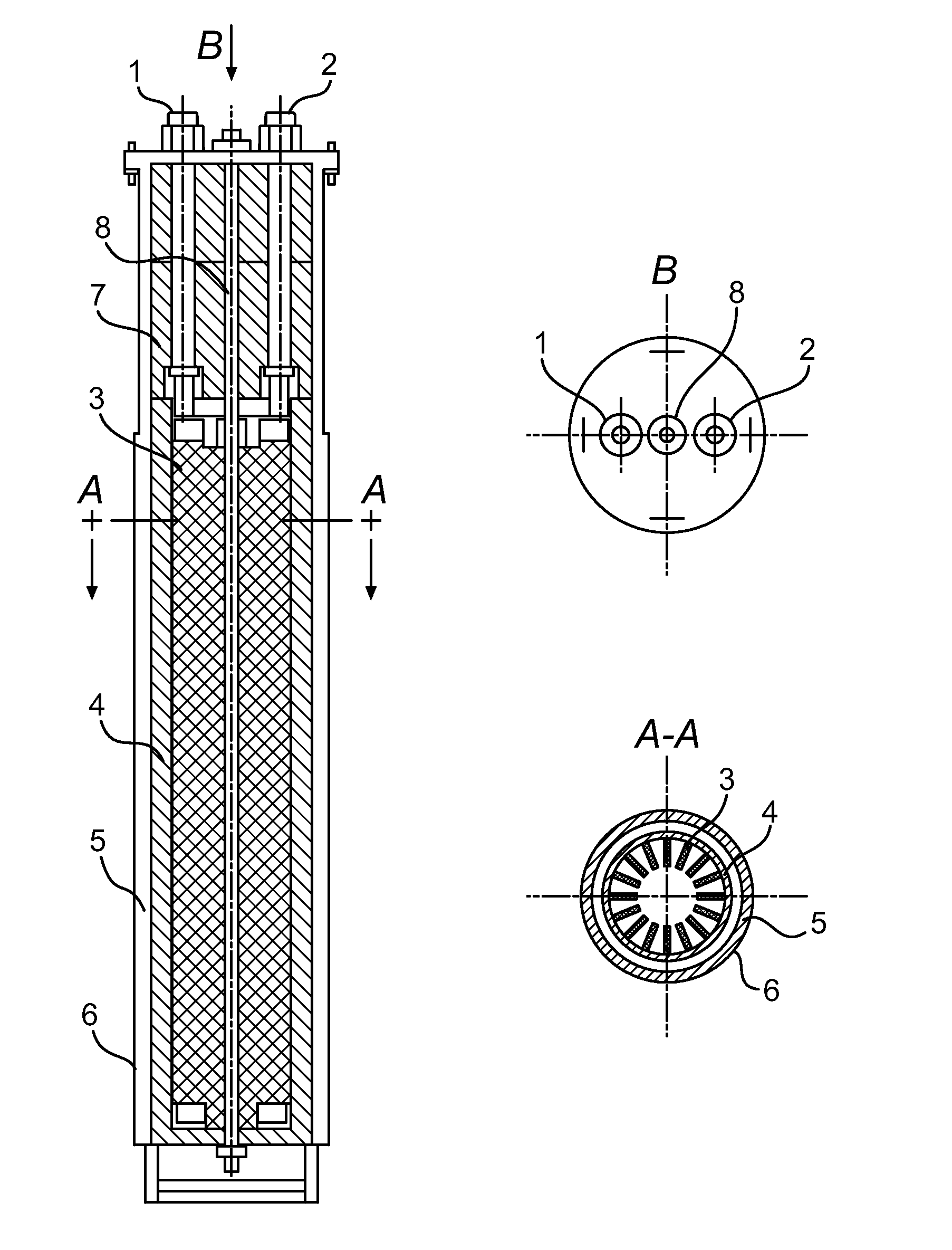
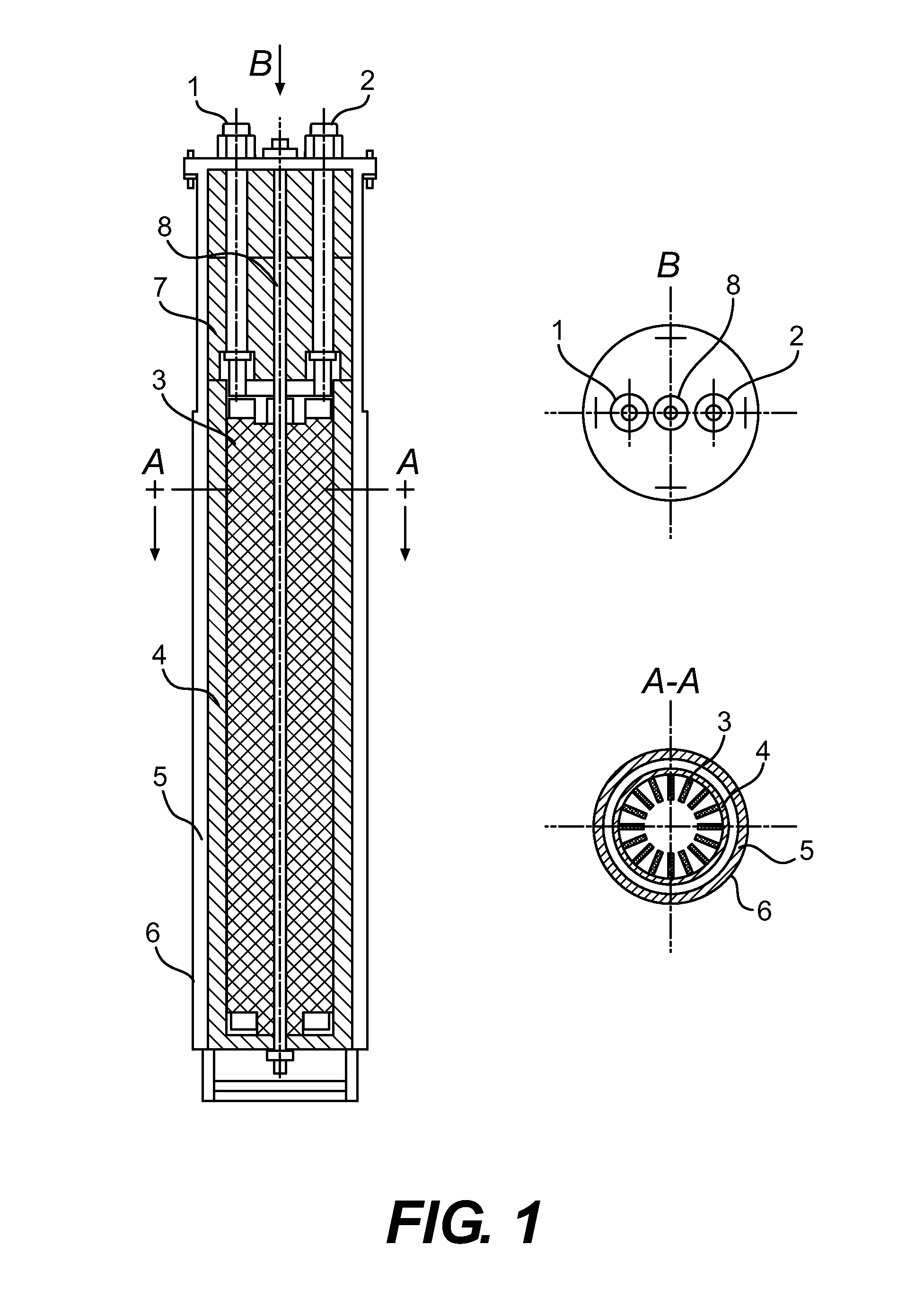
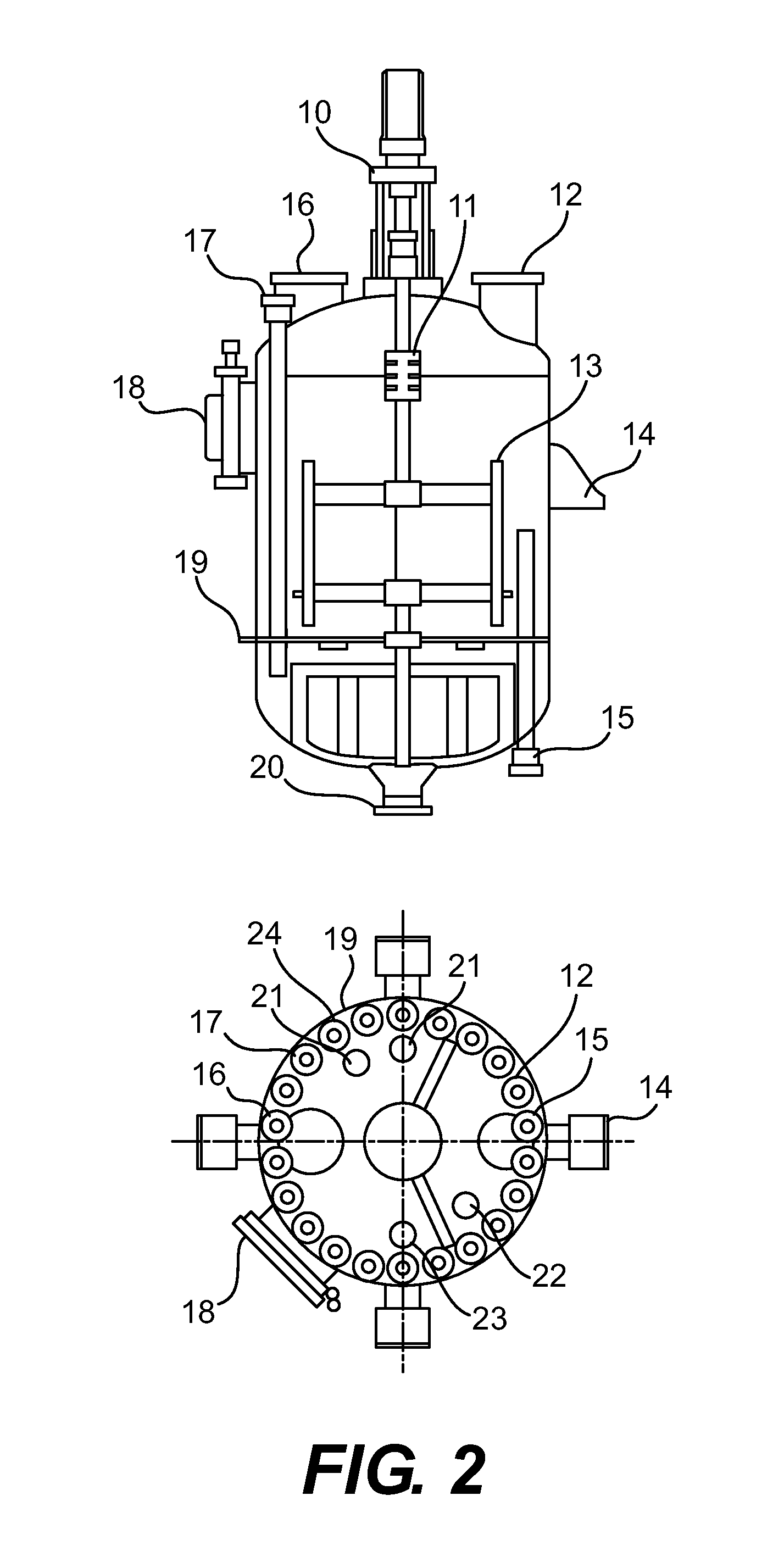
Decomposition of waste plastics
a technology of waste plastics and decomposition methods, applied in the field of decomposition of waste plastics, can solve the problems of low conductivity coefficient of typical waste plastics, low heating efficiency of reactors, and low heating efficiency, and achieve the effects of enhancing the emission of far infrared radiation, high heating efficiency, and high resistance to high temperature, high pressure and corrosion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 2
[0028]In this experiment, 170.5 / g of waste plastic from weaving bags made from polypropylene (PP) are put into the reactor for cracking. The temperature in the bottom of the reactor quickly increases and the top temperature rises to 57° C. The condensed oil begins to flow out of the condenser. After 10 minutes as the bottom temperature climbs and the top temperature reaches 146° C., oil continues to flow and gas is produced and ignited as in example 1. The molten plastic liquid continues to flow and gas is produced and ignited as in example 1. The molten plastic liquid continues to be cracked and as the upper temperature reaches 251° C., fuel oil and gas continue to flow at a rapid pace out of the top of the reactor for 25 minutes. Distillate oil obtained is 118.0 / g with a yield of 69.2% while the gas and loss is about 34.0 / g or 19.44% and the coke in this run, which also contains oil, is 18.5 / g or 10.85%.
ActionWeight / g%Fuel out of top of11869.2reactor*Cracking gas & loss34.019.44Co...
example 3
[0029]In this experiment, 47.5 / g of waste plastic food bags made from polyethylene (PE) is put into the reactor for cracking. The temperature in the bottom of the reactor is slowly increased to 200° C. and the bags begin to liquefy. The condensed oil begins to flow out of the condenser. As the bottom temperature climbs and the top temperature reaches 180° C. for 15 minutes and is maintained this temperature for 1 hour, oil is produced. Distillate oil obtained is 42.6 / g with a yield of 89.68% while the gas and loss is about 3.4 / g or 7.16% and the coke in this run is 1.5 / g or 3.16%. No residual heavy oil is obtained in this experiment.
ActionWeight / g%Fuel oil out of top of42.689.68reactor*Cracking gas & loss3.47.16Coke1.53.16*HQ Fuel oil yield total42.689.68Total w / debris47.5100
example 4
[0030]In this experiment, 314.9 / g of waste plastic from a white plastic barrel is put into the reactor for cracking. The reactor is heated for 25 minutes at which time a white gas like fog flows out of the reactor. The bottom temperature climbs to 208° C. and the top temperature reaches 56° C.; the plastic is fully liquefied at 330° C. at the bottom side of the reactor. The molten plastic liquid continues to be cracked and as the upper temperature reaches 120° C., fuel oil and gas continue to flow at a rapid pace out of the top of the reactor for 20 minutes at which time the cracking reaction finished. Distillate oil containing wax is 207.5 / g with a yield of 66.0% and the residual oil is 87.5 / g or 27.8%.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Percent by mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com