Medical instrument and method of use
a technology of medical instruments and methods, applied in the field of surgical instruments, can solve the problems of high “control” and achieve the effect of preventing desiccation, eschar, smoke and tissue sticking
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
embodiment 500
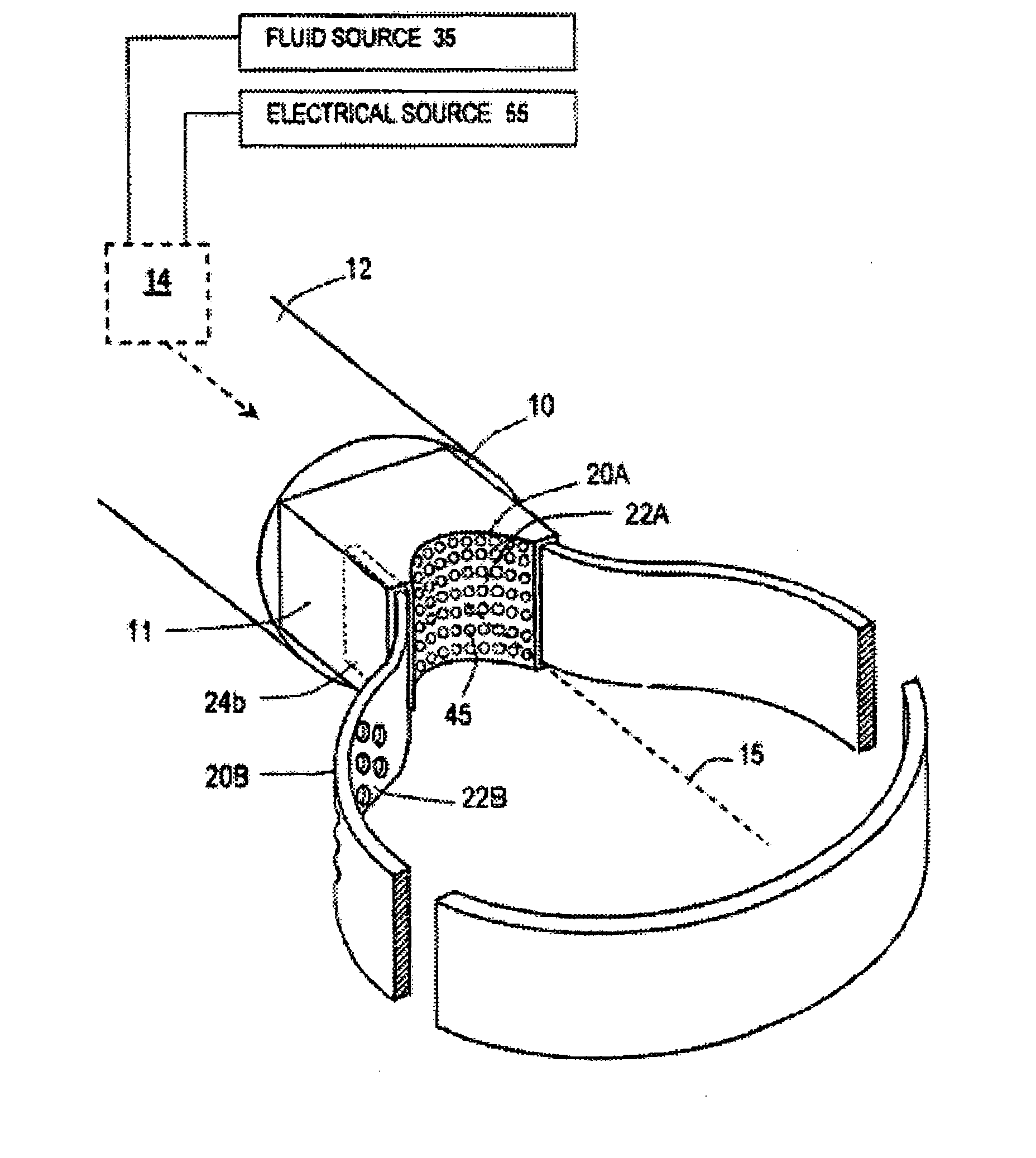
[0080]FIG. 21 illustrates another system embodiment 500 which includes components and features as in the embodiments of FIGS. 12-20 except that the configuration is adapted for the working end of a small diameter rigid probe or a flexible catheter. In FIG. 21, the interior chamber 510 comprises an elongate lumen of a member 512 having an insulated wall 514. A flow diffuser is located in a proximal portion of lumen 510 (not shown). In one embodiment, the interior of the lumen 510 comprises an NTCR surface indicated at 515. The NTCR surface 515 is coupled to insulated lead 518 and the Rf source 420 to thus comprise a series circuit. The NTCR surface 515 is capable of internal I2R heating to thereby cause heating and vaporization of media flows in the lumen. A conductive filament 520 is carried in lumen 510 with the filament having kinks or bends 522 so that the filament does not continuously contact the NTCR surface. The filament 520 is electrically conductive and is coupled to the Rf...
embodiment 600
[0082]FIG. 22-24 illustrate another probe embodiment 600 that is adapted for tissue ablation, tissue disintegration and tissue extraction. The probe has a handle portion and vapor source that is similar to any of the handle embodiments of FIGS. 7, 11, 12, and 14-20 for providing a flow of a vapor media. Probe 600 of FIG. 22 has electrical source 420, fluid inflow source 435A and controller 435B as described with reference to FIGS. 12 and 14-20. Probe 600 also has a negative pressure source 270 as described generally with reference to FIGS. 7 and 11 above.
[0083] The probe 600 of FIG. 22 has handle portion 602 that transitions to extension member 605 having axis 608 that extends to working end 610. The probe 600 has a central aspiration lumen 615 extending through the probe body to an open distal termination. The probe has a vapor flow channel 620 for providing a flow of vapor to working end 610 that is configured as a concentric channel between first and second walls, 622 and 624 res...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com