Fungi adapted to metabolize phosphite as a source of phosphorus
a technology of phosphite and phosphite, which is applied in the field of phosphite metabolization fungi as a source of phosphorus, can solve the problems of reducing the amount of available phosphorus, phosphate-based fertilizers common to modern agriculture are non-renewable, and can not be used efficiently by cultivated plants
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Exemplary Generation of Transgenic Plants Expressing a Bacterial Phosphite Dehydrogenase Enzyme
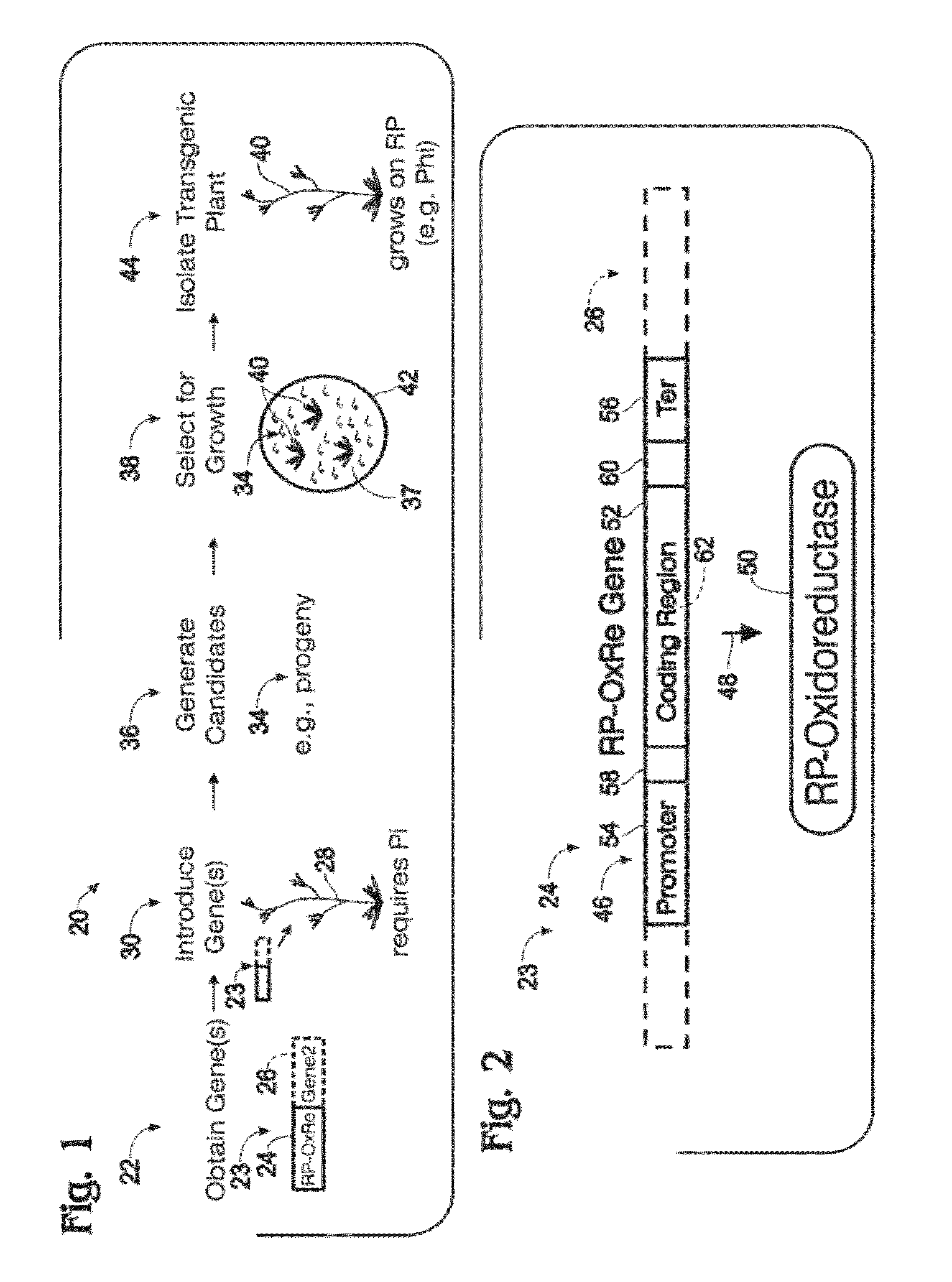
[0091]This example describes an exemplary method of generating transgenic plants with modified phosphorus metabolism; see FIGS. 4-6.
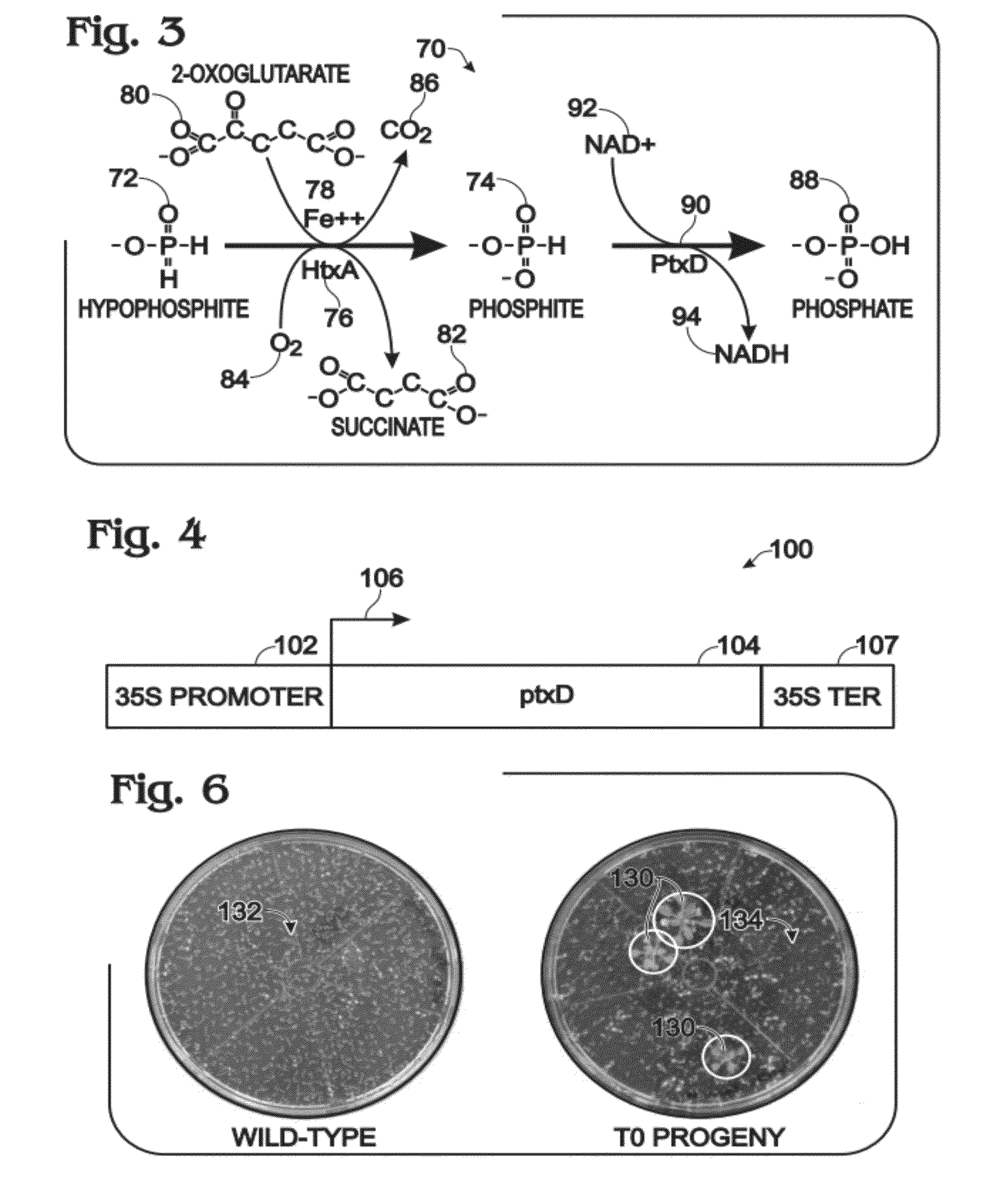
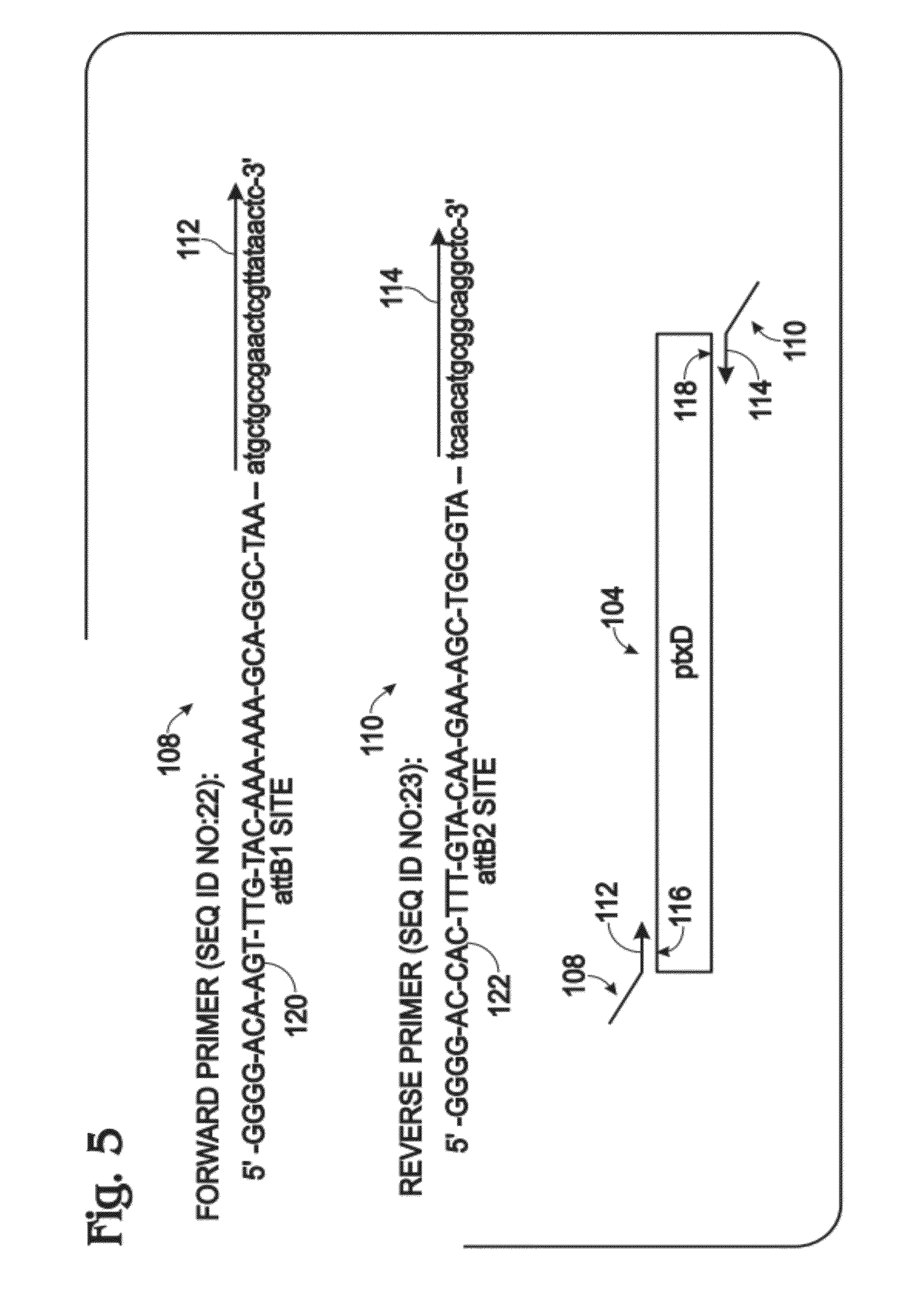
[0092]FIG. 4 shows an exemplary nucleic acid, a chimeric gene 100, constructed for use in generating a transgenic plant that metabolizes phosphite to phosphate, to permit growth on phosphite in the absence of phosphate. The gene was constructed using the Gateway® system (Gateway® Technology, 2003, Invitrogen) as described in the following paragraphs.
[0093]Gene 100 includes a 35S promoter sequence 102 from Cauliflower Mosaic Virus (CaMV) operatively linked to a coding sequence 104 (SEQ ID NO:21) from ptxD of Pseudomonas stutzeri WM88. Expression of gene 100, indicated at 106, to produce the PtxD polypeptide (a phosphite dehydrogenase enzyme) is thus controlled / driven by 35S promoter 102. Gene 100 optionally may include a termination sequence 107, such as a 35S ...
example 2
Characterization of Arabidopsis Plants Expressing PtxD
[0102]This example presents an investigation of the growth characteristics of the parental (“wild-type” (WT) or control) Arabidopsis line, Col-0, and two of the transgenic Arabidopsis lines described in Example 1 and comprising the ptxD expression construct of Example 1; see FIGS. 7-12.
[0103]Two transgenic Arabidopsis lines, dubbed PTXD-3 and PTXD-5, were prepared and isolated as described in Example 1. Each line is homozygous for the ptxD expression construct of Example 1.
[0104]The parental line and the PTXD-3 and PTXD-5 transgenic lines were tested for the ability to grow on a liquid medium, with or without inorganic phosphate (Pi) as the source of phosphorus. Seeds from the parental and transgenic lines were germinated in liquid media and tested for growth. In the absence of phosphate (and phosphite), neither the parental line nor the transgenic lines showed significant growth beyond germination. (Each line exhibited paltry gr...
example 3
Transgenic Tobacco Plants Expressing PtxD
[0113]This example describes the creation and characterization of transgenic Nicotiana tabacum (tobacco) comprising the ptxD expression construct of Example 1; see FIG. 13.
[0114]Nicotiana tabacum was transformed with the expression construct described in Example 1. In particular, tobacco leaf explants were co-cultivated with an Agrobacterium strain harboring a 35S::PtxD construct (Example 1) within its T-DNA. Leaf discs were allowed to regenerate in MS media containing 1 mM phosphite as the only phosphorus source. Plants regenerated from these leaf discs on phosphite-containing media were transferred to soil and allowed to set seed under greenhouse conditions.
[0115]FIG. 13 shows photographs of T2 transgenic tobacco seeds, homozygous for the 35S::PtxD gene, and control tobacco seedlings taken 25 days after germination in MS media containing either phosphate (1 mM Pi) or phosphite (1 mM Phi) as the only phosphorus source. The presence or absenc...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com