Method for forming oxide semiconductor film and method for manufacturing semiconductor device
a semiconductor film and oxide technology, applied in the direction of semiconductor devices, basic electric elements, electrical equipment, etc., can solve the problems of unsatisfactory filling of oxygen vacancies and generation of charges, and achieve the effect of shortening the distance between oxygen ions traveling to the oxide semiconductor film formed over the base insulating film, favorable electrical characteristics, and unfavorable electrical characteristics
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
embodiment 1
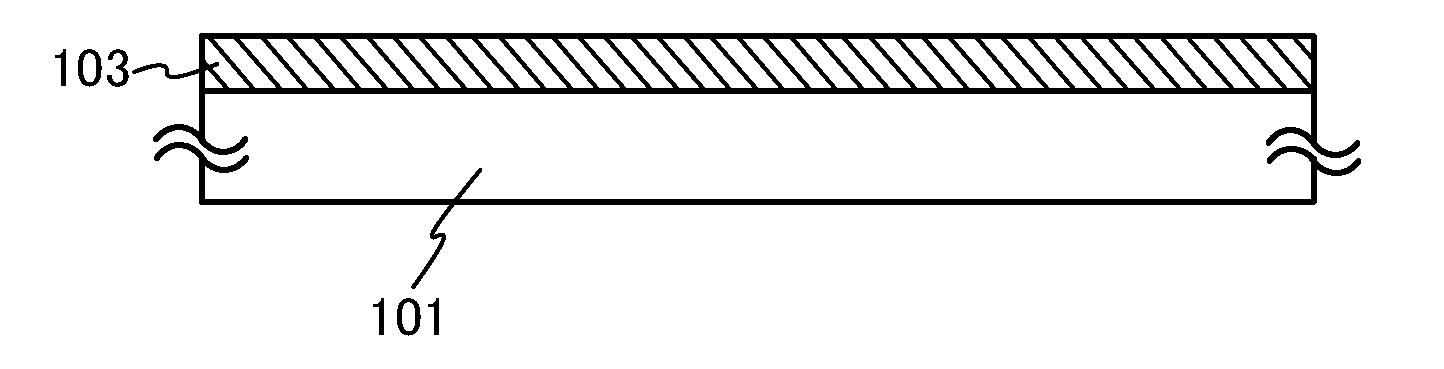
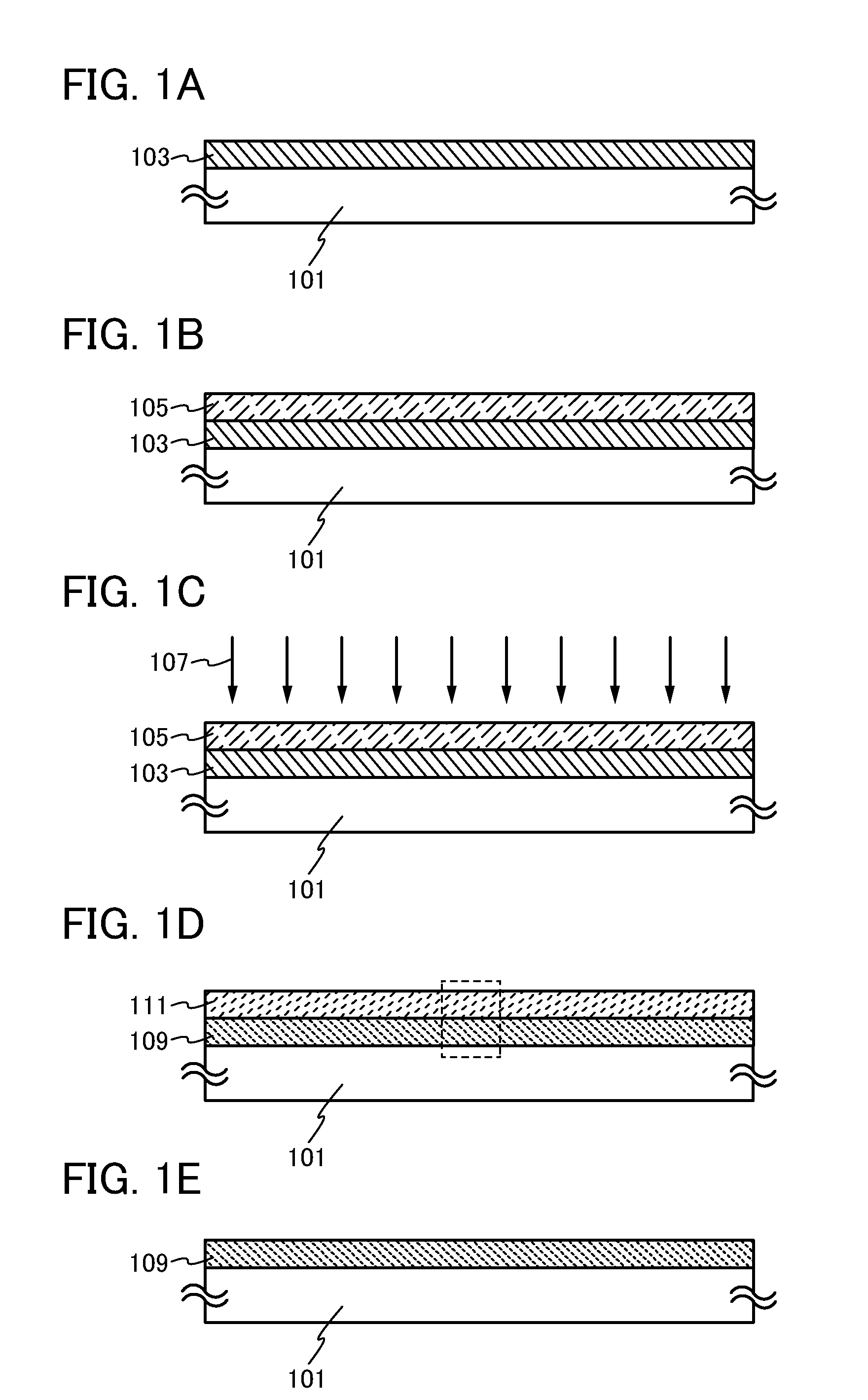
[0060]In this embodiment, a method for forming an oxide semiconductor film in which oxygen is contained uniformly in the depth direction of the oxide semiconductor film is described with reference to FIGS. 1A to 1E and FIG. 16A. FIGS. 1A to 1E are schematic cross-sectional views illustrating a method for forming an oxide semiconductor film, which is one embodiment of the present invention.
[0061]First, an oxide semiconductor film 103 is formed over a substrate 101 (see FIG. 1A). The oxide semiconductor film 103 may be formed using any of metal oxide materials (oxide semiconductor materials) given below by a chemical vapor deposition (CVD) method, a sputtering method, a molecular beam epitaxy (MBE) method, or a pulsed laser deposition (PLD) method, and is preferably formed by a sputtering method.
[0062]The oxide semiconductor film 103 may have an amorphous structure or a crystalline structure.
[0063]For the oxide semiconductor film 103, a metal oxide material containing at least indium ...
embodiment 2
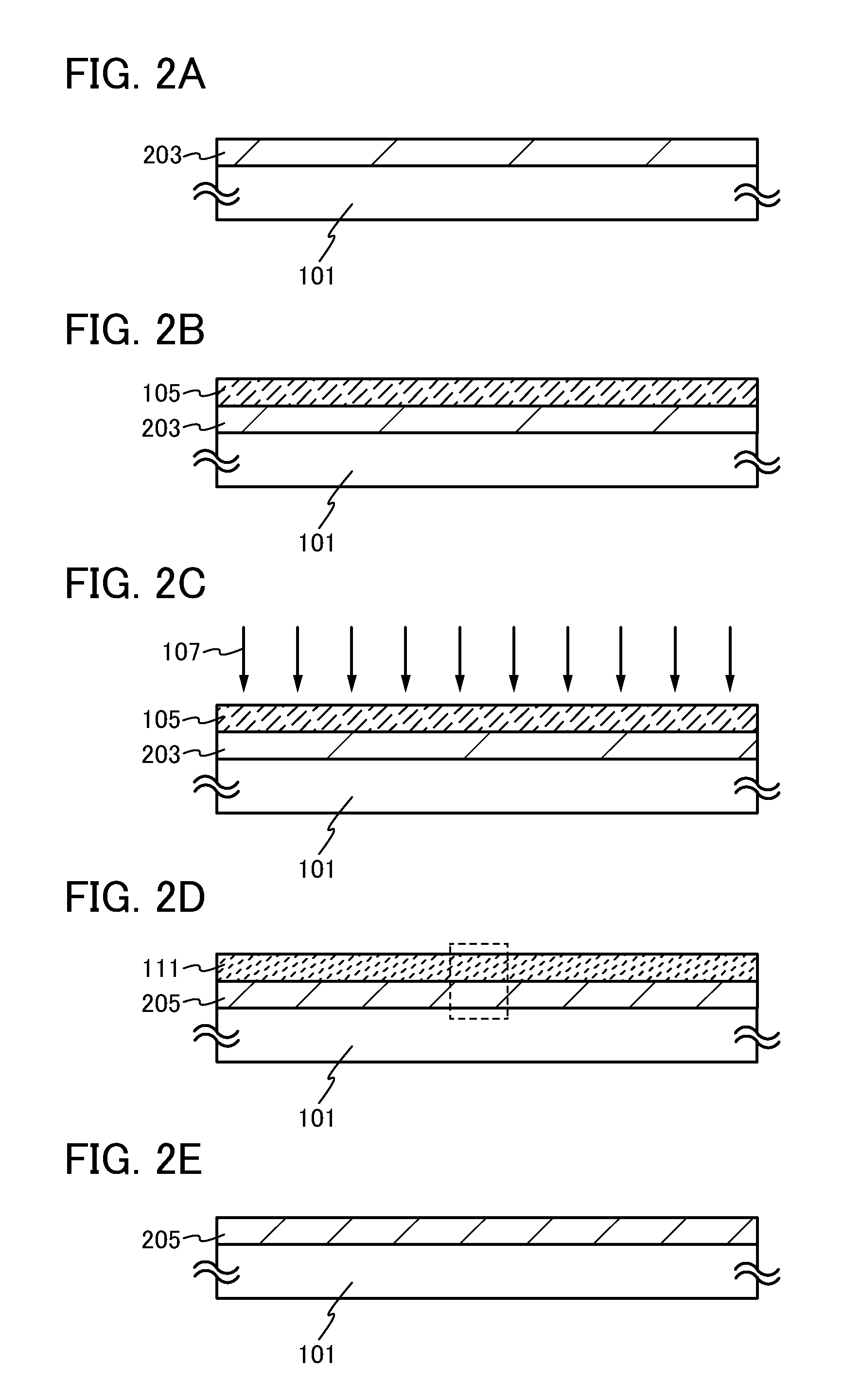
[0088]In this embodiment, a method for forming an insulating film in which oxygen is contained uniformly in the depth direction of the insulating film is described with reference to FIGS. 2A to 2E and FIG. 16B. FIGS. 2A to 2E are schematic cross-sectional views illustrating a method for forming an insulating film, which is one embodiment of the present invention.
[0089]First, an insulating film 203 is formed over the substrate 101 (see FIG. 2A). The insulating film 203 may be formed by a CVD method, a sputtering method, an MBE method, or a PLD method.
[0090]There is no particular limitation on the insulating film 203 as long as it is an insulator. For example, an oxide insulating film of silicon oxide or the like, a nitride insulating film of silicon nitride or the like, an oxynitride insulating film of silicon oxynitride or the like, or a nitride oxide insulating film of silicon nitride oxide or the like can be used.
[0091]Note that silicon oxynitride refers to a substance that contai...
embodiment 3
[0112]In this embodiment, a method for manufacturing a semiconductor device with the use of the method for forming an oxide semiconductor film described in Embodiment 1 is described. Note that a transistor using an oxide semiconductor is described as an example of the semiconductor device in this embodiment. In addition, the method for forming an oxide semiconductor film described in Embodiment 1 can be applied to the manufacture of transistors having a variety of structures, such as a top-gate transistor, a bottom-gate transistor, and a dual-gate transistor; a top-gate transistor is described here as an example.
[0113]FIGS. 3A to 3D are schematic cross-sectional views illustrating a method for manufacturing a transistor using an oxide semiconductor in this embodiment.
[0114]First, the substrate 101 is prepared. Although there is no particular limitation on the substrate 101, it is preferable that the substrate 101 have an insulating surface and at least heat resistance high enough to...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com