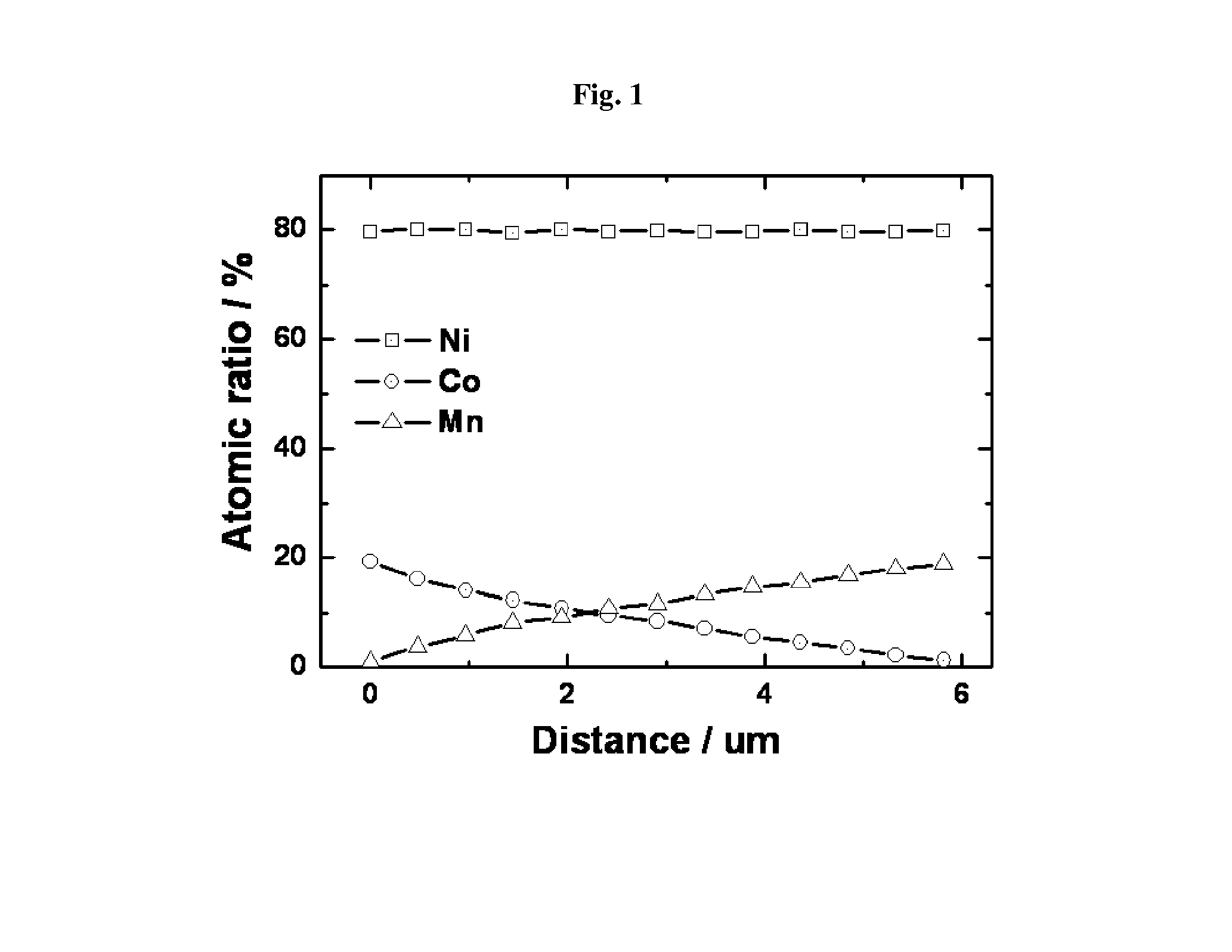
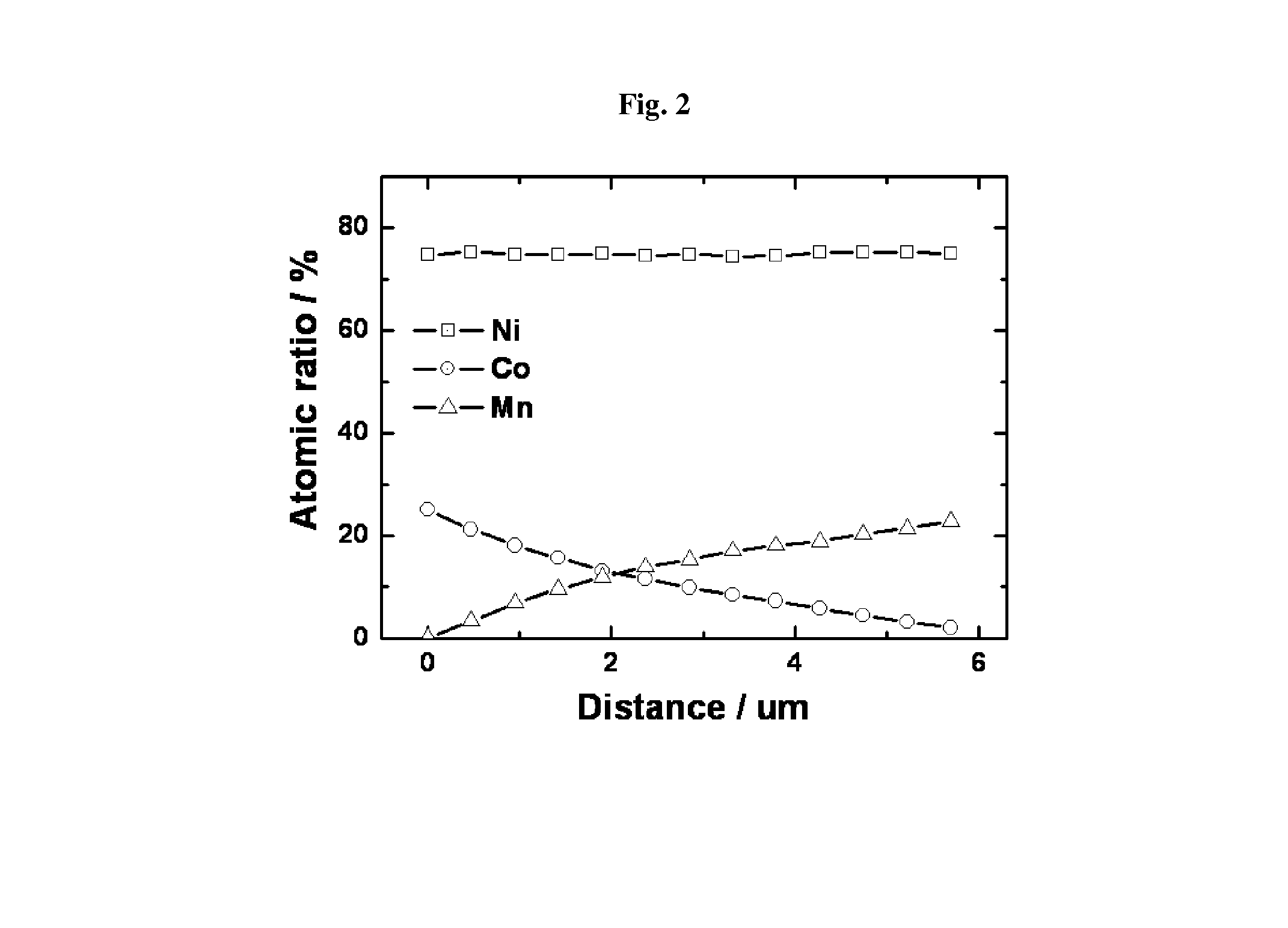
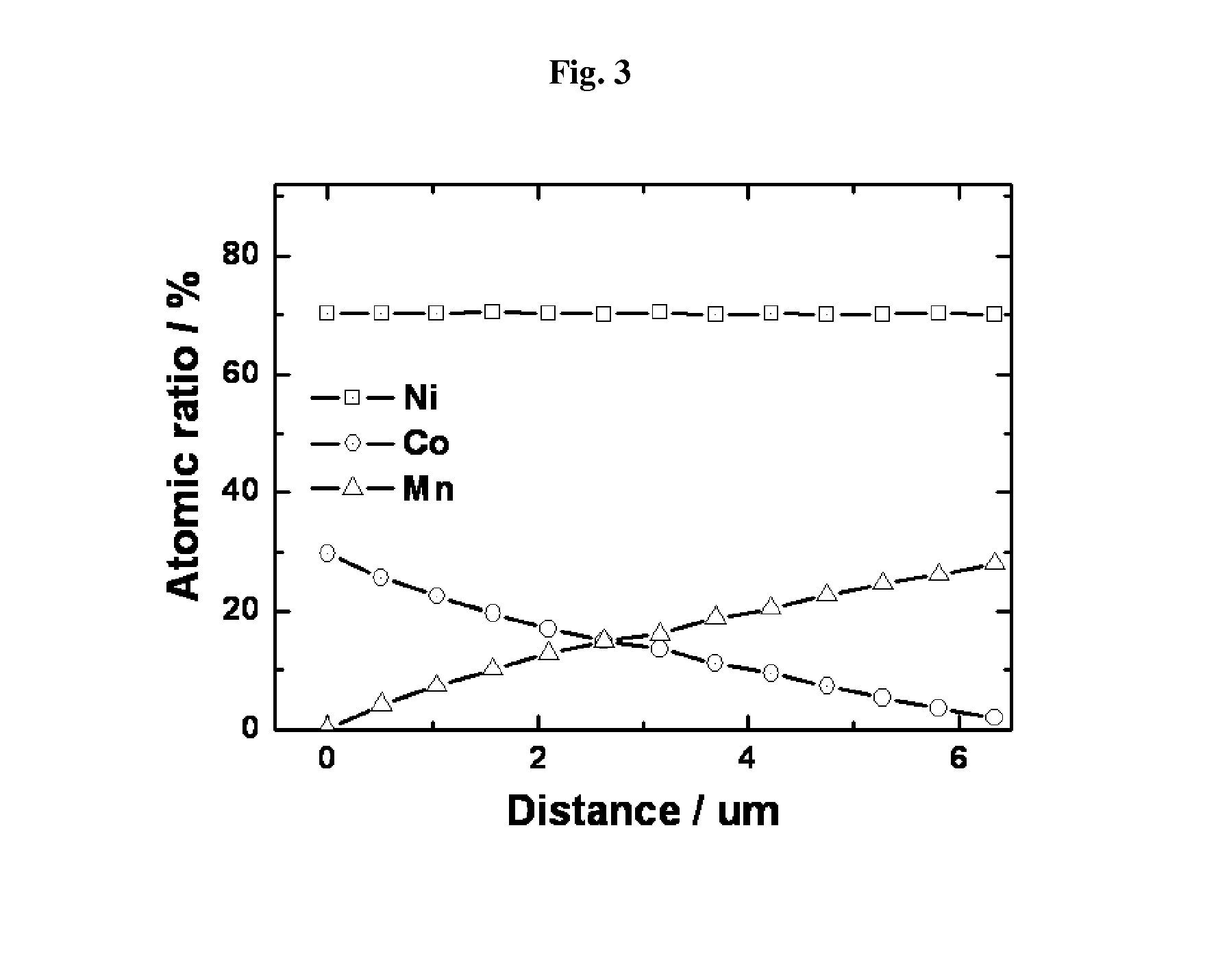
Anode active material with whole particle concentration gradient for lithium secondary battery, method for preparing same, and lithium secondary battery having same
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Case of Constant Nickel Concentration
Example 1-1
[0072]In order to prepare a compound, wherein the Ni concentration is constant from the core to the surface, the Co concentration is decreased, and the Mn concentration is increased, a 2.4 M metal aqueous solution, prepared by mixing nickel sulfate and cobalt sulfate at the molar ratio of 80:20, as a metal salt aqueous solution for forming the core and a metal aqueous solution containing nickel sulfate and manganese sulfate at the molar ratio of 80:20 as a metal salt aqueous solution for forming the surface part were prepared.
[0073]Distilled water 4 L was put into a coprecipitation reactor (Capacity: 4 L, power of a rotation motor: 80 W); nitrogen gas was supplied to the reactor at the speed of 0.5 L / min so as to remove dissolved oxygen; and stirred at 1000 rpm while maintaining the temperature of the reactor at 50° C.
[0074]The metal salt aqueous solution for forming the core and the metal salt aqueous solution for forming the surface ...
example 1-2 to example 1-4
[0076]In order to prepare a compound, wherein the Ni concentration is constant from the core to the surface, the Co concentration is decreased and the Mn concentration is increased, the procedure of Example 1 was repeated except for mixing nickel sulfate, cobalt sulfate and manganese sulfate of the metal salt aqueous solution for forming the core and the metal salt aqueous solution for forming the surface part at the molar ratio as listed in the following Table 1 so as to obtain an active material particle.
example 1-5
[0077]A cathode active material, which has the same composition and the same structure with Examples 1-3 was prepared by using a batch reactor.
[0078]Distilled water 2.5 L was put into a coprecipitation batch reactor (Capacity: 8 L, power of a rotation motor: 180 W); nitrogen gas was supplied to the reactor at the speed of 0.6 L / min so as to remove dissolved oxygen; and stirred at 450 rpm while maintaining the temperature of the reactor at 50° C.
[0079]The metal salt aqueous solution for forming the core and the metal salt aqueous solution for forming the surface part having the same concentration with Example 1-3 were mixed at a certain ratio, and simultaneously supplied into the reactor at the rate of 0.2 L / hour. Further, 4.8 M ammonia solution was continuously supplied into the reactor at the rate of 0.1 L / hour. Further, for adjusting pH, 10 M NaOH aqueous solution was supplied to maintain pH in the reactor at 11. Then, the impeller speed of the reactor was controlled to 450 rpm, a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com