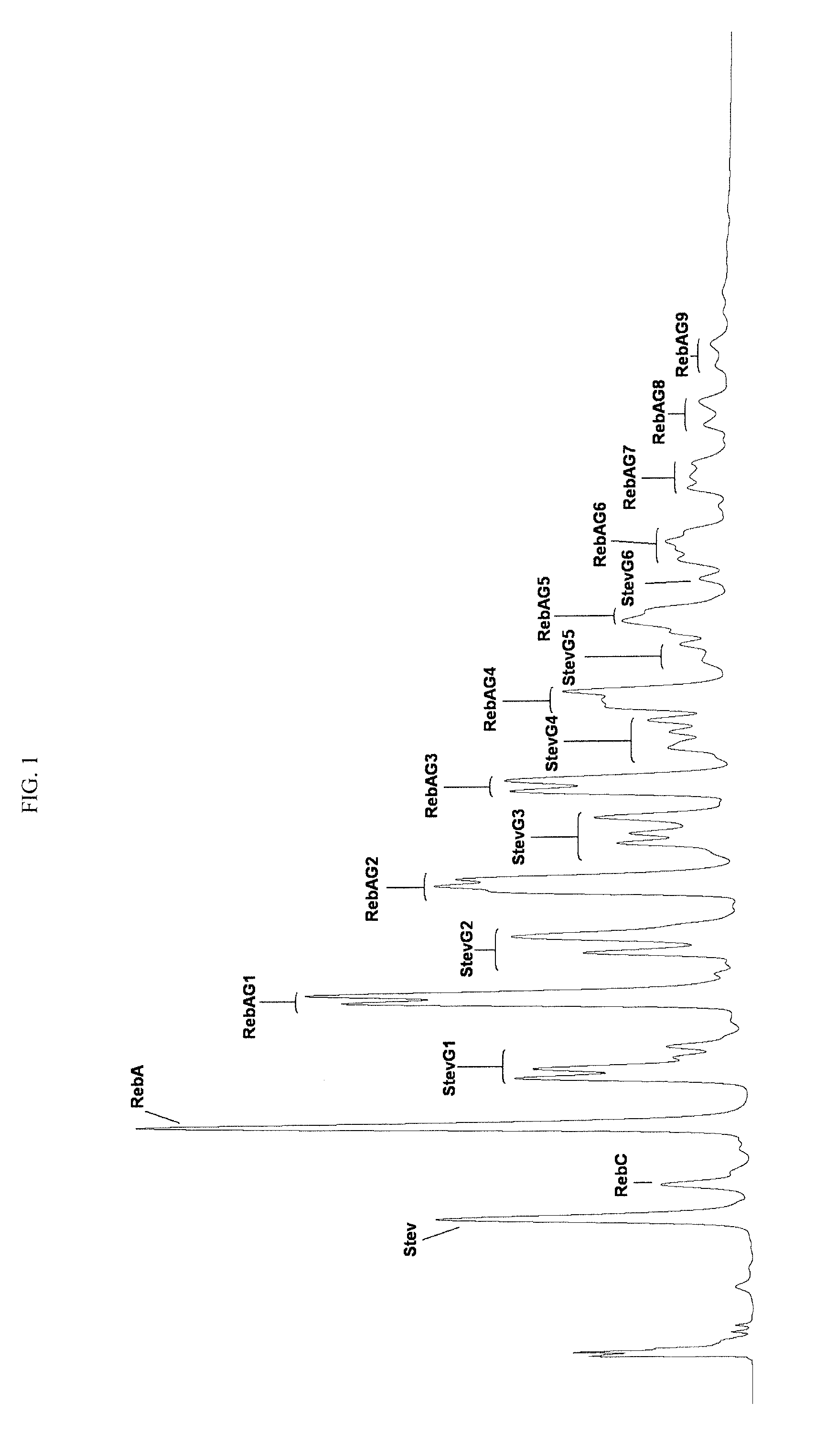
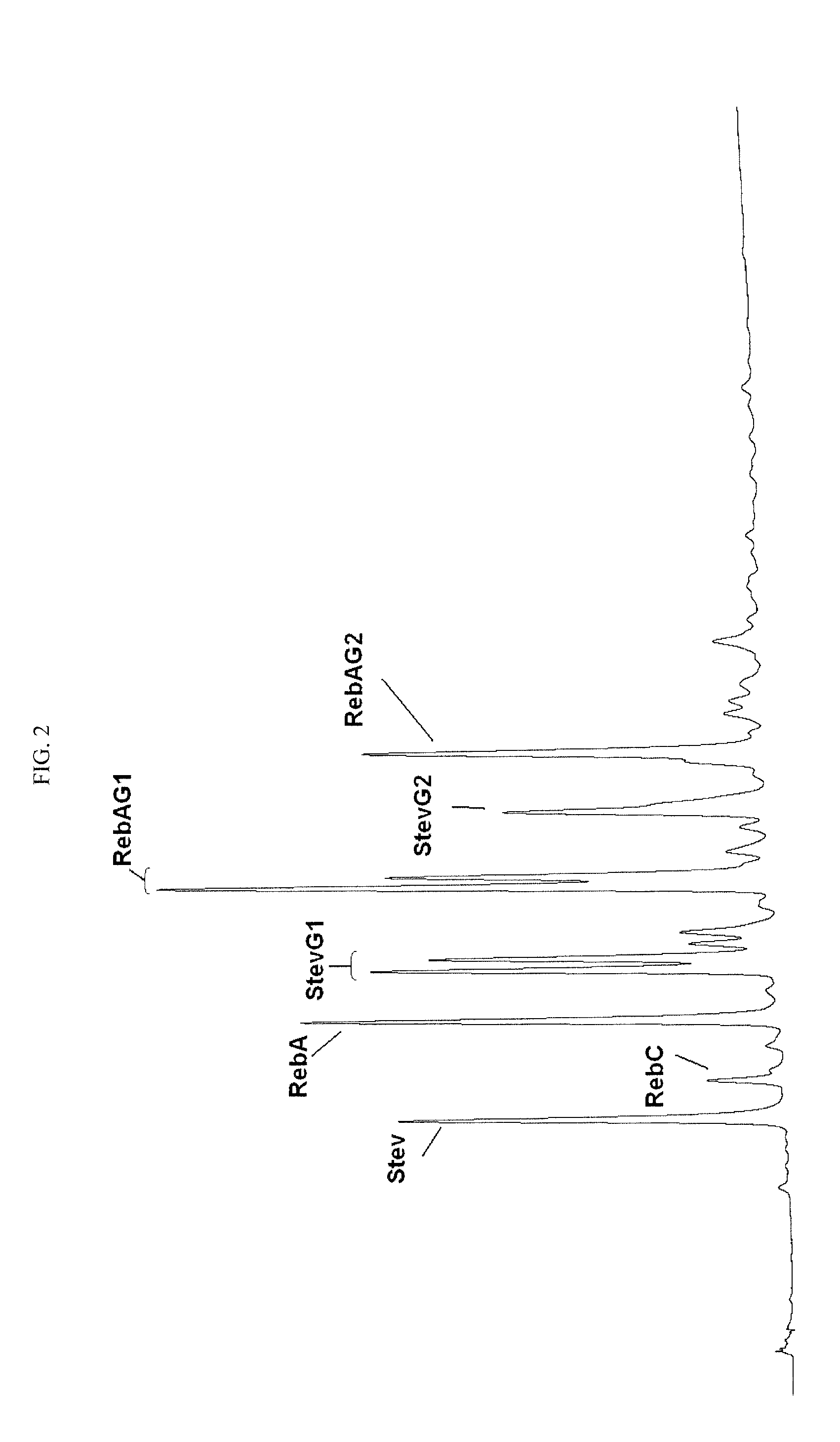
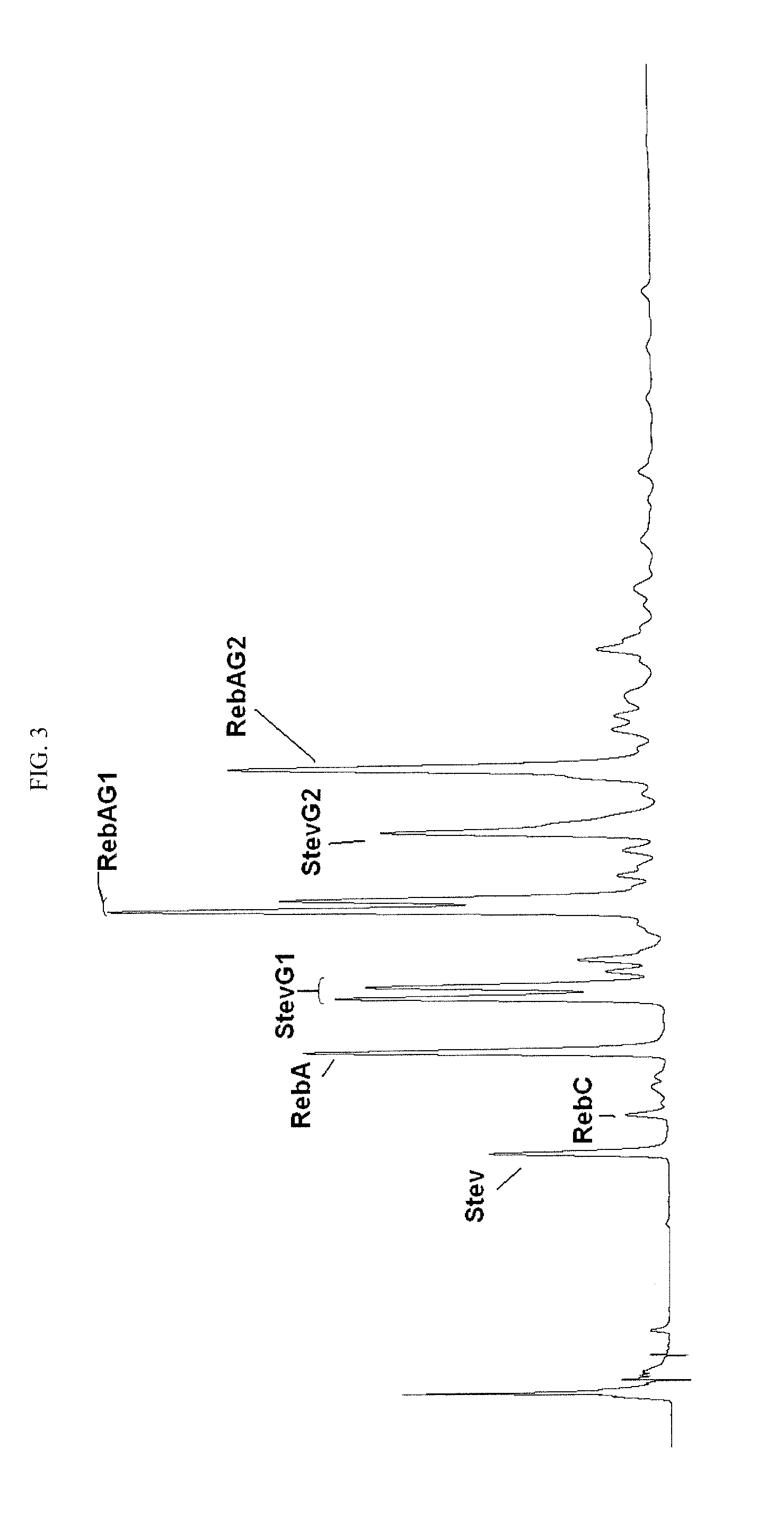
Glucosyl stevia composition
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Preparation of CGTase
[0072]A strain of Bacillus stearothermophilus St-100 was inoculated in 2,000 liters of sterilized culture medium containing 1.0% starch, 0.25% corn extract, 0.5% (NH4)2SO4, and 0.2% CaCO3 (pH 7.0-7.5) at 56° C. for 24 hrs with continuous aeration (2,000 L / min) and agitation (150 rpm). The obtained culture broth was filtered using Kerasep 0.1 μm ceramic membrane (Novasep, France) to separate the cells. The cell-free permeate was further concentrated 2-fold on Persep 10 kDa ultrafilters (Orelis, France). The activity of the enzyme was determined according to Hale, Rawlins (1951). A crude enzyme preparation with activity of about 2 unit / mL was obtained.
example 2
Preparation of β-Amylase
[0073]A strain of Bacillus polymyxa St-3504 was inoculated in 2,000 liters of sterilized culture medium containing 1.0% starch, 0.5% peptone, 0.5% corn extract, 0.5% NaCl, 0.02% MnSO4 and 0.1% CaCO3 (pH 7.0-7.5) at 32° C. for 24 hrs with continuous aeration (2,000 L / min) and agitation (150 rpm). The obtained culture broth was filtered using Kerasep 0.1 μm ceramic membrane (Novasep, France) to separate the cells. 10% of glucose was added to the cell-free permeate which was further concentrated on Persep 10 kDa ultrafilters (Orelis, France) and dried using Alpha 1-4 LSC freeze drier unit (Christ, Germany) to obtain a powder with 20,000 AUN / g activity. β-Amylase activity unit (1 AUN) was defined as the activity which liberates 100 mg of reducing sugar (expressed by dextrose equivalent) per minute under the following conditions: 1 mL of enzyme solution is mixed with 5 mL of 1.2% starch solution (pH 5.5, M / 20 Acetate Buffer) and kept for 20 min at 40° C.
example 3
Preparation of Short-Chain Glucosyl Stevia Composition
[0074]100 g of tapioca starch was suspended in 300 mL of water (pH 6.5). 2 KNU of α-amylase (Termamyl Classic, Novozymes, Denmark) and 30 units of CGTase obtained according to EXAMPLE 1 were added, and the liquefaction of starch was carried out at 80° C. for about one hour to dextrose equivalent about 15. The pH of reaction mixture was adjusted to pH 2.8 by hydrochloric acid and the mixture was boiled at 100° C. during 5 minutes to inactivate the enzymes. After cooling to 65° C., the pH was adjusted to pH 6.0 with sodium hydroxide solution. 100 g stevia extract produced by PureCircle (JiangXi) Co., Ltd. (China), containing stevioside 29.2%, Rebaudioside A 54.3%, Rebaudioside C 9.0%, Rebaudioside F (1.7%) and other glycosides amounting to total steviol glycosides content of about 96.4% was added to liquefied starch and stirred until a homogeneous solution was obtained. 200 units of CGTase was added to the solution and the mixture ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com