Property enhancing fillers for transparent coatings and transparent conductive films
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Effect of Nanodiamonds on Commercial Overcoat on a Transparent Substrate
[0098]This example tests the effect on the hardness of a commercial overcoat loaded with nanodiamonds on PET substrate with an initial polymer binder overcoat.
[0099]The substrate was prepared by coating a base ink with a cellulose based polymer binder but without any silver nanowires was coated onto a transparent PET substrate and dried. The coated substrate had a haze of 0.72%. A commercial coating polymer from Dexerials was dissolved in N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF). Six samples were prepared with two samples at each of 2 wt %, 3 wt % and 4 wt % polymer concentrations. In one sample at each polymer concentration, hydrogen terminated nanodiamonds were added, respectively, at 0.2 wt %, 0.3 wt %, or 0.4 wt % concentrations, so that in each diamond containing sample, the diamond concentrations were about one tenth the polymer concentration. The coating solutions were deposited onto the substrate by slot coating at 1...
example 2
Effect of Nanodiamond in Conductive Inks
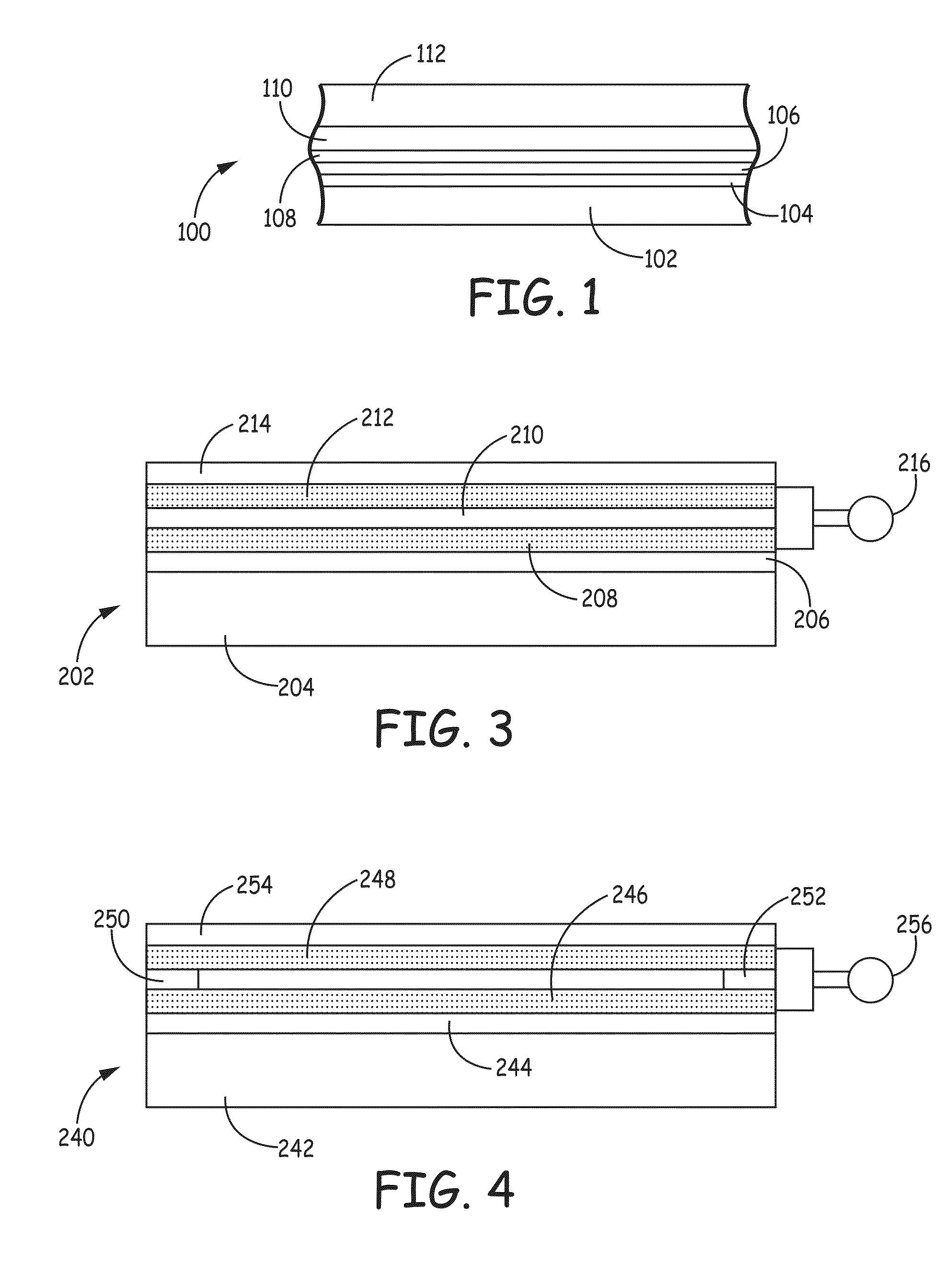
[0100]This example tests the hardness of films having a fused metal nanostructured layers with nanodiamonds incorporated into the conductive layer with a hard coating applied over the conductive layer.
[0101]A silver nanowire ink was prepared as described above except for the addition of 0.036 wt % nanodiamonds with hydrogen terminated surface in the ink. The nanodiamonds were initially dispersed in a gamma-butyrolactone solvent prior to mixing into the silver nanowire inks. The nanowire inks were slot coated onto a PET film substrate and dried to fuse the nanowires into a fused metal nanostructured network forming a conductive layer. An overcoating composition was prepared as described in Example 1 except at a polymer concentration of 0.5 wt % and without nanodiamonds. The overcoat was processed similarly as described in Example 1 with slot coating onto the dried fused metal conductive layer, drying of the coating and UV curing the coating.
[01...
example 3
Effect of Nanodiamonds in Commercial Overcoats Over a Transparent Conductive Layer
[0103]This example tests the hardness of transparent conductive films incorporating commercial overcoats incorporating nanodiamonds.
[0104]The silver nanowire was deposited and processed as described above. Following drying, the layer comprised fused metal nanostructured network within the sparse metal conductive layer. The sheet resistances for the conductive layers were between 50 and 60 ohms / sq., and the thin overcoat layers did not significantly change the sheet resistance of the film after applying the and curing the overcoat. Two different metal nanowire ink systems were tested in combination with 3 different commercial overcoats, three different corresponding solvent systems and three different initial nanodiamond dispersions. The substrates with the fused metal nanostructured network had an initial haze prior to application of the overcoat of 1.12% with the first ink system and 1.28% with the se...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Power | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com