Method for varnishing plated parts
a technology of chromium plated parts and varnishing, which is applied in the direction of electrolytic coatings, electrolytic inorganic material coatings, liquid/solution decomposition chemical coatings, etc. it can solve the problems of difficult industrial application, difficult to achieve the effect of reducing the risk of deterioration of non-metal substrates, and relatively expensive methods
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
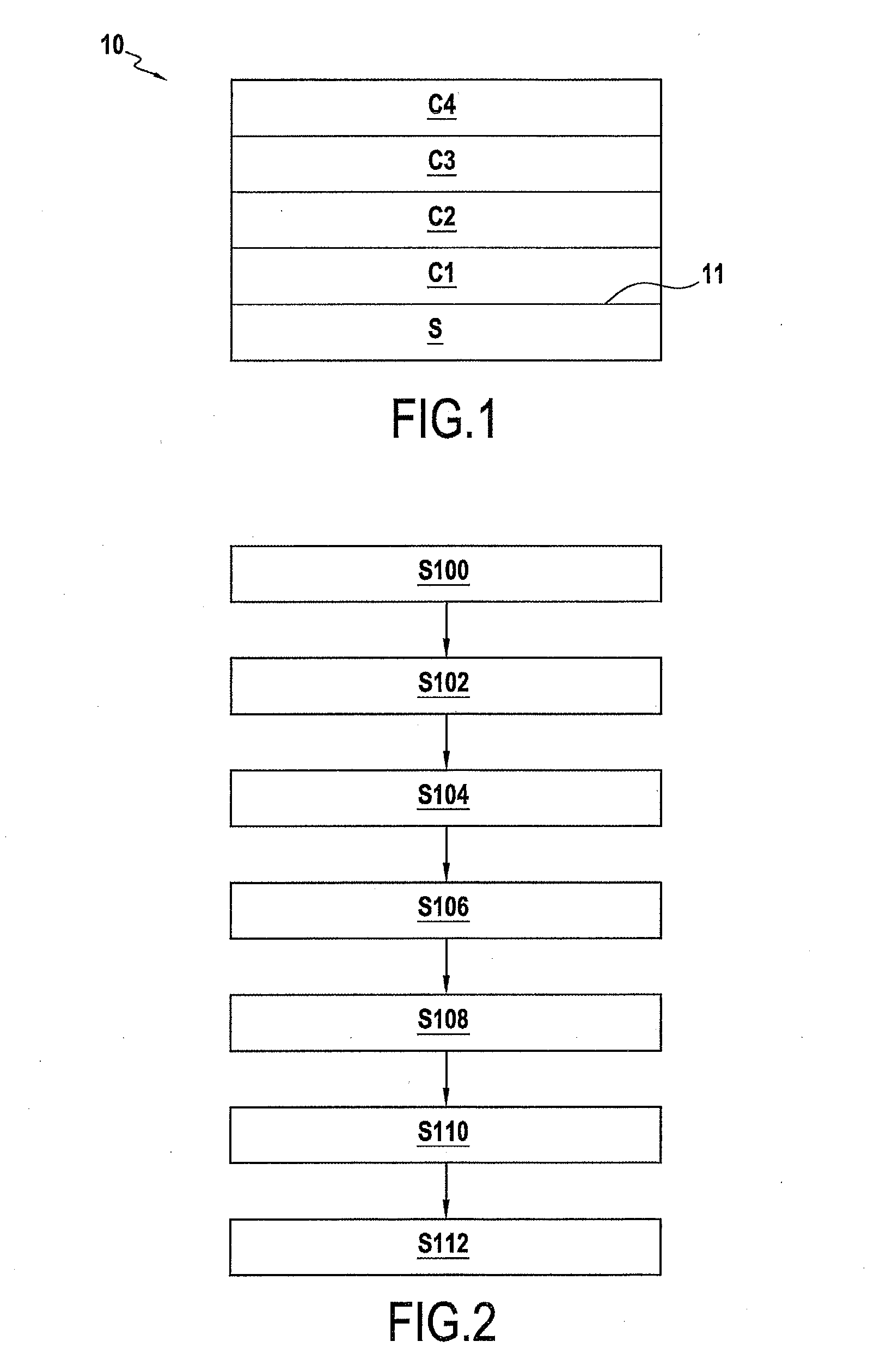
[0055]FIG. 1 schematically illustrates a plated part 10 free of chromium conforming to the invention. This part comprises a non-metal substrate S on which layers C1 to C4 will be deposited. The non-metal substrate S has a surface 11.
[0056]In this example, the non-metal substrate S is a part in plastic material. In this example, the substrate consists of ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) which has good mechanical strength and corrosion resistance. In one variant, a copolymer is used comprising acrylonitrile butadiene styrene and a polycarbonate.
[0057]In addition, in another example, the metal substrate can composed of a polyamide.
[0058]In another variant, the non-metal substrate S comprises polypropylene.
[0059]In FIG. 2, a first step S100 is the step at which the substrate S in plastic material receives chemical treatment on its surface 11 to obtain roughness of said surface 11.
[0060]In this example, the chemical attack of the surface 11 of a part containing an acrylonitrile buta...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperatures | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com