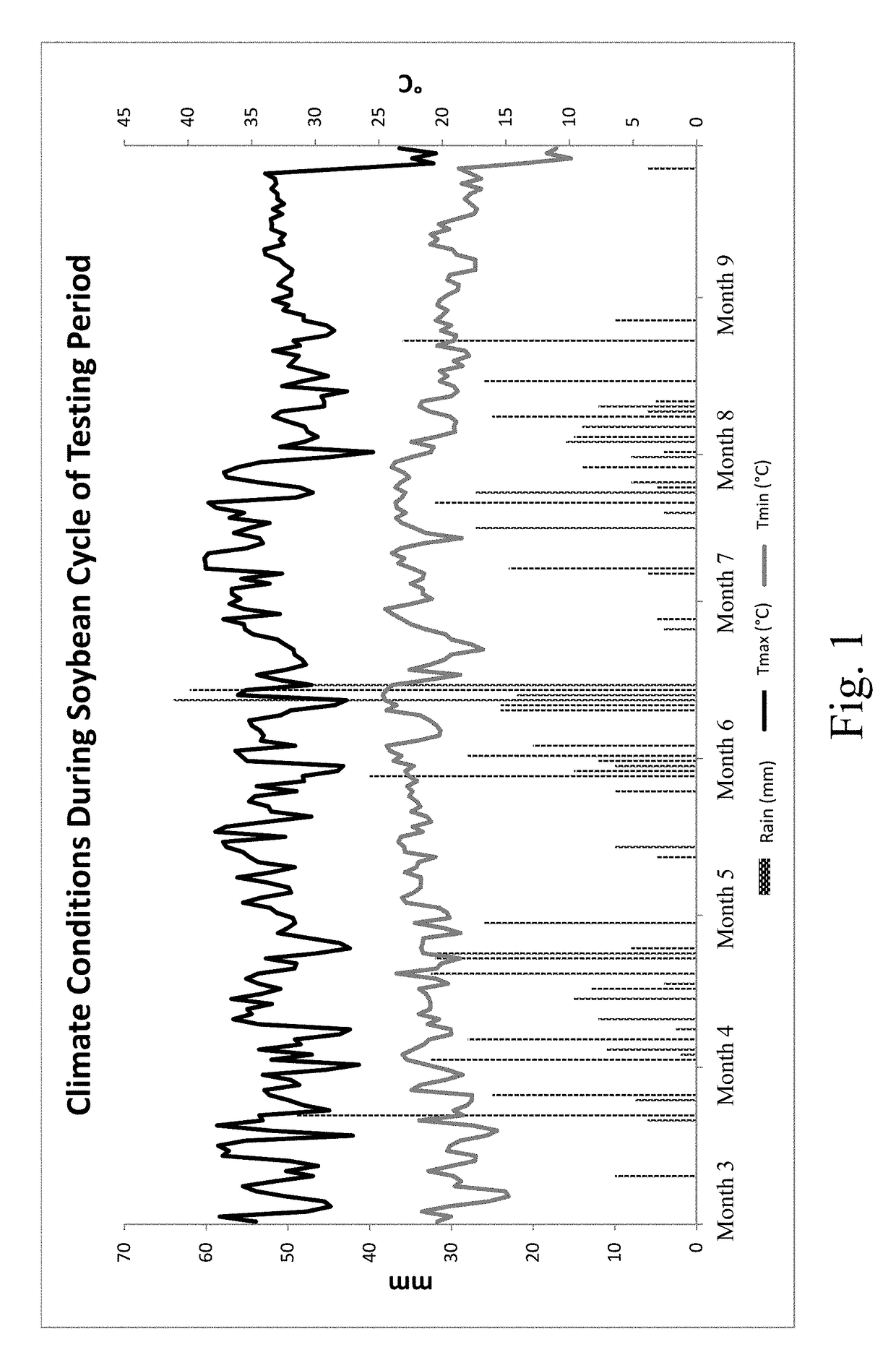
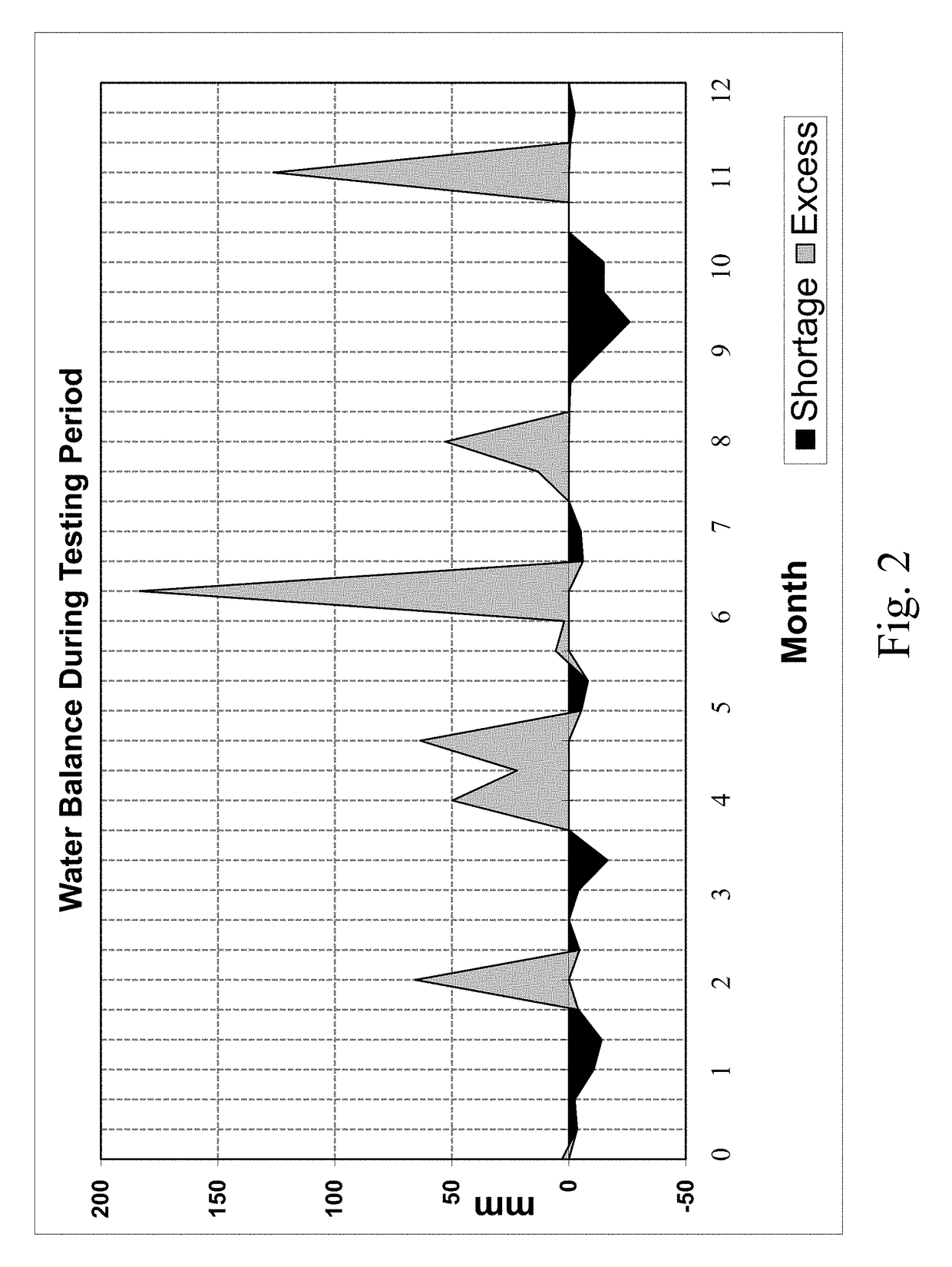
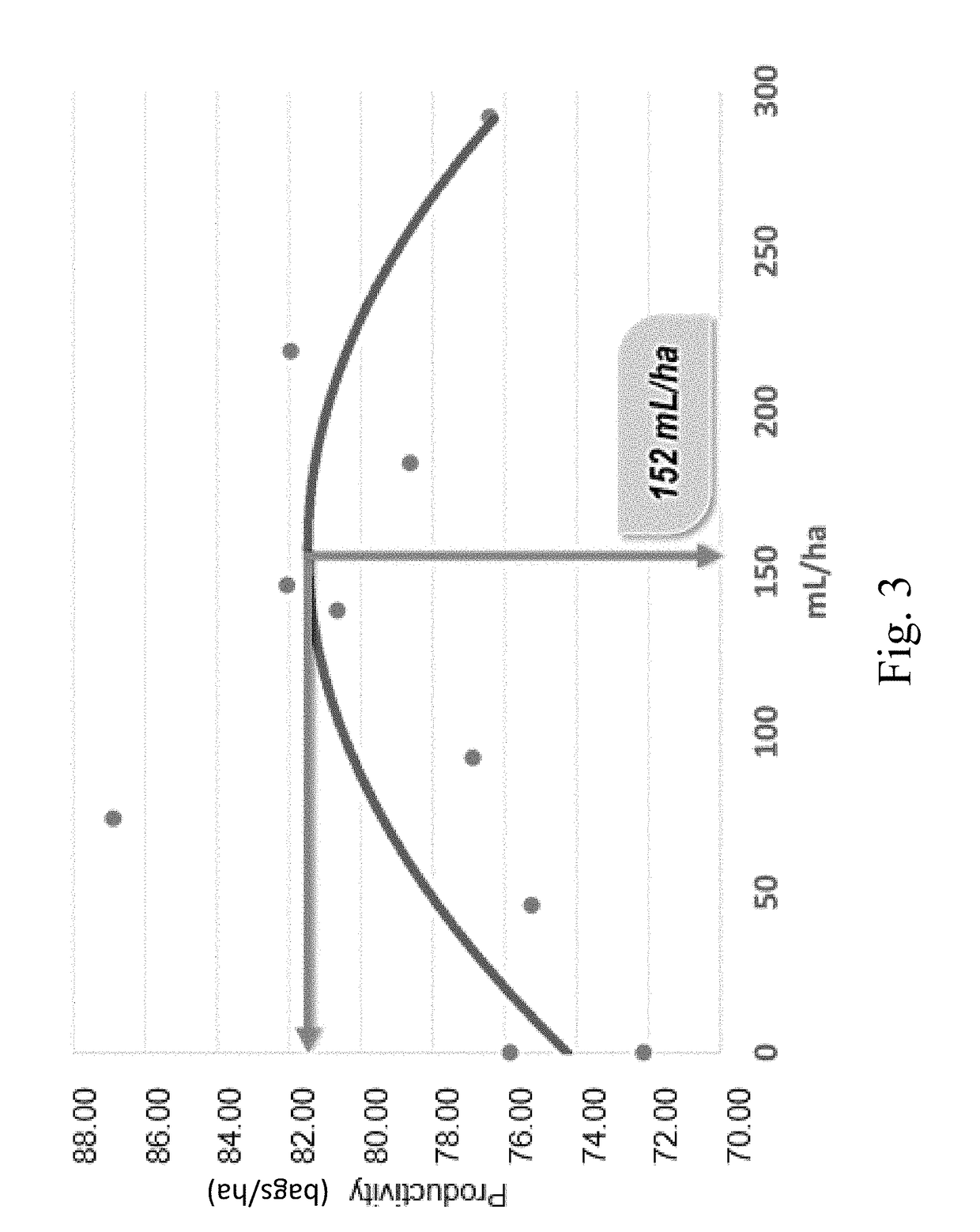
Liquid fertilizer compositions comprising nickel, cobalt, and molybdenum, and methods of forming and using the same
a technology of liquid fertilizer and composition, which is applied in the field of liquid fertilizer composition, can solve the problems of difficult to produce fertilizer having ph, failure to achieve biological nitrogen fixation, and difficulty in developing fertilizers for the treatment of seeds
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples
[0026]The following examples set forth methods of producing formulations according to embodiments of the present invention and efficacy trials using these formulations. It is to be understood, however, that these examples are provided by way of illustration and nothing therein should be taken as a limitation upon the overall scope of the invention.
example i
[0027]A first formulation was prepared in accordance with an embodiment of the present invention (Formulation A). Seaweed (Brandon XT48) is an extract solution having about 480 g / L of solids, and it was added to a reactor (reactor A). In another reactor (reactor B), the rest of the water (99.08 kg) was added, and the heating was activated. Molybdic acid (Produquimica, 50% Mo content, more preferably minimum 25% Mo content) was added to reactor B, keeping heating at 60° C. and stirring until homogenization. MEA (Oxiteno, Brazil, 99.2% minimum MEA content) was added to reactor B by slowly dosing. At this time, there was release of heat (exotherm). Stirring continued, and heating was kept at 60° C. until the solution was clear. Subsequently, tryptophan (ADT 30T) and anhydrous citric acid (Cargill, 99.5% minimum citric acid content) were added, stirring until complete dissolution. Next, nickel (Chelate Nickel-EDTA, 13.6% Ni, Produquimica) and cobalt chelate (Chelate Cobalt-EDTA, 13.6% C...
example ii
[0028]In this experiment, Formulation A (described in Example I) was tested for compatibility with favorable microbial inoculants for N2 biological fixation (NBF) on seeds.
1. Introduction
[0029]This report relates to an evaluation of a chemical fertilizer, Formulation A, with inoculants containing Bradyrhizobium strains for soybean cultivation, for sowing on the day or pre-sowing.
2. Equipment and Methods
2.1. Methodology for Analyzing Recovery of Rhizobacteria Cells in Soybean Seeds
[0030]The methodologies used were based on MAPA [Ministry of Agriculture, Livestock and Supply] normative instructions. To evaluate the concentration and purity of inoculants, IN [normative instructions] No. 30 of 11 / 12 / 2010 (MAP 2010) was used. To evaluate the recovery of cells in soybean seeds, method 2 of IN No. 30 11 / 12 / 2010 (MAP 2010) was used.
2.2. Treatments
2.2.1. Formulations
[0031]Formulation A (described above) was evaluated.
2.2.2. Inoculants
[0032]Two commercially-available inoculants were used in t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| electrical conductivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| electrical conductivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| electrical conductivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com