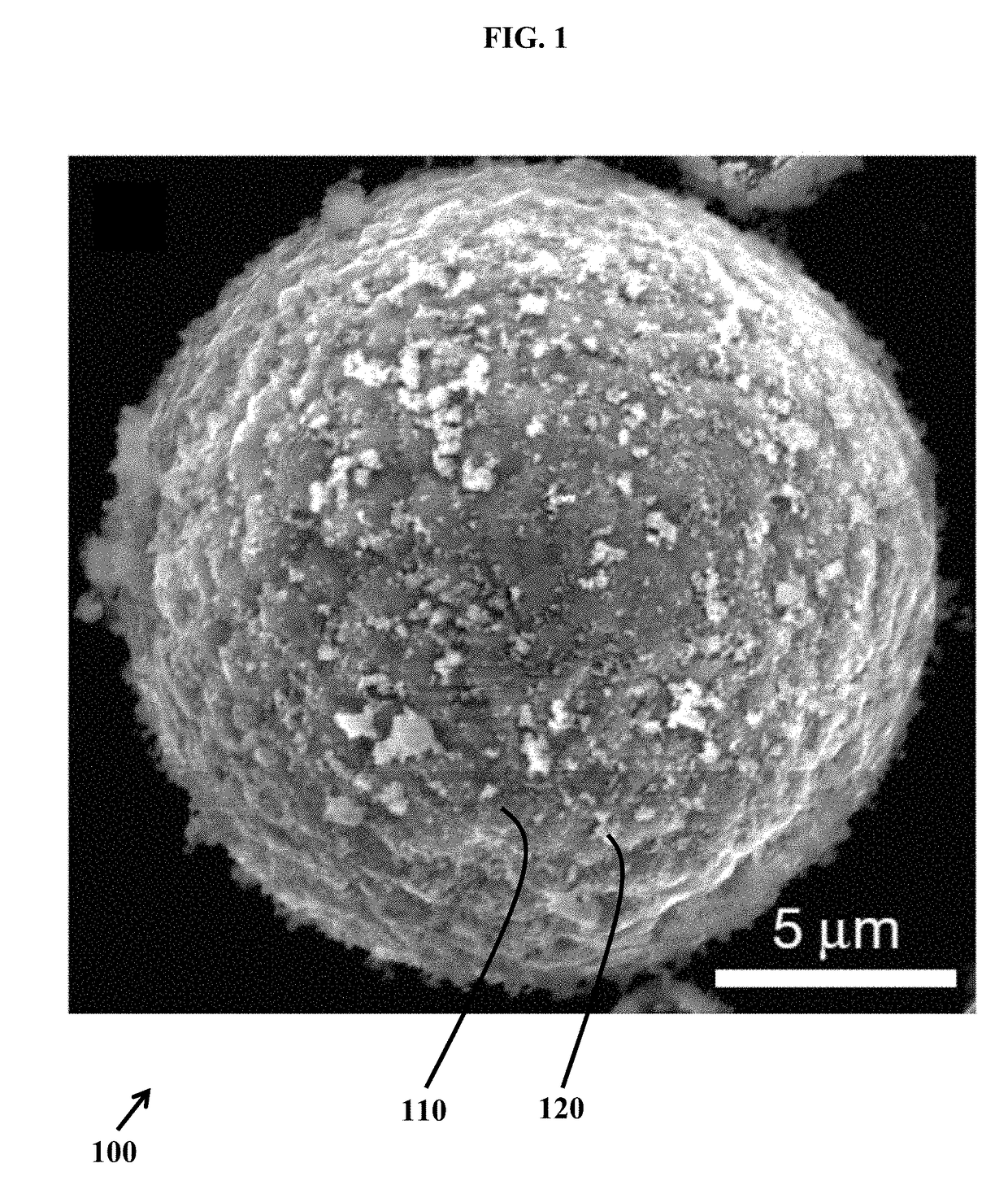
Aluminum alloys with grain refiners, and methods for making and using the same
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
inement of Pure Aluminum
[0307]In this example, tantalum (Ta) particles are added to pure aluminum as a grain refiner, and compared to pure aluminum with no Ta particle addition. The concentration of Ta in the aluminum-tantalum material is about 1 vol %. The average Ta particle size is approximately 50 nm. In both cases, the metal or functionalized metal is melted and resolidified by selective laser melting.
[0308]FIG. 6A shows an image of non-grain-refined pure aluminum, revealing large columnar grains. FIG. 6B shows an image of grain-refined aluminum with Ta particles, revealing fine equiaxed growth and a substantially crack-free microstructure.
[0309]This example demonstrates the effectiveness of grain refinement of pure aluminum using Ta addition.
example 2
inement of Aluminum Alloy Al 7075
[0310]In this example, zirconium (Zr) nanoparticles are added to aluminum alloy Al 7075 as a grain refiner, and compared to pure Al 7075 with no Zr nanoparticle addition. The concentration of Zr in the functionalized alloy is about 1 vol %. The average Zr nanoparticle size is approximately 500-1500 nm. In both cases, the alloy or functionalized alloy is melted and resolidified by selective laser melting.
[0311]FIG. 7A shows an image of non-grain-refined aluminum alloy Al 7075, revealing columnar grains and significant cracking. FIG. 7B shows an image of grain-refined aluminum alloy Al 7075 with Zr particles, revealing fine equiaxed grains and a substantially crack-free microstructure. Without being limited by theory, it is believed that Zr forms a preferred nucleating phase at sufficient concentration to reduce the critical undercooling required for equiaxed nucleation.
[0312]It is also noted that both of FIGS. 7A and 7B (scale bars 100 μm) exhibit a c...
example 3
Manufacturing of Aluminum Alloy Al 7075 with Zr Grain Refiner
[0314]In this example, zirconium (Zr) nanoparticles are first added to aluminum alloy Al 7075. The concentration of Zr in the functionalized alloy is about 1 vol %. The average Zr nanoparticle size is approximately 500-1500 nm. The functionalized alloy is solution heat-treated and artificially aged, which is indicated by “T6” in the alloy name (Al 7075+Zr-T6), as described above. A control aluminum alloy, Al 7075-T6, is compared to Al 7075+Zr-T6, as is AlSi10Mg, another common alloy for comparison.
[0315]The functionalized alloy (Al 7075+Zr-T6) is 3D-printed by selective laser melting. The control alloys Al 7075-T6 and AlSi10Mg are 3D-printed with the same technique. It is believed that at least a portion of the Zr nanoparticles are in the form of Al3Zr nucleant particles following 3D printing.
[0316]FIG. 9 shows a stress-strain curve of the functionalized aluminum alloy versus the two non-functionalized aluminum alloys, ind...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Grain size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Grain size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Grain size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com