Adeno-Associated Virus Vector Delivery of Muscle Specific Micro-Dystrophin To Treat Muscular Dystrophy
a technology of adenoassociated virus and microdystrophin, which is applied in the direction of drug compositions, peptide/protein ingredients, peptide sources, etc., can solve the problems of muscle function deficits that produce muscular dystrophies (mds), serious impact on quality of life, and membrane fragility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Generation of the pAAV.MHCK7.Micro-Dystrophin Construct
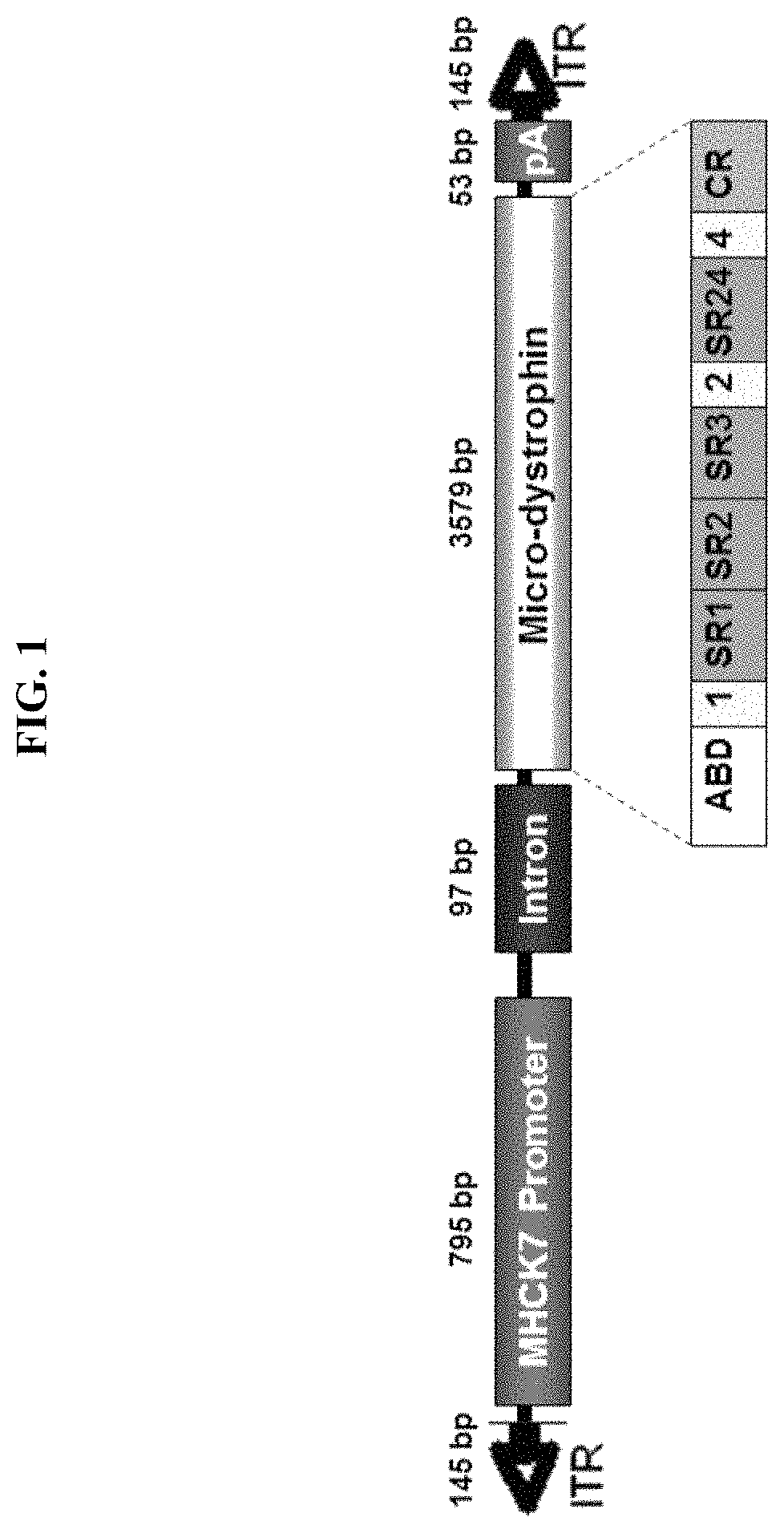
[0119]The pAAV.MHCK7.micro-dystrophin plasmid contains a human micro-dystrophin cDNA expression cassette flanked by AAV2 inverted terminal repeat sequences (ITR) (see FIG. 1). The micro-dystrophin construct was characterized by an in-frame rod deletion (R4-R23), while hinges 1, 2 and 4 and cysteine rich domain remain producing a 138 kDa protein. The expression of the micro-dystrophin protein (3579 bp) was guided by a MHCK7 promoter (795 bp). The plasmid was constructed from the pAAV.MCK.micro-dystrophin plasmid by removing the MCK promoter and inserting the MHCK7 promoter. After the core promoter, the 53 bp endogenous mouse MCK Exon1 (untranslated) is present for efficient transcription initiation, followed by the SV40 late 16S / 19S splice signals (97 bp) and a small 5′UTR (61 bp). The intron and 5′ UTR are derived from plasmid pCMVß (Clontech). The micro-dystrophin cassette had a consensus Kozak immediately in front of the ATG s...
example 2
Intramuscular Expression Studies Using rAAV.MHCK7.Micro-Dystrophin
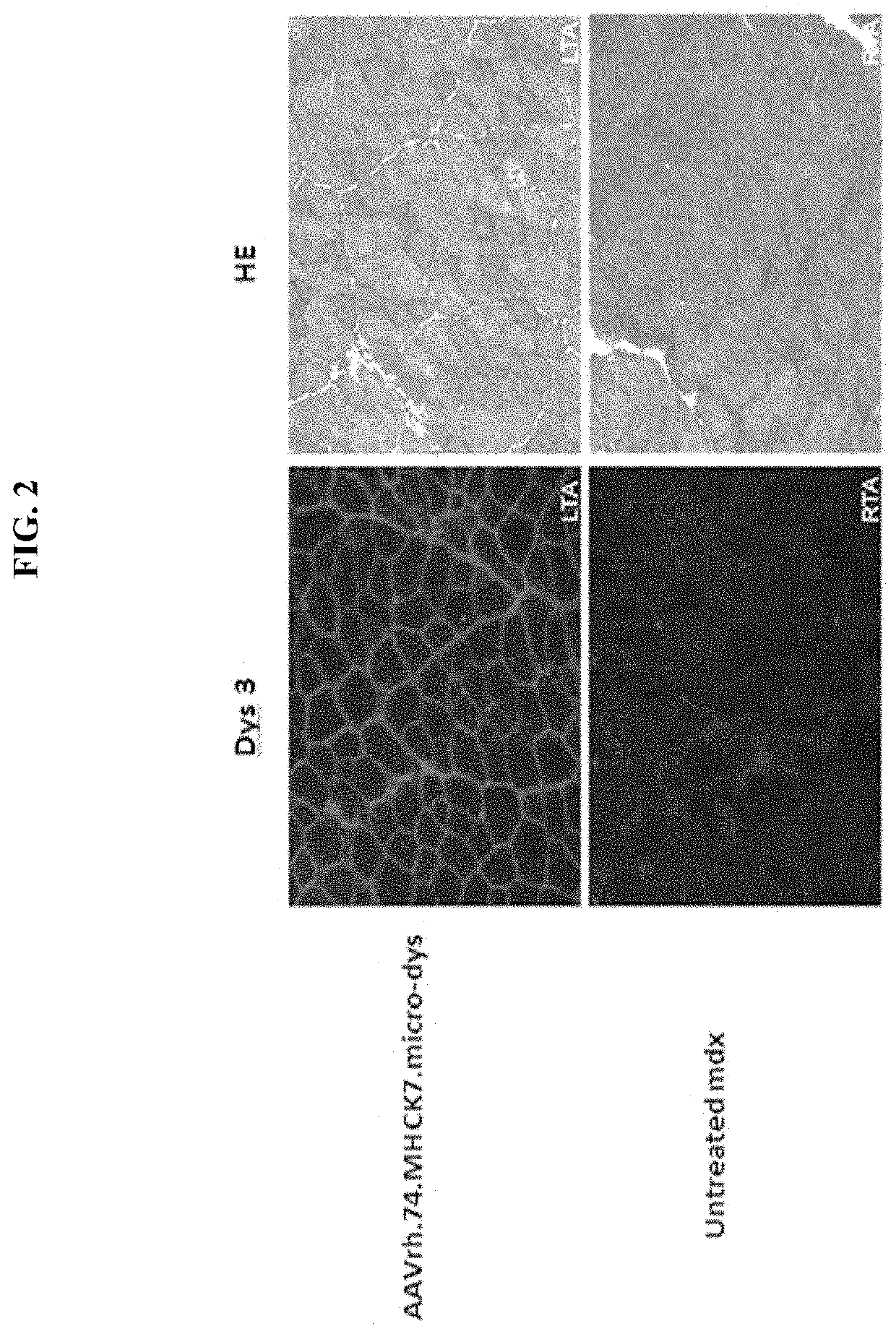
[0121]Expression studies were conducted with the human micro-dystrophin construct (rAAVrh74.MHCK7. micro-dystrophin; described in Example 1) by intramuscular injection. The tibialis anterior muscle of mdx mice (spontaneous Dmdmdx (mutant mice that do not express dystrophin) were injected with 1×1011 vg of the cassette (n=5 per group). Six weeks later the muscles were harvested and stained for dystrophin (Dys3) expression with an N-terminal antibody for dystrophin and hematoxylin and eosin (HE) staining. FIG. 2 shows diffuse gene expression and reduction in centrally located nuclei with 1×1011 vg dose compared to the untreated muscle. Furthermore, a decrease in central nucleation with an increase in average fibers / frame was observed following treatment with micro-dystrophin construct. Expression levels of the rAAVrh74.MHCK7. micro-dystrophin construct were quantified at about 73%.
[0122]In addition to measuring micro-dy...
example 3
Systemic Delivery of rAAVrh.74.MHCK7.Micro-Dystrophin to Mdx Mice
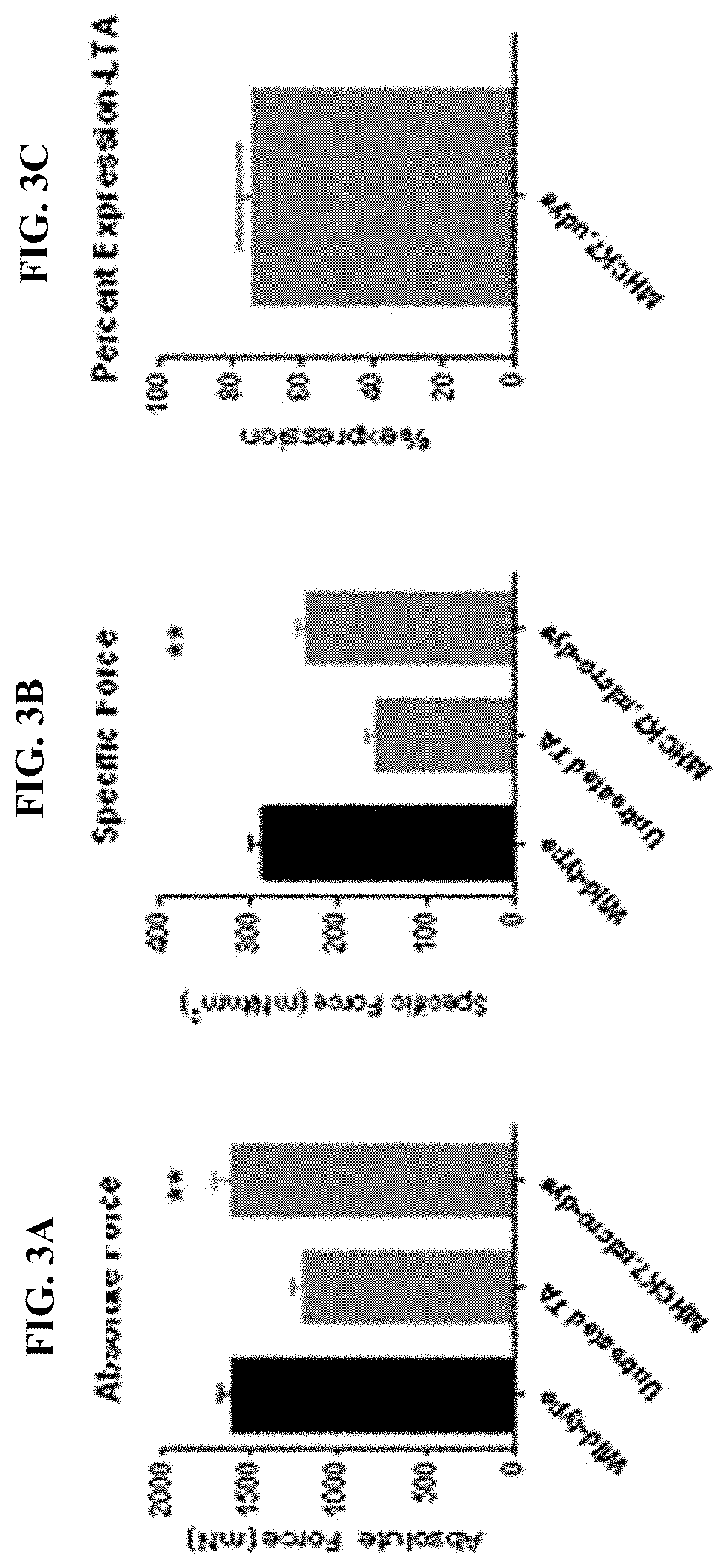
[0123]Cohorts of mdx mice were injected via tail vein with either 2×1012 vg (8×1013 vg / kg) or high dose (planned clinical dose) 6×1012 vg (2×1014 vg / kg) of rAAVrh.74.MHCK7.micro-dystrophin at 6 weeks of age. Following 12 weeks of treatment, all muscles were harvested and stained for dystrophin and restoration of DAPC components. Systemically injected (tail vein) mice showed high levels of staining of dystrophin throughout all muscles. FIG. 4A represents the widespread transduction of skeletal, diaphragm and cardiac muscle fibers after a 6×1012 vg (2×10 14 vg / kg) systemic dose. FIG. 4B shows quantification of the percentage of muscle fibers expressing micro-dystrophin in each tissue. Finally the diaphragm was tested for functional improvement (FIG. 4C). No significant difference was seen at low dose; however there was significant improvement at the high dose. Importantly, FIG. 5 demonstrates other components of the DAPC...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| muscular force | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com